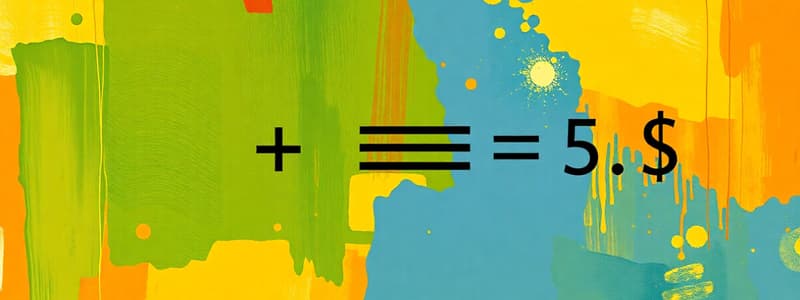Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does a balance sheet primarily provide a snapshot of?
What does a balance sheet primarily provide a snapshot of?
- The total expenditures of a business over a period
- The financial health of a business at a specific point in time (correct)
- The cash flow of a business throughout a year
- The income earned from sales in a given timeframe
Which of the following is NOT a major component of a balance sheet?
Which of the following is NOT a major component of a balance sheet?
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Assets
- Revenue (correct)
How can a business owner determine the liquidity of their business from a balance sheet?
How can a business owner determine the liquidity of their business from a balance sheet?
- By assessing the total assets available for immediate use (correct)
- By analyzing total equity against liabilities
- By calculating the net profit over the last year
- By checking the total amount of liabilities owed
What financial question can a balance sheet help answer regarding obligations?
What financial question can a balance sheet help answer regarding obligations?
Why might lenders and investors analyze a balance sheet?
Why might lenders and investors analyze a balance sheet?
What is the basic accounting equation represented in a balance sheet?
What is the basic accounting equation represented in a balance sheet?
What does a balanced balance sheet signify?
What does a balanced balance sheet signify?
What does a balance sheet NOT do?
What does a balance sheet NOT do?
If a balance sheet does not balance, what might that indicate?
If a balance sheet does not balance, what might that indicate?
Which of the following is NOT classified as a current asset?
Which of the following is NOT classified as a current asset?
Which of the following is NOT typically included in a balance sheet?
Which of the following is NOT typically included in a balance sheet?
What is indicated by accounts receivable on a balance sheet?
What is indicated by accounts receivable on a balance sheet?
What does total assets represent in a balance sheet?
What does total assets represent in a balance sheet?
Which type of asset is described as having a long-term investment that cannot be easily converted to cash within the next 12 months?
Which type of asset is described as having a long-term investment that cannot be easily converted to cash within the next 12 months?
Which of the following is a common current liability?
Which of the following is a common current liability?
What are intangible assets typically considered to be?
What are intangible assets typically considered to be?
Which item would you expect to see under non-current assets on a balance sheet?
Which item would you expect to see under non-current assets on a balance sheet?
Which of the following accurately describes inventories on a balance sheet?
Which of the following accurately describes inventories on a balance sheet?
What is the primary difference between current liabilities and long-term liabilities?
What is the primary difference between current liabilities and long-term liabilities?
What is a common example of a short-term liability?
What is a common example of a short-term liability?
Which option is NOT typically classified as a liability?
Which option is NOT typically classified as a liability?
Why is it important for a business to monitor current liabilities?
Why is it important for a business to monitor current liabilities?
Which of the following is a characteristic of liabilities?
Which of the following is a characteristic of liabilities?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the nature of liabilities?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the nature of liabilities?
How is the concept of 'balancing liabilities' typically interpreted in a business?
How is the concept of 'balancing liabilities' typically interpreted in a business?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Balance Sheet
- A balance sheet is a report that summarizes the financial health of a business at a specific point in time.
- It lists total assets (what the business owns), total liabilities (what the business owes to others), and equity (the owner's stake in the business).
- The balance sheet is used to answer several key financial questions, including:
- How much liquid assets does the business have?
- Is the level of debt sustainable given current operations?
- How much is the business worth?
- How much money do others owe the business (accounts receivable), and how much money does the business owe to others (accounts payable)?
- How much money is available to reinvest in the business (working capital)?
Accounting Equation
- The basic accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- This equation shows how a business's assets are financed, either through debt (liabilities) or through owner investments (equity).
- The balance sheet must always balance, meaning the total assets must always equal the total liabilities plus equity.
Types of Assets
- Assets are categorized as either current or non-current.
- Current assets are items expected to be converted into cash within the next 12 months, and include:
- Cash: The amount of cash available in the business's bank account on the balance sheet date.
- Inventories: Products available for sale, including raw materials.
- Accounts receivable: Money owed to the business by customers that is expected to be received within the next 12 months.
- Non-current assets are long-term investments or assets that are not expected to be converted into cash within the next 12 months, and include:
- Investments: Long-term investments in other companies or assets.
- Fixed assets: Tangible, long-lasting assets such as property, buildings, equipment, vehicles, machinery, and leasehold improvements.
- Intangible assets: Assets that do not have physical form but are valuable to the business, such as trademarks, patents, domain names, and brand names.
Types of Liabilities
- Liabilities are obligations that the business owes to others, and are categorized as either current or non-current.
- Current liabilities are debts expected to be settled within the next 12 months, and include:
- Accounts payable: Money owed to vendors for goods or services received but not yet paid for.
- Short-term loans: Loans with terms of less than 12 months.
- Credit card balances: These are considered current liabilities because they are expected to be repaid quickly.
- Other payables: These include obligations like sales tax payable, payroll taxes payable, and income taxes payable.
- Non-current liabilities are long-term debts that are not expected to be paid in full within the next 12 months, and include:
- Business loans: Loans with terms longer than 12 months.
- Tax liabilities: Tax obligations, including any outstanding tax payments from previous years.
- Mortgages: Payments made towards the mortgage on a building or property.
Equity
- Equity represents the owner's stake in the business.
- It is calculated as: Equity = Assets - Liabilities
- It reflects the value of the business that is owned by the owner(s), after taking into account what the business owes to others (liabilities).
- It is often used to represent the amount of money that would be available to the owner(s) if the business were to be sold and all its debts paid off.
- Equity can be increased by owner investments or profits made by the business, and decreased by owner withdrawals or losses incurred by the business.
Balance Sheet
- A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business's financial health at a specific point in time.
- It lists total assets (what the business owns), total liabilities (what the business owes to others), and equity (the owner's stake in the business).
- The balance sheet helps answer financial questions about a business's liquidity, debt sustainability, valuation, and cash flow.
- It can also be used by lenders and investors to assess the financial risk of a business.
Accounting Equation
- The accounting equation states: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- This equation reflects that all the money in a business must be accounted for.
- If the total liabilities and equity do not equal the total assets, there is an accounting error that needs to be addressed.
Types of Assets
- Current assets are assets that can be converted to cash within 12 months. These include:
- Cash: money held in bank accounts.
- Inventories: items available for sale, including raw materials.
- Accounts receivable: money owed by customers for goods or services.
- Non-current assets are assets that cannot be easily converted to cash within 12 months and include:
- Investments: long-term investments.
- Fixed assets: property, equipment, vehicles, machinery, leasehold improvements.
- Intangible assets: trademarks, patents, domain names, brand names.
Types of Liabilities
- Current liabilities are debts that are due within 12 months. These include:
- Accounts payable: money owed to vendors for goods or services.
- Short-term loans: loans that are expected to be repaid within one year.
- Credit card balances: outstanding balances on credit cards.
- Non-current liabilities are debts that are not due within 12 months. These include:
- Business loans: loans with terms longer than 12 months.
- Tax liabilities: taxes owed from prior years.
- Mortgages: loans on buildings or property.
Equity
- Equity represents the owner's stake in the business.
- It is the difference between assets and liabilities.
- Changes in equity can be due to owner contributions, profit or loss, and dividend distributions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.