Podcast
Questions and Answers
What phase comes immediately after Prophase in mitosis?
What phase comes immediately after Prophase in mitosis?
- Prometaphase (correct)
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Metaphase
Cytokinesis occurs simultaneously with the earlier stages of mitosis.
Cytokinesis occurs simultaneously with the earlier stages of mitosis.
False (B)
Who developed dyes to observe chromosomes?
Who developed dyes to observe chromosomes?
Walther Flemming
The phase of mitosis where chromosomes align in the middle of the cell is called __________.
The phase of mitosis where chromosomes align in the middle of the cell is called __________.
Match the cellular components with their functions:
Match the cellular components with their functions:
Which structure is responsible for holding sister chromatids together?
Which structure is responsible for holding sister chromatids together?
Chromosomes become visible when they are in their highly condensed state.
Chromosomes become visible when they are in their highly condensed state.
What is the approximate length of a eukaryotic chromosome during observation?
What is the approximate length of a eukaryotic chromosome during observation?
What is the primary function of kinetochore microtubules during mitosis?
What is the primary function of kinetochore microtubules during mitosis?
The anaphase is the longest stage of mitosis.
The anaphase is the longest stage of mitosis.
At which stage do chromosomes align at the metaphase plate?
At which stage do chromosomes align at the metaphase plate?
During prophase, the __________ envelope fragments.
During prophase, the __________ envelope fragments.
Match the stages of mitosis with their descriptions:
Match the stages of mitosis with their descriptions:
What happens to cohesion proteins during anaphase?
What happens to cohesion proteins during anaphase?
The centrosomes move toward each other during mitosis.
The centrosomes move toward each other during mitosis.
What drives the movement of centrosomes apart during prophase?
What drives the movement of centrosomes apart during prophase?
How many pairs of chromosomes are found in human somatic cells?
How many pairs of chromosomes are found in human somatic cells?
A karyotype displays chromosomes in a random order.
A karyotype displays chromosomes in a random order.
During which phase do the two daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell?
During which phase do the two daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell?
What are the two chromosomes in a homologous pair called?
What are the two chromosomes in a homologous pair called?
In plant cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow.
In plant cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow.
What forms around the daughter chromosomes during telophase?
What forms around the daughter chromosomes during telophase?
Chromosomes in a homologous pair carry genes controlling the same inherited ________.
Chromosomes in a homologous pair carry genes controlling the same inherited ________.
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms with their definitions:
By the end of anaphase, the two ends of the cell have _____ collections of chromosomes.
By the end of anaphase, the two ends of the cell have _____ collections of chromosomes.
What happens to spindle microtubules during late telophase?
What happens to spindle microtubules during late telophase?
The chromosomes become more condensed during telophase.
The chromosomes become more condensed during telophase.
What appears shortly after the end of mitosis?
What appears shortly after the end of mitosis?
Match the following processes with their corresponding features:
Match the following processes with their corresponding features:
What process occurs during cytokinesis in animal cells?
What process occurs during cytokinesis in animal cells?
The cell plate formation is a characteristic of animal cells.
The cell plate formation is a characteristic of animal cells.
What are two types of regulatory proteins involved in cell cycle control?
What are two types of regulatory proteins involved in cell cycle control?
During __________, the chromosomes become aligned at the metaphase plate.
During __________, the chromosomes become aligned at the metaphase plate.
Match the phases of mitosis with their characteristics:
Match the phases of mitosis with their characteristics:
Which structure is responsible for the formation of the cleavage furrow in animal cells?
Which structure is responsible for the formation of the cleavage furrow in animal cells?
The nucleolus disappears during prophase of mitosis.
The nucleolus disappears during prophase of mitosis.
The centrosome is duplicated during the __________ phase of interphase.
The centrosome is duplicated during the __________ phase of interphase.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Chromosomes and Cell Division
- Walther Flemming developed chromosome dyes in 1882, enabling the observation of stained chromosomes.
- Eukaryotic chromosomes, visible in the nucleus, are typically about 20 micrometers in size.
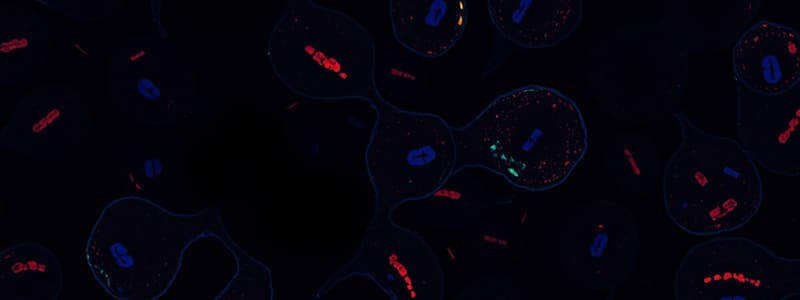
- Chromosomes appear as purple stained structures with red cytoskeletal threads in the surrounding cytoplasm during cell division.
Mitosis Phases
- Mitosis consists of five distinct stages: Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
- Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, occurs concurrently with the final stages of mitosis.
Interphase
- The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus, which contains one or more nucleoli.
- In preparation for mitosis, centrosomes duplicate, forming two centrosomes, each containing two centrioles.
- Chromosomes, previously duplicated during the S phase, are initially invisible due to their non-condensed state.
Prophase
- Chromatin coils tightly to form visible sister chromatids joined at their centromeres.
- The mitotic spindle starts forming, and centrosomes separate, propelled by elongating microtubules.
Prometaphase
- The nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing microtubules to enter the nuclear area.
- Chromosomes condense further, and kinetochores develop on each chromatid, facilitating movement.
Metaphase
- Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, an equidistant plane between the spindle's poles.
- Kinetochores of sister chromatids attach to microtubules from opposite poles.
Anaphase
- Cohesion proteins are cleaved, separating sister chromatids into individual chromosomes.
- Daughter chromosomes move toward opposite ends of the cell, elongating the cell.
Telophase
- Two daughter nuclei form, as nuclear envelopes regenerate from the parent cell's fragments.
- Chromosomes de-condense, nucleoli reappear, and any remaining spindle microtubules disassemble.
Cytokinesis
- In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms to pinch the cell into two, while in plant cells, a cell plate develops to separate daughter cells.
Cell Cycle Regulation
- Cell cycle control involves two regulatory proteins: cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks).
Human Chromosomes
- Human somatic cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total).
- A karyotype displays the ordered arrangement of these chromosome pairs.
- Homologous chromosomes are identical in length and shape, carrying genes for the same inherited traits.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.