Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does arthrokinematics primarily focus on?
What does arthrokinematics primarily focus on?
- The overall movement patterns of the body
- The motion of the bones
- The position of the limbs in space
- The motion between joint surfaces (correct)
Which term describes the rotary or angular motion where multiple points of one surface contact multiple points of another?
Which term describes the rotary or angular motion where multiple points of one surface contact multiple points of another?
- Rolling (correct)
- Sliding
- Spinning
- Pivoting
What is the main difference between arthrokinematics and osteokinematics?
What is the main difference between arthrokinematics and osteokinematics?
- Osteokinematics is concerned with muscle action, whereas arthrokinematics is not.
- Osteokinematics focuses on the bones themselves, while arthrokinematics focuses on joint movement. (correct)
- Arthrokinematics and osteokinematics are the same concepts.
- Osteokinematics deals with joint surfaces, while arthrokinematics deals with bones.
Which of the following motions is NOT one of the basic arthrokinematic motions?
Which of the following motions is NOT one of the basic arthrokinematic motions?
What important clinical concept is described by the concave-convex rule?
What important clinical concept is described by the concave-convex rule?
What describes the process of shoulder abduction during joint movement?
What describes the process of shoulder abduction during joint movement?
What characterizes the motion known as spinning in joint movement?
What characterizes the motion known as spinning in joint movement?
What happens if there is no concomitant slide during femoral rolling in the knee?
What happens if there is no concomitant slide during femoral rolling in the knee?
What is the screw home mechanism associated with?
What is the screw home mechanism associated with?
What does joint distraction involve?
What does joint distraction involve?
During the McMurray test, what is the purpose of externally rotating the tibia?
During the McMurray test, what is the purpose of externally rotating the tibia?
What effect does joint compression have during physical assessments?
What effect does joint compression have during physical assessments?
What occurs concurrently with the roll during knee flexion?
What occurs concurrently with the roll during knee flexion?
Which joint movement is associated with a rotary or angular motion?
Which joint movement is associated with a rotary or angular motion?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Arthrokinematics vs. Osteokinematics
- Arthrokinematics describes joint surface motion (from Greek "arthro" - joint, "kinema" - motion).
- Osteokinematics focuses on bone movement.
Arthrokinematic Motions
- Three basic arthrokinematic motions: rolling (or rocking), sliding (or gliding), and spinning.
- Rolling: Multiple points on one surface contact multiple points on another (e.g., shoulder abduction).
- Sliding: Single point on one surface contacts multiple points on another (e.g., shoulder abduction). In shoulder abduction, sliding occurs opposite to rolling.
- Spinning: Single point on one surface contacts a single point on another (e.g., radius rotating on humerus during pronation/supination).
- Most joint movements combine rolling, sliding, and spinning. Without the appropriate slide, rolling can cause joint surfaces to lose contact (e.g., femur rolling off tibia without a simultaneous slide).
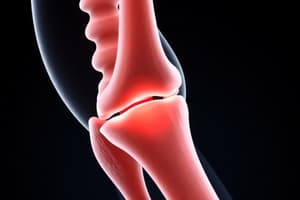
Joint Play (Accessory Motion)
- Small arthrokinematic motions enabling full active joint motion.
- Therapists use joint compression (surfaces move together, improves stability, e.g., McMurray test for meniscus tear) and distraction (surfaces pulled apart, increases mobility, e.g., Lachman test for ACL tear) to assess joint integrity.
Convex-Concave Rule
- Convex-on-concave: If the convex surface moves, the slide occurs in the opposite direction of the roll.
- Concave-on-convex: If the concave surface moves, the slide occurs in the same direction as the roll.
Instantaneous Axis of Rotation
- The center of motion changes as a joint moves.
- The evolute describes the path of the instantaneous axis of rotation. Goniometer measurements are approximations; the true center of rotation is rarely fixed.
Closed-Packed vs. Open-Packed Joint Positions
- Closed-packed: Maximum surface contact; accessory motion is minimized; ligaments are taut; joint is compressed (e.g., full knee extension).
- Open-packed (loose-packed): Joint surfaces don't fit perfectly; ligaments are slack; allows for joint distraction (e.g., knee flexion at 20-30 degrees). Joint play is measured in the open-packed position.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.