Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which ion is primarily associated with muscle contraction and plays a crucial role in stimulating this process?
Which ion is primarily associated with muscle contraction and plays a crucial role in stimulating this process?
- Calcium (Ca2+) (correct)
- Sodium (Na+)
- Iron (Fe)
- Magnesium (Mg)
What is the first stage in the biochemical cycle of muscle contraction?
What is the first stage in the biochemical cycle of muscle contraction?
- Relaxation of the muscle fiber
- Hydrolysis of ATP by myosin (correct)
- Fusion of actin and myosin
- Formation of the actin-myosin complex
During the actin-myosin interaction, the angle of the transverse bridge changes from what to what as myosin pulls actin?
During the actin-myosin interaction, the angle of the transverse bridge changes from what to what as myosin pulls actin?
- 180° to 90°
- 90° to 45° (correct)
- 45° to 90°
- 0° to 90°
What happens to the myosin head after a new ATP molecule binds to the myosin-F-actin complex?
What happens to the myosin head after a new ATP molecule binds to the myosin-F-actin complex?
In the resting state of a muscle, which protein undergoes positional change allowing for contraction?
In the resting state of a muscle, which protein undergoes positional change allowing for contraction?
Which of the following accurately describes a function of lipids in muscle tissue?
Which of the following accurately describes a function of lipids in muscle tissue?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in muscle tissue?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in muscle tissue?
What are the two types of filaments found in myofibrils?
What are the two types of filaments found in myofibrils?
Which protein is primarily responsible for hydrolyzing ATP to release energy for muscle contraction?
Which protein is primarily responsible for hydrolyzing ATP to release energy for muscle contraction?
What is the structure that makes up the thick filaments in muscle fibers?
What is the structure that makes up the thick filaments in muscle fibers?
What is the role of calcezvestrine in muscle contraction?
What is the role of calcezvestrine in muscle contraction?
Which of the following components make up the thin filament structure?
Which of the following components make up the thin filament structure?
Myosin is composed of which structural features?
Myosin is composed of which structural features?
How are the actin filaments arranged?
How are the actin filaments arranged?
What is the primary role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What percentage of all proteins involved in muscle contraction do myosin, actin, and tropomyosin represent?
What percentage of all proteins involved in muscle contraction do myosin, actin, and tropomyosin represent?
What is the primary structure of a protein characterized by?
What is the primary structure of a protein characterized by?
What distinguishes alpha helices from beta sheets in protein secondary structure?
What distinguishes alpha helices from beta sheets in protein secondary structure?
Which of the following is true about the tertiary structure of proteins?
Which of the following is true about the tertiary structure of proteins?
What is meant by the isoelectric point of a protein?
What is meant by the isoelectric point of a protein?
Which proteins are typically characterized by beta sheet structures?
Which proteins are typically characterized by beta sheet structures?
How is the quaternary structure of a protein formed?
How is the quaternary structure of a protein formed?
What role does the heme group play in hemoglobin?
What role does the heme group play in hemoglobin?
What is coagulation in the context of proteins?
What is coagulation in the context of proteins?
Which statement is correct regarding intermolecular hydrogen bonding in proteins?
Which statement is correct regarding intermolecular hydrogen bonding in proteins?
What occurs during the denaturation of proteins when they are exposed to heat?
What occurs during the denaturation of proteins when they are exposed to heat?
Which type of protein primarily serves as an enzyme?
Which type of protein primarily serves as an enzyme?
Which of the following is an example of a complete protein?
Which of the following is an example of a complete protein?
What chemical agents can disrupt hydrogen bonds in the denaturation process?
What chemical agents can disrupt hydrogen bonds in the denaturation process?
What does hydrolysis of proteins involve?
What does hydrolysis of proteins involve?
Which of the following statements is true concerning simple and complex proteins?
Which of the following statements is true concerning simple and complex proteins?
Which proteins are categorized as contractile proteins?
Which proteins are categorized as contractile proteins?
Which of the following is a common method of protein denaturation?
Which of the following is a common method of protein denaturation?
What is the effect of heavy metal ions on proteins?
What is the effect of heavy metal ions on proteins?
What defines an incomplete protein?
What defines an incomplete protein?
What is the role of troponin I in the muscle contraction process?
What is the role of troponin I in the muscle contraction process?
What happens when the heads of myosin bind to actin?
What happens when the heads of myosin bind to actin?
Which nitrogenous compound is primarily responsible for regenerating ATP during muscle contraction?
Which nitrogenous compound is primarily responsible for regenerating ATP during muscle contraction?
What is the main function of carnitine in muscle tissue?
What is the main function of carnitine in muscle tissue?
Which of the following is a primary energy source for muscles during contraction?
Which of the following is a primary energy source for muscles during contraction?
What is the primary role of glycogen in muscle tissue?
What is the primary role of glycogen in muscle tissue?
Which branched-chain amino acids primarily enter muscle tissue?
Which branched-chain amino acids primarily enter muscle tissue?
Which compound primarily reduces muscle fatigue and enhances contraction amplitude?
Which compound primarily reduces muscle fatigue and enhances contraction amplitude?
In which conditions does glycogen accumulate the most in muscle tissue?
In which conditions does glycogen accumulate the most in muscle tissue?
What impact does myosin and actin interaction have on muscle filaments?
What impact does myosin and actin interaction have on muscle filaments?
Flashcards
Primary Structure of Proteins
Primary Structure of Proteins
The linear arrangement of amino acids in a protein, like beads on a string.
Secondary Structure of Proteins
Secondary Structure of Proteins
The 3D arrangement of the polypeptide backbone, mainly due to hydrogen bonding, forming structures like alpha helix and beta sheets.
Tertiary Structure of Proteins
Tertiary Structure of Proteins
The overall 3D shape of a protein, influenced by interactions between side chains of amino acids.
Quaternary Structure of Proteins
Quaternary Structure of Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isoelectric Point of a Protein
Isoelectric Point of a Protein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Coagulation
Protein Coagulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alpha Helix
Alpha Helix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beta Sheet
Beta Sheet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrogen Bonding in Proteins
Hydrogen Bonding in Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Denaturation
Protein Denaturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Structure
Primary Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Structure
Secondary Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tertiary Structure
Tertiary Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quaternary Structure
Quaternary Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Proteins
Simple Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complex Proteins
Complex Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complete Proteins
Complete Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Incomplete Proteins
Incomplete Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Hydrolysis
Protein Hydrolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myoglobin
Myoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcezvestrine
Calcezvestrine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thick Filaments
Thick Filaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thin Filaments
Thin Filaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myosin
Myosin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Actin (G-actin)
Actin (G-actin)
Signup and view all the flashcards
F-actin (Fibrillar Actin)
F-actin (Fibrillar Actin)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tropomyosin
Tropomyosin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Troponin
Troponin
Signup and view all the flashcards
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is muscle contraction?
What is muscle contraction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does muscle contraction start?
How does muscle contraction start?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens during the 'power stroke' in muscle contraction?
What happens during the 'power stroke' in muscle contraction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
What's the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do calcium ions affect muscle contraction?
How do calcium ions affect muscle contraction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to myosin in a relaxed muscle?
What happens to myosin in a relaxed muscle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the troponin complex?
What is the troponin complex?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is actomyosin?
What is actomyosin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is glycogen in muscles?
What is glycogen in muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is phosphocreatine's role in muscle contraction?
What is phosphocreatine's role in muscle contraction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are carnosine and anserine?
What are carnosine and anserine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of carnitine in muscles?
What is the role of carnitine in muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and why are they important for muscles?
What are branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and why are they important for muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the primary function of muscles?
What is the primary function of muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some of the roles of muscles besides movement?
What are some of the roles of muscles besides movement?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some of the nitrogenous compounds found in muscles?
What are some of the nitrogenous compounds found in muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Biochemistry of Muscles
- Proteins: Major components of muscle, skin, nails, hair.
- Primary Structure: Linear chain of amino acids, ending in "yl". Sequence starts with amino acid at end and continues to the carboxyl end.
- Secondary Structure: 3D spatial conformation of polypeptide backbone, excluding side chains. Key structures: alpha helix, beta sheets. Held together by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups.
- Tertiary Structure: 3D arrangement of the polypeptide chain. Stabilized by interactions like hydrophilic/hydrophobic interactions and ionic bonds between amino acid side chains.
- Quaternary Structure: Combination of multiple tertiary units. Example: hemoglobin (two alpha chains and two beta chains).
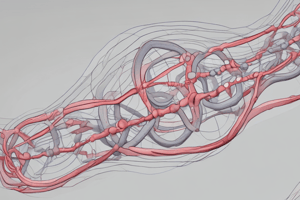
- Types of Protein Structures: Image depicting the different levels of protein structure.
- Isoelectric Point: The pH at which a protein carries no net electrical charge.
Physico-chemical Properties of Proteins
- Isoelectric Point: The pH where a molecule carries no net electrical charge.
Simple proteins
- Simple proteins: Contain only amino acids. Examples: albumins, globulins, protamines, histones, prolamins, glutelins, scleroproteins
- Complex proteins: Contain amino acids and other components (carbohydrates, lipids etc.). Examples: nucleoproteins, chromoproteins, glycoproteins, phosphoproteins, lipoproteins
Classification and function of proteins
- Catalytic proteins: Enzymes
- Structural proteins: Collagen, elastin
- Contractile proteins: Myosin, actin
- Transport proteins: Hemoglobin, myoglobin, albumin, transferrin
- Regulatory proteins (hormones): Insulin, growth hormone.
- Protective proteins (immunoglobulins): Interferons, clotting factors.
Complete and Incomplete Proteins
- Complete Proteins: Contain all essential amino acids for growth.
- Incomplete Proteins: Lack one or more essential amino acids, though still have nutritional value and may be enough to sustain an adult. Example: proteins from pulses are deficient in methionine.
Precipitations and Qualitative Reactions of Proteins
- Qualitative reactions used to identify proteins.
Hydrolysis of Proteins
- Proteins are broken down into peptides and amino acids via hydrolysis.
- Hydrolysis occurs in digestion and amino acid synthesis.
Proteins in Muscles
- Sacroplasma proteins: Water-soluble proteins, e.g., myoglobin.
- Fibrillar myofibril proteins: Insoluble, e.g., myosin, actin.
Myofibrils Proteins
- Thick filaments: Myosin (200-400 molecules)
- Thin filaments: Actin, tropomyosin, troponin.
- Myosin and actin are key in muscle contraction.
Muscle Protein Functions
- Body movement
- Respiration (diaphragm, intercostals)
- Digestion
- Blood circulation
- Excretion
- Mechanical work (chemical energy to kinetic).
Muscles Nitrogenous Compounds (Non-protein)
- Nucleotides (ATP, ADP, AMP)
- Creatine, phosphocreatine
- Carnosine, anserine
- Carnitine
- Amino acids
- Glycogen
- Lactate, pyruvate, other carboxylic acids
- Lipids (phospholipids, sterols, triglycerides)
- Inorganic salts (K+, Na+, Mg, Ca, Fe)
Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
- Muscle contraction is a complex process involving biochemical interactions.
- Electrical impulses initiate contraction.
- Interaction of actin, myosin, and various other proteins.
- Calcium ions are critical for muscle contraction activity.
- ATP hydrolysis powers the process.
Stages of Muscle Contraction
- Myosin heads bind to actin filaments.
- Myosin heads rotate (power stroke) and pull filaments.
- ATP binds to myosin, causing release from actin.
- Cycle repeats.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.