Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of arteries in the vascular system?
What is the primary function of arteries in the vascular system?
- To carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (correct)
- To facilitate gas exchange in the capillaries
- To return deoxygenated blood to the heart
- To maintain low blood pressure
Which statement accurately describes the structure of arteries?
Which statement accurately describes the structure of arteries?
- They are incapable of changing shape
- They have a single layer wall that is weak
- They have three layered walls providing strength and elasticity (correct)
- They are primarily responsible for nutrient absorption
What mechanism allows arteries to adjust to varying blood flow demands?
What mechanism allows arteries to adjust to varying blood flow demands?
- Lymphatic expansion
- Capillary osmosis
- Vein constriction
- Vasoconstriction and vasodilation (correct)
How do veins function in the circulatory system?
How do veins function in the circulatory system?
Which fluid compartments are primarily involved in fluid transport within the body?
Which fluid compartments are primarily involved in fluid transport within the body?
What is one characteristic of arterial wounds?
What is one characteristic of arterial wounds?
What role does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) play in the vascular response during stress?
What role does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) play in the vascular response during stress?
Which of the following describes the main difference between the venous and lymphatic systems?
Which of the following describes the main difference between the venous and lymphatic systems?
What is the primary function of lymphatics in the body?
What is the primary function of lymphatics in the body?
Which of the following structures is NOT a part of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following structures is NOT a part of the lymphatic system?
Where is lymph fluid first absorbed in the body?
Where is lymph fluid first absorbed in the body?
What mechanism primarily aids lymph movement in collector vessels?
What mechanism primarily aids lymph movement in collector vessels?
Which factor does NOT influence lymphangion contraction?
Which factor does NOT influence lymphangion contraction?
What type of changes do lymphatic vessels undergo which makes them thinner and more likely to collapse than veins?
What type of changes do lymphatic vessels undergo which makes them thinner and more likely to collapse than veins?
What type of pressure changes aid the movement of lymph back to the heart during normal breathing?
What type of pressure changes aid the movement of lymph back to the heart during normal breathing?
Which lymphatic structure is responsible for draining fluid from the right side of the head and upper body?
Which lymphatic structure is responsible for draining fluid from the right side of the head and upper body?
Which of the following statements best describes how manual lymphatic drainage works?
Which of the following statements best describes how manual lymphatic drainage works?
What is the composition of lymph fluid primarily responsible for?
What is the composition of lymph fluid primarily responsible for?
What structures do superficial veins run above?
What structures do superficial veins run above?
Which function do the valves in veins primarily serve?
Which function do the valves in veins primarily serve?
What leads to the formation of varicose veins?
What leads to the formation of varicose veins?
The lymphatic system is involved in protecting the body from what?
The lymphatic system is involved in protecting the body from what?
What is a consequence of weakened valves in the venous system?
What is a consequence of weakened valves in the venous system?
Which type of vein connects superficial and deep veins?
Which type of vein connects superficial and deep veins?
What causes venous wounds to be wet?
What causes venous wounds to be wet?
How do skeletal muscle contractions assist veins in blood flow?
How do skeletal muscle contractions assist veins in blood flow?
Which of the following statements about the venous walls is correct?
Which of the following statements about the venous walls is correct?
What role does the lymphatic system play alongside the venous system?
What role does the lymphatic system play alongside the venous system?
What is dehydration commonly caused by?
What is dehydration commonly caused by?
What term describes fluid that shifts from one space to another, typically due to trauma or inflammation?
What term describes fluid that shifts from one space to another, typically due to trauma or inflammation?
Which of the following describes passive movement from high to low concentration?
Which of the following describes passive movement from high to low concentration?
What is the role of the plasma membrane in fluid transport?
What is the role of the plasma membrane in fluid transport?
In which mode of transport do large particles move against their concentration gradient?
In which mode of transport do large particles move against their concentration gradient?
What component of fluid transport can be represented as Kool-Aid powder?
What component of fluid transport can be represented as Kool-Aid powder?
Which condition can lead to the formation of ascites?
Which condition can lead to the formation of ascites?
What are the two main types of fluid in the body?
What are the two main types of fluid in the body?
Which of the following fluids is NOT considered part of the transcellular space?
Which of the following fluids is NOT considered part of the transcellular space?
What is the primary ion that influences water retention and loss?
What is the primary ion that influences water retention and loss?
What condition is characterized by weight gain and edema of the extremities?
What condition is characterized by weight gain and edema of the extremities?
Which space contains about 2/3 of the body's fluid?
Which space contains about 2/3 of the body's fluid?
What clinical manifestation can occur due to excessive loss of water?
What clinical manifestation can occur due to excessive loss of water?
Fluid imbalance can occur due to changes in which of the following?
Fluid imbalance can occur due to changes in which of the following?
What is a sign that might indicate excess fluid in the intravascular space?
What is a sign that might indicate excess fluid in the intravascular space?
Under which conditions does lymph flow get adversely affected?
Under which conditions does lymph flow get adversely affected?
What is the term for the condition resulting from inadequate intake of water?
What is the term for the condition resulting from inadequate intake of water?
Flashcards
Arterial system function
Arterial system function
Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to tissues.
Venous system function
Venous system function
Returns deoxygenated blood from tissues back to the heart.
Capillary function
Capillary function
Exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between blood and tissues.
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasodialation
Vasodialation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arterial wound characteristics
Arterial wound characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid exchange in tissues
Fluid exchange in tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic system role in blood return
Lymphatic system role in blood return
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the lymphatic system?
What is the lymphatic system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does lymph fluid transport?
What does lymph fluid transport?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are lymphangions?
What are lymphangions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do lymphangions contract?
How do lymphangions contract?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does lymph drain back to?
Where does lymph drain back to?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are lymphatic vessels?
What are lymphatic vessels?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of lymph nodes?
What is the role of lymph nodes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the lymphatic system NOT found?
Where is the lymphatic system NOT found?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the lymphatic system in immune defense?
What is the role of the lymphatic system in immune defense?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) work?
How does Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous blood flow
Venous blood flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous wall features
Venous wall features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous valves
Venous valves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous blood flow mechanism
Venous blood flow mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Varicose veins
Varicose veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous reflux
Venous reflux
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous wound characteristics
Venous wound characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic system function
Lymphatic system function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic system role in immunity
Lymphatic system role in immunity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Relationship between lymphatic and venous systems
Relationship between lymphatic and venous systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is dehydration?
What is dehydration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is fluid shift?
What is fluid shift?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is third-space fluid?
What is third-space fluid?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is ascites?
What is ascites?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is pleural effusion?
What is pleural effusion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a solute?
What is a solute?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a solvent?
What is a solvent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Compartments
Fluid Compartments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Imbalance
Fluid Imbalance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Edema
Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypervolemia
Hypervolemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Volume Deficit
Fluid Volume Deficit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypovolemia
Hypovolemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymph Flow
Lymph Flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thoracic Duct
Thoracic Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Arteries, Veins, and Lymphatic Systems
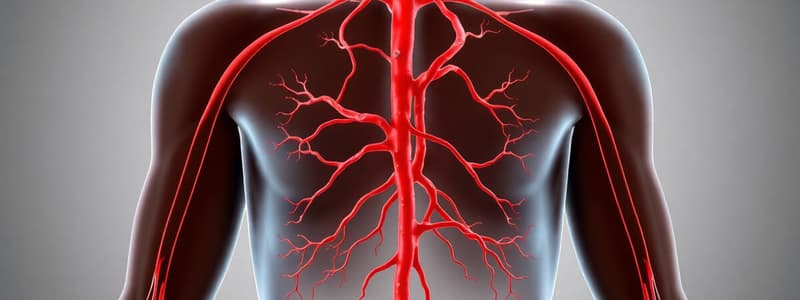
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, branching into arterioles and capillaries.
- Arterial walls are thick and strong, with three layers, enabling them to withstand high pressure. Blood flow through arteries is dependent on the heart's function.
- Veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, beginning in capillaries and progressing to venules then into veins.
- Unlike arteries, veins are not as elastic.
- Veins have three layers, but they are not elastic or muscular.
- Venous pressure is low and the walls are thin, which can lead to venous collapse or tears when stretched.
- Veins contain valves that prevent backflow, facilitated by muscle contractions primarily from skeletal movement.
- The lymphatic system works in parallel with the venous system and plays a crucial role in fluid balance and immune response.
Lymphatic System
- Functions include: -Protecting the body from infection and disease through immune response. -Facilitating movement of fluids, blood waste, and protein molecules between the bloodstream and interstitial space.
- Composed of lymph vessels, lymph fluid, and lymph tissues (like nodes, tonsils, spleen, and thymus).
- Fluid moves throughout the body by several methods, including diffusion and filtration.
- Lymph moves through larger vessels due to their contractions called lymphangions.
- Lymph is transported back to the heart to re-enter the venous circulation.
- Fluid from the right side of the body (head, neck, thorax, and right upper limb) enters the right lymphatic duct.
- Fluid from the left side of the body enters the thoracic duct.
- The lymphatic system is crucial in fluid balance and immune function. Fluid does not flow uphill, under normal circumstances, flow is not affected by gravity.
Fluid Compartments
- About 45-60% of the adult body is water, containing electrolytes.
- Compartments include intracellular, interstitial, intravascular, and transcellular.
- Intracellular: inside cells.
- Interstitial: between cells.
- Intravascular: within blood vessels.
- Transcellular: separated from body tissues (includes digestive juice, CSF, synovial, intraocular fluids etc).
Fluid Imbalance
- Fluid volume excess (edema): Overabundance of interstitial or intravascular fluids, often leading to swelling (particularly in extremities).
- Fluid volume deficit (dehydration): Fluid loss or lack of intake, can result in tissue dehydration. Potentially dangerous.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.