Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of acetyl-CoA in the tricarboxylic acid cycle?
What is the role of acetyl-CoA in the tricarboxylic acid cycle?
- It acts solely as a building block for amino acid synthesis.
- It is exclusively utilized for fatty acid oxidation.
- It serves as a major fuel for the TCA cycle. (correct)
- It is primarily used to replenish glucose levels in the liver.
Which alternative fate of pyruvate is crucial for tissues with high oxidative capacity?
Which alternative fate of pyruvate is crucial for tissues with high oxidative capacity?
- Oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl-CoA. (correct)
- Direct conversion to glucose.
- Conversion to ethanol.
- Carboxylation to lactate.
What is the consequence of a deficiency in the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase?
What is the consequence of a deficiency in the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase?
- Improved fatty acid synthesis.
- Deficiency of oxaloacetate necessary for the TCA cycle. (correct)
- Enhanced gluconeogenesis from lactate.
- Increased production of acetyl-CoA.
How does the carboxylation of pyruvate contribute to the citric acid cycle?
How does the carboxylation of pyruvate contribute to the citric acid cycle?
What metabolic defect is associated with impaired pyruvate dehydrogenase activity?
What metabolic defect is associated with impaired pyruvate dehydrogenase activity?
What is the primary role of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in metabolism?
What is the primary role of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in metabolism?
Which of the following correctly describes the energy yield from the TCA cycle?
Which of the following correctly describes the energy yield from the TCA cycle?
Which of the following enzymes is NOT considered one of the key regulatory enzymes of the TCA cycle?
Which of the following enzymes is NOT considered one of the key regulatory enzymes of the TCA cycle?
What occurs to acetyl CoA during its entry into the TCA cycle?
What occurs to acetyl CoA during its entry into the TCA cycle?
What is the primary output of the TCA cycle related to ATP production?
What is the primary output of the TCA cycle related to ATP production?
Flashcards
Alternate fates of pyruvate
Alternate fates of pyruvate
Pyruvate can be converted to acetyl-CoA or oxaloacetate, depending on the cell's needs.
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
A key pathway where pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, crucial for the TCA cycle.
Pyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase
Enzyme important in converting pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
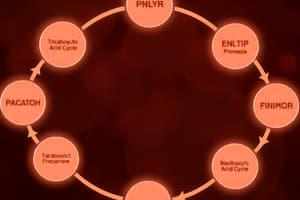
TCA cycle
TCA cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metabolic defects in oxidative metabolism
Metabolic defects in oxidative metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amphibolic pathway
Amphibolic pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to excess carbohydrates?
What happens to excess carbohydrates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why can't fatty acids be converted to carbohydrates?
Why can't fatty acids be converted to carbohydrates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 3 key enzymes regulating the TCA cycle?
What are the 3 key enzymes regulating the TCA cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Lecture 20: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TAC)
- The lecture focuses on the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TAC), also known as the Citric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle.
- Key learning objectives include understanding the alternative fates of pyruvate, the importance of TAC in major nutrient metabolism, and the energy molecules released by TAC.
Integration of Major Metabolic Pathways
- Carbohydrates are broken down through glycolysis, producing pyruvate, which is then converted to acetyl CoA and enters the citric acid cycle.
- Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation to form acetyl CoA, which then enters the cycle.
- Amino acids, after transamination, enter the cycle at various points.
- The citric acid cycle plays a crucial role in integrating metabolic pathways.
Alternate Fates of Pyruvate
- Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate is a crucial pathway in tissues with high oxidative capacity, such as cardiac muscle.
- Acetyl CoA is a key fuel for the TAC cycle and a building block for fatty acid synthesis.
Carboxylation of Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate
- This reaction is essential for replenishing TAC intermediates and providing a substrate for gluconeogenesis.
Metabolic Defects
- Defects in pyruvate dehydrogenase or pyruvate carboxylase can lead to lactic acidosis, neurological disorders, and other abnormalities in TCA cycle function.
Overview of TAC
- The TAC (also known as Krebs cycle or CAC) is a crucial metabolic pathway occurring entirely within the mitochondria.
- The TAC is an amphibolic pathway, meaning involved in both anabolism and catabolism.
Energy Production
- One molecule of acetyl-CoA oxidation produces 12 molecules of ATP.
Regulation of the TCA Cycle
- The TCA cycle's rate is regulated by citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex.
Excess Carbohydrates to Fat
- Excess carbohydrates are stored as neutral fat in adipose tissue.
- Glucose is converted to pyruvate, then into acetyl CoA, and finally into fatty acids, which combine with glycerol to form triacylglycerol (neutral fat).
No Net Synthesis of Carbohydrates from Fatty Acids
- Fatty acids, through beta-oxidation, are broken down into acetyl CoA and enter the TAC.
- Acetyl CoA is completely oxidized to CO2 within the cycle.
- Therefore, acetyl-CoA cannot be used for gluconeogenesis.
- There is no net synthesis of carbohydrates from fatty acids.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.