Podcast
Questions and Answers
What percentage of axons in the optic tract project to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus?
What percentage of axons in the optic tract project to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus?
- 80%
- 100%
- 95%
- 90% (correct)
Which structure is responsible for controlling the pupillary light reflex?
Which structure is responsible for controlling the pupillary light reflex?
- Pretectum (correct)
- Lateral geniculate nucleus
- Suprachiasmatic nucleus
- Superior colliculus
What is the primary function of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
What is the primary function of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
- Controlling eye movements
- Relaying visual information to the primary visual cortex (correct)
- Processing visual information
- Regulating hormonal changes
What is the location of the visual cortex?
What is the location of the visual cortex?
What type of field loss occurs when there is damage to one optic nerve before crossing over?
What type of field loss occurs when there is damage to one optic nerve before crossing over?
What is the function of the superior colliculus in the midbrain?
What is the function of the superior colliculus in the midbrain?
What is the destination of the optic radiations?
What is the destination of the optic radiations?
What is the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus?
What is the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus?
What is the significance of the lateral geniculate nucleus in processing visual information?
What is the significance of the lateral geniculate nucleus in processing visual information?
What is the location of the optic chiasm?
What is the location of the optic chiasm?
What is the main function of the photoreceptor cells in the retina?
What is the main function of the photoreceptor cells in the retina?
Where does the optic nerve partially cross to join left and right eye information?
Where does the optic nerve partially cross to join left and right eye information?
What is the function of the lens in the eye?
What is the function of the lens in the eye?
What type of vision do rods primarily support?
What type of vision do rods primarily support?
What is the path of information transmission from the photoreceptors in the retina?
What is the path of information transmission from the photoreceptors in the retina?
What is the location of the optic tract after the optic chiasma?
What is the location of the optic tract after the optic chiasma?
What is the function of the cornea in the eye?
What is the function of the cornea in the eye?
What type of cells converge at the optic disc to form the optic nerve?
What type of cells converge at the optic disc to form the optic nerve?
What is the function of the suspensory ligament in the eye?
What is the function of the suspensory ligament in the eye?
What is the main function of the cones in the retina?
What is the main function of the cones in the retina?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
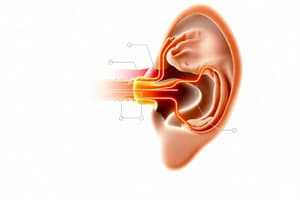
Auditory Pathway
- The auditory pathway is the sensory system for the sense of hearing, including both peripheral and central auditory pathways.
Peripheral Auditory Pathway
- Composed of the outer, middle, and inner ear, which feed directly into the nervous system.
- Converts sound waves into neural action potentials.
Outer Ear
- Consists of the pinna (auricle) and ear canal (auditory canal).
- The pinna receives sound waves and directs them down the ear canal.
- The ear canal is a simple tube that focuses sound waves onto the tympanic membrane.
- It amplifies/intensifies sounds and contains modified sweat glands that secrete cerumen or earwax.
Eardrum (Tympanic Membrane)
- A thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
- Marks the beginning of the middle ear.
- Transmits sound waves from the auditory canal to the middle ear.
Structure of the Eardrum
- The two general regions of the tympanic membrane are:
- Pars flaccida (smaller upper triangular region)
- Pars tensa (larger region)
Inner Ear
- Consists of the bony labyrinth (osseous cochlea, osseous semicircular canals, and osseous vestibule) and membranous labyrinth (membranous cochlea, membranous semicircular canals, and membranous vestibule).
- The bony labyrinth contains fluid called perilymph, while the membranous labyrinth contains fluid called endolymph.
Cochlea
- The auditory portion of the inner ear.
- A fluid-filled, coiled, hollow, conical chamber where waves propagate from the base to the apex.
- Divided into three chambers: scala vestibuli, scala tympani, and scala media (cochlear duct).
- The basement membrane separates the scala media from the scala tympani.
Organ of Corti (Body's Microphone)
- The sensory element of hearing, distributed along the basement membrane.
- Contains inner and outer hair cells that generate nerve impulses required for hearing.
- Hair cells are columnar cells with specialized cilia at the top.
Function of the Cochlea
- Converts sound energy into neural impulses.
- The cochlea fluid moves in response to vibrations from the middle ear, stimulating the hair cells.
- The hair cells sense the motion and convert it to neural signals, which travel along the auditory nerve to the brain stem for further processing.
Central Auditory Pathway
- The sound information is re-encoded in the vestibulocochlear nerve and travels to the cochlear nuclei in the brainstem.
- Auditory/cochlear nerve fibers terminate in the brainstem, where they first form synapses with the cochlear nuclei ipsilaterally.
- Most fibers leaving each cochlear nucleus cross to the opposite (contralateral) superior olivary nucleus of the brainstem.
- The lateral lemniscus (tract of axons) in the brainstem carries the information to the inferior colliculus in the midbrain, which receives fibers from both ears.
- Then to the medial geniculate nucleus in the thalamus onto the primary auditory cortex.
Auditory Cortex
- Located bilaterally in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum.
- Processes auditory information.
- Two functional areas of the auditory cortex:
- Primary auditory cortex (Brodmann area 41) decodes the stimulus.
- Secondary auditory cortex (Brodmann area 42) is responsible for localization and analysis of complex sounds and has a role in auditory memory.
Descending Auditory Pathway
- Follows a similar path to the auditory pathway, but in reverse, from the cortex to the cochlear nuclei.
Clinical Anatomy
- Deafness refers to a partial or total loss of the ability to hear, which may be unilateral or bilateral.
Visual Pathway
Optic Pathway
- The optic pathway transmits information from the eye to the brain.
Optic Nerve
- The optic nerve is a sensory nerve that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.
Optic Chiasm
- The optic chiasm is the part of the optic pathway where the optic nerves from each eye cross over.
Optic Tract
- The optic tract is a bundle of nerve fibers that carries visual information from the optic chiasm to the lateral geniculate nucleus.
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
- A sensory relay nucleus in the thalamus that receives visual information from the optic tract.
- The neurons of the LGN then relay the visual image to the primary visual cortex (Brodmann area 17).
Optic Radiation
- Carries information from the lateral geniculate nucleus to the visual cortex.
Visual Cortex
- Receives fibers from the optic radiation.
- Located in the posterior pole of the occipital lobe.
- The largest system in the human brain, responsible for processing the visual image.
Clinical Anatomy
- Lesions of the optic pathway:
- Unilateral field loss: Loss of vision on one side, caused by damage to one optic nerve (before crossing over).
- Bilateral field loss: Loss of vision on both sides, occurs with damage at the optic chiasm (after crossing over).
Auditory Pathway
- The cochlea fluid moves in response to vibrations from the middle ear, stimulating hair cells in the organ of Corti.
- The hair cells convert the motion into neural signals, which travel along the auditory nerve to structures in the brain stem for further processing.
- Afferent neurons innervate cochlear inner hair cells, transmitting signals from the hair cells to the dendrites of primary auditory neurons via the neurotransmitter glutamate.
- Efferent neurons project from the brain to the cochlea, synapsing on hair cells.
- The cochlear nerve carries neural impulses from the organ of Corti to the brain.
- The vestibular nerve travels from the vestibular system of the inner ear.
- The two form the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), consisting of the cochlear nerve for hearing and the vestibular nerve for equilibrium.
Central Auditory Pathway
- The sound information is re-encoded in the vestibulocochlear nerve and travels to the cochlear nuclei in the brainstem.
- Auditory/cochlear nerve fibers terminate in the brainstem, forming synapses with the cochlear nuclei ipsilaterally (fibers from the right ear terminate in the right cochlear nucleus, and fibers from the left ear terminate in the left cochlear nucleus).
- Most fibers leaving each cochlear nucleus cross to the opposite (contralateral) superior olivary nucleus of the brainstem (pons), while the remaining fibers run on the ipsilateral side.
- The lateral lemniscus (tract of axons) in the brainstem carries the information to the inferior colliculus in the midbrain, which receives fibers from both ears and further integrates.
Visual Pathway
- The visual system is the part of the central nervous system that gives organisms the ability to process visual input.
- Functions of the visual system include reception of light, formation of monocular representations, identification and categorization of visual objects, and assessing distances to and between objects.
The Eye
- Rays of light from an object pass through the cornea and then through the pupil (controlled by the iris).
- The light then passes through the lens, which helps to refract light and focus the image on the retina.
- The retina contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones), which are directly sensitive to light.
- Rods function mainly in dim light and provide black-and-white vision, while cones support daytime vision and the perception of color.
Optic Pathway
- The information leaves the eye by way of the optic nerve.
- Impulses are transmitted from the photoreceptors in the retina (rods and cones) to bipolar cells, which then synapse to ganglion cells.
- Axons of the ganglion cells converge at the optic disc to form the optic nerve.
- The optic nerve partially crosses at the optic chiasma, joining left and right eye information.
- The optic tract wraps around the midbrain to get to the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) in the thalamus.
Clinical Anatomy
- Unilateral field loss: loss of vision on one side, caused by damage to one optic nerve (before crossing over).
- Bilateral field loss: loss of vision on both sides, occurs with damage at the optic chiasm (after crossing over).
- Treatment for lesions of the optic pathway includes antibiotics and hearing aids.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.