Podcast
Questions and Answers
What do binding pockets in a protein structure represent?
What do binding pockets in a protein structure represent?
- Sites of protein synthesis
- Regions of flexibility in the protein structure
- Regions involved in gene expression
- Potential sites where other molecules can interact with the protein (correct)
What is the primary function of DNA?
What is the primary function of DNA?
- To regulate cell metabolism
- To synthesize proteins
- To carry the hereditary information passed down from parents to offspring (correct)
- To provide structural support to cells
What is the genome of an organism compared to?
What is the genome of an organism compared to?
- A complete set of genetic information for a particular species (correct)
- A manual for building a house
- The entire instruction book for an organism's life
- A recipe book for cooking
What is the primary focus of bioinformatics?
What is the primary focus of bioinformatics?
What is the primary indicator of gene expression levels?
What is the primary indicator of gene expression levels?
Which of the following cells do not carry a complete copy of the genome?
Which of the following cells do not carry a complete copy of the genome?
Why is it useful to compare gene expression patterns between different cell types or tissues?
Why is it useful to compare gene expression patterns between different cell types or tissues?
What is the main purpose of bioinformatics tools in biological databases?
What is the main purpose of bioinformatics tools in biological databases?
What is the main goal of structural bioinformatics?
What is the main goal of structural bioinformatics?
What is the sugar component of a nucleotide in DNA?
What is the sugar component of a nucleotide in DNA?
What is the primary function of genes within the genome?
What is the primary function of genes within the genome?
How many types of nitrogenous bases are found in DNA?
How many types of nitrogenous bases are found in DNA?
What does gene expression analysis allow scientists to understand?
What does gene expression analysis allow scientists to understand?
What is a biomarker?
What is a biomarker?
What type of data is often generated by DNA sequencing?
What type of data is often generated by DNA sequencing?
What can be revealed by studying gene expression patterns during cellular differentiation?
What can be revealed by studying gene expression patterns during cellular differentiation?
What is the primary goal of bioinformatics in solving complex biological problems?
What is the primary goal of bioinformatics in solving complex biological problems?
What is the process by which cells tightly control which genes are expressed called?
What is the process by which cells tightly control which genes are expressed called?
What is the specific pairing rule for adenine and thymine in DNA?
What is the specific pairing rule for adenine and thymine in DNA?
Why do sex cells (sperm and egg) only have half the genome?
Why do sex cells (sperm and egg) only have half the genome?
What is the significance of flexibility in protein structure?
What is the significance of flexibility in protein structure?
What is the role of graphics in bioinformatics?
What is the role of graphics in bioinformatics?
What is the structural component of DNA that is formed by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases?
What is the structural component of DNA that is formed by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases?
What is the main benefit of gene expression analysis in understanding disease mechanisms?
What is the main benefit of gene expression analysis in understanding disease mechanisms?
What is the relationship between the size of the genome and the complexity of the organism?
What is the relationship between the size of the genome and the complexity of the organism?
What is the primary focus of structural bioinformatics?
What is the primary focus of structural bioinformatics?
What is the primary component of the genome?
What is the primary component of the genome?
What is the purpose of mapping gene regulatory networks?
What is the purpose of mapping gene regulatory networks?
What is the result of the specific base pairing in DNA?
What is the result of the specific base pairing in DNA?
What do surface features of a protein structure represent?
What do surface features of a protein structure represent?
What is the main advantage of combining computational and experimental approaches in structural bioinformatics?
What is the main advantage of combining computational and experimental approaches in structural bioinformatics?
What is the purpose of the genome in an organism?
What is the purpose of the genome in an organism?
What is the name of the process by which cells mature and specialize into different cell types?
What is the name of the process by which cells mature and specialize into different cell types?
What type of data is often visualized using informative graphics in bioinformatics?
What type of data is often visualized using informative graphics in bioinformatics?
What is the role of genes in the genome?
What is the role of genes in the genome?
What is the result of advancements in structural bioinformatics and gene expression analysis?
What is the result of advancements in structural bioinformatics and gene expression analysis?
What is the role of bioinformatics in managing biological data?
What is the role of bioinformatics in managing biological data?
What is the main goal of gene expression analysis?
What is the main goal of gene expression analysis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Introduction to Bioinformatics
- Bioinformatics is the application of computational techniques to understand and analyze biological data, including DNA sequencing, protein analysis, and gene expression studies.
- The field helps researchers solve complex biological problems that would be impossible to tackle with traditional methods alone.
Bioinformatics Data
- Bioinformatics deals with all aspects of managing biological data, including representation, storage, and retrieval.
- Data is often visualized using informative graphics like charts, diagrams, and 3D structures to help researchers understand patterns and relationships.
- Biological databases are like digital warehouses that store vast amounts of information, allowing researchers to efficiently search, access, and retrieve specific data.
Basic Molecular Biology: The Recipe of Life
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic blueprint that carries hereditary information passed down from parents to offspring.
- DNA is made up of nucleotides, each consisting of sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
- The specific sequence of nitrogenous bases (A, C, G, and T) determines genetic information.
- The double helix structure of DNA is like a twisted ladder, with sugar-phosphate backbones forming the sides and hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases forming the rungs.
Genomes and Genes: The Code of Life
- A genome is the complete set of genetic information for a particular species, written in the language of DNA.
- The genome includes all the DNA found within an organism's chromosomes.
- Almost every cell in an organism carries a complete copy of the genome, with exceptions being sex cells and mature red blood cells.
- Genes are the functional units of heredity, carrying information needed to create proteins with specific shapes and functions.
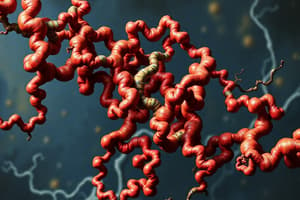
Structural Bioinformatics: Decoding the Shape of Life
- Structural bioinformatics combines computational and experimental approaches to analyze properties of proteins, such as binding pockets, flexibility, and surface features.
- This knowledge fuels advancements in medicine, biotechnology, and our overall understanding of life.
Gene Expression Analysis: Decoding the Cellular Orchestra
- Gene expression analysis is like listening to the cellular orchestra, allowing scientists to understand which genes are "playing" (being turned on) and at what level within a cell.
- Gene expression analysis provides valuable insights into cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
- By measuring mRNA levels, researchers can gauge the level of gene expression and identify genes that are abnormally active in disease.
- Comparing gene expression patterns between different cell types, tissues, or healthy and diseased states can help identify genes involved in disease processes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.