Podcast
Questions and Answers
A patient reports frequent nocturia as their primary symptom. This symptom is related to what condition?
A patient reports frequent nocturia as their primary symptom. This symptom is related to what condition?
- Increased bladder capacity reducing the urge to void during the day.
- Prostate enlargement directly compressing the urethra.
- Inflammation or infection within the urinary tract. (correct)
- Decreased kidney function leading to increased urine production.
Which of the following is an obstructive symptom associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
Which of the following is an obstructive symptom associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
- Dysuria (painful urination)
- Incontinence
- Urinary frequency
- Intermittency (stopping and starting stream while voiding) (correct)
The American Urological Association Symptom Index (AUA-SI) is used for what purpose in the evaluation of BPH?
The American Urological Association Symptom Index (AUA-SI) is used for what purpose in the evaluation of BPH?
- Assessing the severity of voiding symptoms and guiding treatment decisions. (correct)
- Determining the underlying cause of prostate enlargement.
- Predicting the risk of prostate cancer.
- Confirming a definitive diagnosis of BPH.
What is the primary immediate treatment for acute urinary retention caused by BPH?
What is the primary immediate treatment for acute urinary retention caused by BPH?
Why are patients with BPH at an increased risk for urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Why are patients with BPH at an increased risk for urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
What finding on a urinalysis would most strongly suggest that a patient's bladder calculi (stones) are related to BPH?
What finding on a urinalysis would most strongly suggest that a patient's bladder calculi (stones) are related to BPH?
A patient with BPH has elevated serum creatinine levels. What diagnostic study would be most appropriate to evaluate potential complications?
A patient with BPH has elevated serum creatinine levels. What diagnostic study would be most appropriate to evaluate potential complications?
During a digital rectal exam (DRE) on a patient with BPH, what findings are most consistent with the condition?
During a digital rectal exam (DRE) on a patient with BPH, what findings are most consistent with the condition?
What is the mechanism of action of 5α-reductase inhibitors in treating BPH?
What is the mechanism of action of 5α-reductase inhibitors in treating BPH?
A patient with mild BPH symptoms (AUA score of 5) is seeking initial management strategies. What is the most appropriate first-line approach?
A patient with mild BPH symptoms (AUA score of 5) is seeking initial management strategies. What is the most appropriate first-line approach?
Which hormonal change associated with aging is thought to contribute to the development of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Which hormonal change associated with aging is thought to contribute to the development of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
A 65-year-old man is diagnosed with BPH. Which of the following lifestyle factors would most likely exacerbate his condition?
A 65-year-old man is diagnosed with BPH. Which of the following lifestyle factors would most likely exacerbate his condition?
In BPH, the enlargement of the prostate gland primarily occurs in which specific region?
In BPH, the enlargement of the prostate gland primarily occurs in which specific region?
Why might a man with only mild prostate enlargement experience severe obstructive symptoms related to BPH?
Why might a man with only mild prostate enlargement experience severe obstructive symptoms related to BPH?
Which of the following factors is least likely to be associated with an increased risk of developing BPH?
Which of the following factors is least likely to be associated with an increased risk of developing BPH?
As men age, the balance between testosterone and estrogen shifts. How does this shift potentially contribute to the development of BPH?
As men age, the balance between testosterone and estrogen shifts. How does this shift potentially contribute to the development of BPH?
A patient with BPH asks why his symptoms have only recently become noticeable, even though his prostate has likely been enlarging for years. What is the best explanation?
A patient with BPH asks why his symptoms have only recently become noticeable, even though his prostate has likely been enlarging for years. What is the best explanation?
Which statement accurately describes the correlation between prostate size and the severity of BPH symptoms?
Which statement accurately describes the correlation between prostate size and the severity of BPH symptoms?
A patient with a severely enlarged prostate (>100g) and bladder damage is likely to be recommended which surgical intervention?
A patient with a severely enlarged prostate (>100g) and bladder damage is likely to be recommended which surgical intervention?
Which of the following BPH treatments involves the use of low-wave radiofrequency to heat the prostate?
Which of the following BPH treatments involves the use of low-wave radiofrequency to heat the prostate?
A patient is experiencing irritative voiding symptoms and hematuria after undergoing a BPH procedure, which of the following treatments is most likely the cause?
A patient is experiencing irritative voiding symptoms and hematuria after undergoing a BPH procedure, which of the following treatments is most likely the cause?
What is the primary goal when planning preoperative care for a patient undergoing BPH surgery?
What is the primary goal when planning preoperative care for a patient undergoing BPH surgery?
Which BPH treatment option involves incisions into the prostate to relieve obstruction and is most effective for small to moderate sized prostates?
Which BPH treatment option involves incisions into the prostate to relieve obstruction and is most effective for small to moderate sized prostates?
A patient taking finasteride (Proscar) for BPH should have their PSA levels interpreted with caution because the drug:
A patient taking finasteride (Proscar) for BPH should have their PSA levels interpreted with caution because the drug:
Which of the following mechanisms of action is associated with alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers in the treatment of BPH?
Which of the following mechanisms of action is associated with alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers in the treatment of BPH?
A patient experiences retrograde ejaculation after starting medication for BPH. Which class of medications is most likely responsible for this side effect?
A patient experiences retrograde ejaculation after starting medication for BPH. Which class of medications is most likely responsible for this side effect?
Why is finasteride not recommended for prostate cancer prevention, despite evidence suggesting it may lower the risk in some cases?
Why is finasteride not recommended for prostate cancer prevention, despite evidence suggesting it may lower the risk in some cases?
A patient is scheduled for transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT). What pre-operative instruction is most important to emphasize?
A patient is scheduled for transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT). What pre-operative instruction is most important to emphasize?
Following a photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP), what post-operative symptom is most commonly expected?
Following a photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP), what post-operative symptom is most commonly expected?
Compared to TURP, laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP or ThuLEP) offers what advantage regarding tissue penetration?
Compared to TURP, laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP or ThuLEP) offers what advantage regarding tissue penetration?
Prostatic urethral lift (PUL) is most appropriate for patients with which of the following prostate characteristics?
Prostatic urethral lift (PUL) is most appropriate for patients with which of the following prostate characteristics?
What is the primary mechanism by which transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) reduces BPH symptoms?
What is the primary mechanism by which transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) reduces BPH symptoms?
A patient reports using saw palmetto for BPH. What is the most appropriate guidance a healthcare provider should offer?
A patient reports using saw palmetto for BPH. What is the most appropriate guidance a healthcare provider should offer?
Which of the following is a key advantage of Transurethral Vaporization of the Prostate (TUVP) compared to standard TURP?
Which of the following is a key advantage of Transurethral Vaporization of the Prostate (TUVP) compared to standard TURP?
A patient is considering water vapor thermal therapy for BPH. What is a crucial factor that would determine if they are a suitable candidate for this treatment?
A patient is considering water vapor thermal therapy for BPH. What is a crucial factor that would determine if they are a suitable candidate for this treatment?
When is surgical intervention most clearly indicated for a patient with symptomatic BPH?
When is surgical intervention most clearly indicated for a patient with symptomatic BPH?
A patient undergoing TURP develops nausea, vomiting, confusion, and bradycardia postoperatively. What complication should the nurse suspect?
A patient undergoing TURP develops nausea, vomiting, confusion, and bradycardia postoperatively. What complication should the nurse suspect?
Why is it important to discontinue anticoagulant medications like aspirin or warfarin several days before a TURP procedure?
Why is it important to discontinue anticoagulant medications like aspirin or warfarin several days before a TURP procedure?
What is a key distinction between HoLEP/ThuLEP and TURP in the surgical management of BPH?
What is a key distinction between HoLEP/ThuLEP and TURP in the surgical management of BPH?
A patient undergoing Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP) should be informed to expect which of the following in the immediate postoperative period?
A patient undergoing Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP) should be informed to expect which of the following in the immediate postoperative period?
What is a primary advantage of Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL) compared to other surgical interventions for BPH?
What is a primary advantage of Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL) compared to other surgical interventions for BPH?
How does Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT) work to reduce BPH symptoms?
How does Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT) work to reduce BPH symptoms?
For which patient population would Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) be most suitable?
For which patient population would Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) be most suitable?
Flashcards
Irritative Symptoms
Irritative Symptoms
Symptoms like nocturia, urgency, and dysuria indicating inflammation or infection in the urinary tract.
Obstructive Symptoms
Obstructive Symptoms
Symptoms due to prostate enlargement, including weak urine flow and difficulty starting urination.
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)
A group of symptoms including both irritative and obstructive issues affecting urination.
AUA Symptom Index
AUA Symptom Index
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute Urinary Retention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder Infection (UTI)
Bladder Infection (UTI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) Test
Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drug Classes for BPH
Drug Classes for BPH
Signup and view all the flashcards
5α-Reductase Inhibitors
5α-Reductase Inhibitors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Surveillance
Active Surveillance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen and Testosterone Balance
Estrogen and Testosterone Balance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transition Zone
Transition Zone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Factors for BPH
Risk Factors for BPH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Age-related Hormonal Changes
Age-related Hormonal Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outpatient Procedure
Outpatient Procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA)
Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water Vapor Thermal Therapy
Water Vapor Thermal Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Management for BPH Surgery
Nursing Management for BPH Surgery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Finasteride (Proscar)
Finasteride (Proscar)
Signup and view all the flashcards
DHT
DHT
Signup and view all the flashcards
AUA-SI Score
AUA-SI Score
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dual 5α-reductase inhibitor
Dual 5α-reductase inhibitor
Signup and view all the flashcards
α-Adrenergic receptor blockers
α-Adrenergic receptor blockers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retrograde ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP)
Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT)
Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
TUNA
TUNA
Signup and view all the flashcards
TUVP
TUVP
Signup and view all the flashcards
TUIP
TUIP
Signup and view all the flashcards
TURP
TURP
Signup and view all the flashcards
TUR syndrome
TUR syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
HoLEP
HoLEP
Signup and view all the flashcards
PVP
PVP
Signup and view all the flashcards
TUMT
TUMT
Signup and view all the flashcards
PUL
PUL
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vaporization and Desiccation
Vaporization and Desiccation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
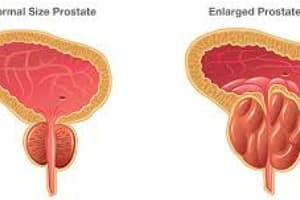
- BPH is a condition where the prostate gland enlarges, restricting urine flow.
- Half of men experience BPH by age 50; this rises to over 70% for men aged 60-69.
- Etiology and Pathophysiology:
- Hormonal changes associated with aging contribute.
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) stimulates prostate growth. Elevated DHT can lead to prostate overgrowth.
- DHT levels increase with age, causing prostate enlargement.
- Increased proportion of estrogen to testosterone is a possible contributor. Testosterone decreases with age, leaving higher estrogen levels in the prostate. This can increase substances promoting prostate growth.
- BPH typically originates in the transition zone.
- Prostate enlargement compresses the urethra, potentially causing obstruction.
- Severity of obstruction does not correlate directly with prostate size; enlargement location is more significant.
- Risk Factors:
- Aging, obesity (especially increased waist circumference), lack of physical activity, high red meat/animal fat intake, alcohol use, erectile dysfunction (ED), smoking, diabetes, and family history of BPH in first-degree relatives.
- Clinical Manifestations:
- Symptoms develop gradually, sometimes unnoticed until significant enlargement.
- Initial symptoms may be mild due to bladder compensation.
- Symptoms worsen as urethral obstruction increases.
- Symptoms classified as irritative or obstructive.
- Irritative: nocturia, urinary frequency, urgency, dysuria, bladder pain, incontinence; these are related to inflammation or infection.
- Obstructive: decreased urine stream caliber/force, difficulty starting urination, intermittency (stopping and starting), dribbling.
- Both groups of symptoms are categorized as lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
- American Urological Association (AUA) symptom index (AUA-SI) assesses symptom severity. Higher scores indicate more severe symptoms.
- Complications:
- Acute urinary retention (sudden inability to urinate, needing catheter insertion).
- Urinary tract infection (UTI) from incomplete bladder emptying. Possible progression to kidney infection (pyelonephritis); sepsis can develop.
- Bladder stones due to residual urine alkalinization.
- Renal failure due to hydronephrosis (kidney swelling).
- Diagnostic Studies:
- Detailed history and physical examination are essential.
- Digital rectal exam (DRE) estimates prostate size, symmetry, and consistency. In BPH, the prostate is symmetrically enlarged, firm, and smooth.
- Urinalysis (UA) and urine culture detect infection/inflammation.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test screens for prostate cancer (slightly elevated in BPH).
- Serum creatinine assesses renal function. High levels may indicate hydronephrosis, requiring further imaging.
- Neurologic exam if symptoms resemble neurogenic bladder.
- Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and prostate biopsy may be necessary, especially in cases with high PSA or abnormal DRE.
- Uroflowmetry measures urine stream data to assess obstruction severity.
- Post-void residual urine volume measures urine remaining after voiding, indicating obstruction.
- Cystoscopy assesses interior of the bladder and urethra.
- Urodynamic/pressure flow studies evaluate bladder function/obstruction if needed.
Treatment Options
-
Treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications, not solely prostate size.
-
Non-surgical options include active surveillance/watchful waiting (mild symptoms, AUA-SI 0-7). Lifestyle changes (diet changes, drug avoidance, fluid restriction), timed voiding schedules (bladder retraining).
-
Drug Therapy:
- 5α-reductase inhibitors: reduce prostate size, delaying DHT conversion.
- Finasteride inhibits type 2. Moderate-severe AUA-SI scores. Improved symptoms may take 6 months, require regular use, potential decreased libido and decreased PSA values (double the PSA if on finasteride for at least 6 months), may lower risk of some prostate cancers (not recommended for prevention). Patients need regular PSA monitoring.
- Dutasteride inhibits both types: similar benefits and risks as finasteride.
- α-adrenergic receptor blockers: relax prostate smooth muscle, improving urine flow.
- Tamsulosin, alfuzosin, doxazosin, prazosin, silodosin. Immediate to weeks symptom improvement. Can cause retrograde ejaculation (seminal fluid in the bladder).
- Combination therapy (5α-reductase inhibitor + α-adrenergic blocker) better than single drug.
- Erectogenic drug (e.g., tadalafil): may alleviate BPH symptoms. Can be used in conjunction with erectile dysfunction.
- Herbal Therapy (e.g., saw palmetto): lacks proven benefits.
- 5α-reductase inhibitors: reduce prostate size, delaying DHT conversion.
-
Minimally Invasive Therapies:
- Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP): Laser vaporization of prostate tissue; effective for larger prostates, rapid symptom improvement.
- Laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP/ThuLEP): precise laser vaporization; better coagulation properties compared to TURP.
- Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL): permanent implants to open urethra, minimal tissue ablation.
- Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT): uses microwaves to heat prostate tissue.
- Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA): uses radiofrequency to heat tissue.
- Transurethral Vaporization of the Prostate (TUVP): electrosurgical modification of TURP, minimizes TUR syndrome risk.
- Water vapor thermal therapy: uses heated water vapor, new.
-
Surgical Therapy (invasive):
- Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP): small incisions to relieve obstruction.
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): removal of obstructing tissue using a resectoscope. Gold standard for obstructing BPH; careful irrigation to prevent blood clots.
- Simple Prostatectomy: larger prostates or complex cases.
Nursing Management (Pre/Post-Operative)
- Assessment of patients with BPH (pre-operative) is important per Table 59.4.
- Pre-operative goals: restore urine drainage, treat/resolve any UTI, patient understanding of procedure, sexual function implications, urinary control.
- Postoperative nursing care outlined per eNursing Care Plan 59.1 (available online).
- Important to monitor for complications like acute urinary retention, infections, bladder complications, and/or post-procedure recovery issues.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.