Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the patient experiencing as a result of landing on the lateral surface of their right ankle?
What is the patient experiencing as a result of landing on the lateral surface of their right ankle?
- Minor hesitancy in using their ankle (correct)
- Severe pain in the ankle
- Total loss of ankle function
- Severe limping
What type of maneuver did the patient fail to stick?
What type of maneuver did the patient fail to stick?
- Heel flip
- Ollie
- Pancake maneuver (correct)
- Kickflip
What is the range of motion for flexion of the ankle?
What is the range of motion for flexion of the ankle?
- 20 degrees
- 30 degrees
- None of the above
- Blank (correct)
What is the range of motion for extension of the ankle?
What is the range of motion for extension of the ankle?
What is the range of motion for inversion of the ankle?
What is the range of motion for inversion of the ankle?
What is the range of motion for eversion of the ankle?
What is the range of motion for eversion of the ankle?
What is the action of the prime movers in flexion of the ankle?
What is the action of the prime movers in flexion of the ankle?
What is the nerve root that innervates the muscles involved in flexion of the ankle?
What is the nerve root that innervates the muscles involved in flexion of the ankle?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
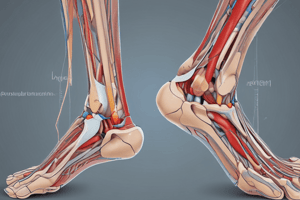
Ankle Injury
- Patient experienced a minor hesitancy in using their right ankle after landing on the lateral surface while skateboarding one month ago.
- Patient is not comfortable jumping on that foot on its own.
Associated Bones
- Not specified, but the ankle joint is formed by the connection of the tibia, fibula, and talus bones.
Articulating Surfaces
- Not specified, but the ankle joint consists of the trochlea of the talus bone and the distal ends of the tibia and fibula bones.
ROM Rules Out
- Not specified, but ROM (Range of Motion) rules out other possible causes of ankle pain.
Myotomes/Dermatomes that would affect this joint
- Not specified, but the ankle joint is innervated by the L4-S1 nerve roots.
Ankle Range of Motion (ROM)
- Flexion: degree of motion not specified
- Extension: degree of motion not specified
- Inversion: degree of motion not specified
- Eversion: degree of motion not specified
Flexion Movement
- Prime movers: not specified, but likely the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles
- Proximal attachment: not specified, but likely the medial aspect of the tibia and fibula bones
- Distal attachment: not specified, but likely the talus and calcaneus bones
- Innervation: not specified, but likely the L4-L5 nerve roots
- Nerve roots: not specified, but likely the L4-L5 nerve roots
Extension Movement
- Prime movers: not specified, but likely the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles
- Proximal attachment: not specified, but likely the medial aspect of the femur bone
- Distal attachment: not specified, but likely the calcaneus bone
- Innervation: not specified, but likely the S1-S2 nerve roots
- Nerve roots: not specified, but likely the S1-S2 nerve roots
Inversion Movement
- Prime movers: not specified, but likely the tibialis posterior and flexor digitorum longus muscles
- Proximal attachment: not specified, but likely the medial aspect of the tibia and fibula bones
- Distal attachment: not specified, but likely the talus and navicular bones
- Innervation: not specified, but likely the L4-L5 nerve roots
- Nerve roots: not specified, but likely the L4-L5 nerve roots
Eversion Movement
- Prime movers: not specified, but likely the peroneus longus and brevis muscles
- Proximal attachment: not specified, but likely the lateral aspect of the fibula bone
- Distal attachment: not specified, but likely the cuboid and metatarsal bones
- Innervation: not specified, but likely the L5-S1 nerve roots
- Nerve roots: not specified, but likely the L5-S1 nerve roots
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.