Podcast
Questions and Answers
The ankle joint's actions include inversion and eversion.
The ankle joint's actions include inversion and eversion.
True (A)
The arches of the foot do not include any supporting ligaments or tendons.
The arches of the foot do not include any supporting ligaments or tendons.
False (B)
The long and short saphenous veins are part of the lower limb anatomy.
The long and short saphenous veins are part of the lower limb anatomy.
True (A)
Radiological imaging is not relevant for assessing ankle joints.
Radiological imaging is not relevant for assessing ankle joints.
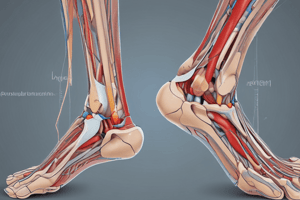
The surface anatomy of the peripheral pulses in the lower limb can be examined.
The surface anatomy of the peripheral pulses in the lower limb can be examined.
The saphenous vein is part of the vascular supply of the foot.
The saphenous vein is part of the vascular supply of the foot.
The plantar arch supplies blood to the dorsal aspect of the foot.
The plantar arch supplies blood to the dorsal aspect of the foot.
Radiological imaging is important for interpreting conditions of the ankle joint.
Radiological imaging is important for interpreting conditions of the ankle joint.
The lower limb does not have identifiable peripheral pulses.
The lower limb does not have identifiable peripheral pulses.
Abrahams, Peter H. is a recommended author for studying human anatomy.
Abrahams, Peter H. is a recommended author for studying human anatomy.
The foot is made up of 7 tarsal bones.
The foot is made up of 7 tarsal bones.
There are 5 metatarsal bones in the foot.
There are 5 metatarsal bones in the foot.
The ankle joint is a hinge joint involving the talus and the femur.
The ankle joint is a hinge joint involving the talus and the femur.
The foot has a total of 14 phalanges.
The foot has a total of 14 phalanges.
Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion are movements allowed by the ankle joint.
Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion are movements allowed by the ankle joint.
A pilon fracture is caused by high axial forces such as falling from a great height.
A pilon fracture is caused by high axial forces such as falling from a great height.
The subtalar joint is responsible for plantarfexion of the foot.
The subtalar joint is responsible for plantarfexion of the foot.
Inversion of the foot involves directing the sole laterally.
Inversion of the foot involves directing the sole laterally.
The tarsal tunnel is located on the lateral side of the ankle.
The tarsal tunnel is located on the lateral side of the ankle.
The bones of the foot lie in a horizontal plane.
The bones of the foot lie in a horizontal plane.
The Medial Plantar Nerve supplies the nail beds and tips of the lateral three and one-half toes.
The Medial Plantar Nerve supplies the nail beds and tips of the lateral three and one-half toes.
The Lateral Plantar Nerve is responsible for motor branches to muscles in the sole of the foot.
The Lateral Plantar Nerve is responsible for motor branches to muscles in the sole of the foot.
The posterior tibial artery divides into the Medial Plantar Artery and the Lateral Plantar Artery.
The posterior tibial artery divides into the Medial Plantar Artery and the Lateral Plantar Artery.
The Lateral Plantar Artery is smaller and supplies the medial side of the big toe.
The Lateral Plantar Artery is smaller and supplies the medial side of the big toe.
Digital arteries to the toes are supplied by branches from the dorsalis pedis artery.
Digital arteries to the toes are supplied by branches from the dorsalis pedis artery.
The veins accompanying the arteries are referred to as the Medial and Lateral Plantar veins.
The veins accompanying the arteries are referred to as the Medial and Lateral Plantar veins.
The Sural nerve is not mentioned as a part of the structures associated with the posterior tibial artery.
The Sural nerve is not mentioned as a part of the structures associated with the posterior tibial artery.
The Midinguinal point is located midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis.
The Midinguinal point is located midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis.
The small saphenous vein drains into the femoral vein.
The small saphenous vein drains into the femoral vein.
The great saphenous vein passes anterior to the medial malleolus.
The great saphenous vein passes anterior to the medial malleolus.
Deep veins of the leg drain into the femoral vein.
Deep veins of the leg drain into the femoral vein.
The femoral vein becomes the external iliac when it passes underneath the inguinal ligament.
The femoral vein becomes the external iliac when it passes underneath the inguinal ligament.
The tibial nerve branches off from the common fibular nerve.
The tibial nerve branches off from the common fibular nerve.
The sural nerve is formed from branches of the tibial nerve.
The sural nerve is formed from branches of the tibial nerve.
Perforating veins connect superficial veins with deep veins.
Perforating veins connect superficial veins with deep veins.
The popliteal vein becomes the femoral vein after passing into the adductor hiatus.
The popliteal vein becomes the femoral vein after passing into the adductor hiatus.
The common fibular nerve is part of the lumbar plexus.
The common fibular nerve is part of the lumbar plexus.
The deep veins of the lower limb accompany arteries.
The deep veins of the lower limb accompany arteries.
The ankle joint primarily functions as a ball-and-socket joint.
The ankle joint primarily functions as a ball-and-socket joint.
The lateral collateral ligament of the ankle provides support against inversion injuries.
The lateral collateral ligament of the ankle provides support against inversion injuries.
The tarsal tunnel contains the tendons of the long flexor muscles along with the posterior tibial artery and nerve.
The tarsal tunnel contains the tendons of the long flexor muscles along with the posterior tibial artery and nerve.
The arches of the foot do not play a role in shock absorption during walking.
The arches of the foot do not play a role in shock absorption during walking.
The plantar arch primarily supplies blood to the ventral aspect of the foot.
The plantar arch primarily supplies blood to the ventral aspect of the foot.
Inversion of the foot involves moving the sole of the foot laterally away from the midline.
Inversion of the foot involves moving the sole of the foot laterally away from the midline.
The great saphenous vein is the longest vein in the body and typically drains into the popliteal vein.
The great saphenous vein is the longest vein in the body and typically drains into the popliteal vein.
The deep veins of the leg always run alongside the superficial veins.
The deep veins of the leg always run alongside the superficial veins.
The lateral plantar artery supplies blood to the lateral side of the foot including the fourth and fifth toes.
The lateral plantar artery supplies blood to the lateral side of the foot including the fourth and fifth toes.
The subtalar joint is primarily responsible for inversion and eversion of the foot.
The subtalar joint is primarily responsible for inversion and eversion of the foot.
A pilon fracture usually occurs due to low axial forces, such as minor falls.
A pilon fracture usually occurs due to low axial forces, such as minor falls.
The ankle joint is a synovial joint involving the talus, tibia, and fibula.
The ankle joint is a synovial joint involving the talus, tibia, and fibula.
The foot consists of 12 tarsal bones.
The foot consists of 12 tarsal bones.
Dorsiflexion involves moving the top of the foot away from the leg.
Dorsiflexion involves moving the top of the foot away from the leg.
Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion are the only movements allowed by the ankle joint.
Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion are the only movements allowed by the ankle joint.
The bones of the foot form both longitudinal and transverse arches, not lying in a horizontal plane.
The bones of the foot form both longitudinal and transverse arches, not lying in a horizontal plane.
Phalanges in the foot are categorized into three types for each digit except for digit 1.
Phalanges in the foot are categorized into three types for each digit except for digit 1.
The cuboid bone is one of the tarsal bones located on the medial side of the foot.
The cuboid bone is one of the tarsal bones located on the medial side of the foot.
The anterior talofibular ligament is injured first during an inversion sprain.
The anterior talofibular ligament is injured first during an inversion sprain.
The medial ligament of the ankle is composed of three separate ligaments.
The medial ligament of the ankle is composed of three separate ligaments.
Ankle sprains can occur from stepping on uneven surfaces.
Ankle sprains can occur from stepping on uneven surfaces.
Pott’s fracture occurs when the foot is forcibly inverted.
Pott’s fracture occurs when the foot is forcibly inverted.
The calcaneofibular ligament is part of the medial ligaments of the ankle.
The calcaneofibular ligament is part of the medial ligaments of the ankle.
Eversion sprains are more likely to occur than inversion sprains.
Eversion sprains are more likely to occur than inversion sprains.
The ankle joint is more stable in dorsiflexion compared to plantarflexion.
The ankle joint is more stable in dorsiflexion compared to plantarflexion.
The deltoid ligament of the ankle attaches to the lateral malleolus.
The deltoid ligament of the ankle attaches to the lateral malleolus.
The Medial Plantar Nerve supplies the medial side of the big toe.
The Medial Plantar Nerve supplies the medial side of the big toe.
The digital arteries to the toes arise from the Medial Plantar Artery.
The digital arteries to the toes arise from the Medial Plantar Artery.
Veins accompany arteries, and the Medial and Lateral Plantar veins are examples of this.
Veins accompany arteries, and the Medial and Lateral Plantar veins are examples of this.
The posterior tibial artery does not divide into the Medial and Lateral Plantar Arteries.
The posterior tibial artery does not divide into the Medial and Lateral Plantar Arteries.
The Midinguinal point is located midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the ischial tuberosity.
The Midinguinal point is located midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the ischial tuberosity.
The Lateral Plantar Nerve is cutaneous to the lateral one and one-half toes.
The Lateral Plantar Nerve is cutaneous to the lateral one and one-half toes.
The Surreal nerve does not accompany any arteries in the lower limb.
The Surreal nerve does not accompany any arteries in the lower limb.
The lateral collateral ligament of the ankle restricts movement during eversion injuries.
The lateral collateral ligament of the ankle restricts movement during eversion injuries.
The tarsal tunnel is located medially and contains the posterior tibial artery and nerve.
The tarsal tunnel is located medially and contains the posterior tibial artery and nerve.
Digital arteries of the toes are exclusively supplied by the anterior tibial artery.
Digital arteries of the toes are exclusively supplied by the anterior tibial artery.
The foot's arches primarily serve to enhance rigidity for force transmission during movement.
The foot's arches primarily serve to enhance rigidity for force transmission during movement.
The subtalar joint primarily facilitates dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot.
The subtalar joint primarily facilitates dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot.
The ankle joint allows for hinge-like movements of dorsi- and plantarflexion.
The ankle joint allows for hinge-like movements of dorsi- and plantarflexion.
Plantarfexion is primarily controlled by the subtalar joint.
Plantarfexion is primarily controlled by the subtalar joint.
The tarsal bones include both the cuboid and calcaneus.
The tarsal bones include both the cuboid and calcaneus.
The ankle joint does not involve any of the leg's bones.
The ankle joint does not involve any of the leg's bones.
The vascular supply of the sole of the foot is largely provided by the plantar arch.
The vascular supply of the sole of the foot is largely provided by the plantar arch.
The medial plantar nerve innervates the majority of the intrinsic muscles of the foot.
The medial plantar nerve innervates the majority of the intrinsic muscles of the foot.
The great saphenous vein traverses posterior to the medial malleolus.
The great saphenous vein traverses posterior to the medial malleolus.
The talocalcaneonavicular joint is involved in dorsiflexion of the foot.
The talocalcaneonavicular joint is involved in dorsiflexion of the foot.
Tarsal joints allow for both inversion and eversion movements.
Tarsal joints allow for both inversion and eversion movements.
The subtalar joint allows for dorsi- and plantar flexion of the foot.
The subtalar joint allows for dorsi- and plantar flexion of the foot.
A pilon fracture involves a single fracture of the fibula due to low axillary forces.
A pilon fracture involves a single fracture of the fibula due to low axillary forces.
Radiological imaging is essential for accurately interpreting fractures in the ankle joint.
Radiological imaging is essential for accurately interpreting fractures in the ankle joint.
The Tarsal tunnel contains tendons of the long flexor muscles and is located on the medial side of the ankle.
The Tarsal tunnel contains tendons of the long flexor muscles and is located on the medial side of the ankle.
Eversion of the foot involves the medial movement of the foot's sole away from the midline.
Eversion of the foot involves the medial movement of the foot's sole away from the midline.
The transverse arch does not include the cuboid bone.
The transverse arch does not include the cuboid bone.
The plantar aponeurosis plays no role in maintaining the arches of the foot.
The plantar aponeurosis plays no role in maintaining the arches of the foot.
The medial part of the longitudinal arch only involves the calcaneus and the cuboid.
The medial part of the longitudinal arch only involves the calcaneus and the cuboid.
The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is also known as the short plantar ligament.
The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is also known as the short plantar ligament.
The lateral plantar nerve supplies sensory innervation to the medial side of the foot.
The lateral plantar nerve supplies sensory innervation to the medial side of the foot.
The sole of the foot is organized into three layers of muscles.
The sole of the foot is organized into three layers of muscles.
The longitudinal arch's lateral part includes the calcaneus, cuboid, and proximal ends of the fourth and fifth metatarsals.
The longitudinal arch's lateral part includes the calcaneus, cuboid, and proximal ends of the fourth and fifth metatarsals.
The deep fascia in the sole of the foot does not thicken to form structures supporting the foot's arches.
The deep fascia in the sole of the foot does not thicken to form structures supporting the foot's arches.
The Lateral Plantar Nerve provides cutaneous sensation to the medial three and one-half toes.
The Lateral Plantar Nerve provides cutaneous sensation to the medial three and one-half toes.
The Medial Plantar Artery is larger and supplies blood to the lateral side of the big toe.
The Medial Plantar Artery is larger and supplies blood to the lateral side of the big toe.
The digital arteries to the toes are supplied by the Medial Plantar Artery.
The digital arteries to the toes are supplied by the Medial Plantar Artery.
The posterior tibial artery forms the deep plantar arch after passing deep to the muscles of the sole of the foot.
The posterior tibial artery forms the deep plantar arch after passing deep to the muscles of the sole of the foot.
The medial and lateral plantar veins contain no valves.
The medial and lateral plantar veins contain no valves.
The sural nerve is a continuation of the femoral nerve.
The sural nerve is a continuation of the femoral nerve.
The Midinguinal point is located midway between the pubic symphysis and the medial malleolus.
The Midinguinal point is located midway between the pubic symphysis and the medial malleolus.
The deep plantar arch primarily supplies blood to the dorsal aspect of the foot.
The deep plantar arch primarily supplies blood to the dorsal aspect of the foot.
Flashcards
Ankle Joint Osteology
Ankle Joint Osteology
Study of bone structure in the ankle joint.
Foot Arches
Foot Arches
Structures in the foot that support weight.
Inversion/Eversion Movements
Inversion/Eversion Movements
Turning foot inward (inversion) or outward (eversion).
Peripheral Pulses Lower Limb
Peripheral Pulses Lower Limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Tunnel
Tarsal Tunnel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vascular supply of the sole of the foot
Vascular supply of the sole of the foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar arch
Plantar arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surface anatomy of the lower limb
Surface anatomy of the lower limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral pulses
Peripheral pulses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiological imaging of the foot and ankle
Radiological imaging of the foot and ankle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talus Movement
Talus Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pilon Fracture
Pilon Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subtalar Joint
Subtalar Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midtarsal Joint
Midtarsal Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Bones
Tarsal Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsals
Metatarsals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phalanges
Phalanges
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Joint
Ankle Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibia and Fibula
Tibia and Fibula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial Nerve Branches
Tibial Nerve Branches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Plantar Nerve
Medial Plantar Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Plantar Nerve
Lateral Plantar Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Tibial Artery Branches
Posterior Tibial Artery Branches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Plantar Artery
Medial Plantar Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Plantar Artery
Lateral Plantar Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Plantar Arch
Deep Plantar Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midinguinal Point
Midinguinal Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpable pulse location
Palpable pulse location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpable pulse location 2
Palpable pulse location 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small saphenous vein
Small saphenous vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Great saphenous vein
Great saphenous vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral vein
Femoral vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal vein
Popliteal vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep veins of the lower limb
Deep veins of the lower limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common fibular nerve
Common fibular nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial fibular nerve
Superficial fibular nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep fibular nerve
Deep fibular nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Pulses in the Lower Limb
Peripheral Pulses in the Lower Limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot's Vascular Supply
Foot's Vascular Supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Identifying Lower Limb Pulses
Identifying Lower Limb Pulses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiological Imaging of Foot and Ankle
Radiological Imaging of Foot and Ankle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surface Anatomy of Lower Limb
Surface Anatomy of Lower Limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
What bones form the ankle joint?
What bones form the ankle joint?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Malleolus Fracture
Lateral Malleolus Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibula Articular Surface
Fibula Articular Surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Ligaments
Ankle Ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Sprain: Inversion
Ankle Sprain: Inversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pott's Fracture
Pott's Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talus
Talus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Malleolus
Medial Malleolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Malleolus
Lateral Malleolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Tibial Artery
Posterior Tibial Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the Midinguinal Point?
Where is the Midinguinal Point?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the Palpable Pulse Location?
Where is the Palpable Pulse Location?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inversion
Inversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eversion
Eversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extensor Retinacula
Extensor Retinacula
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the bones of the lower leg?
What are the bones of the lower leg?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inversion Ankle Sprain
Inversion Ankle Sprain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dorsiflexion of the Foot
Dorsiflexion of the Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantarflexion of the Foot
Plantarflexion of the Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Longitudinal Arch
Longitudinal Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Arch
Transverse Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Aponeurosis
Plantar Aponeurosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcaneus
Calcaneus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Calcaneonavicular (Spring) Ligament
Plantar Calcaneonavicular (Spring) Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpable Pulse Location (Foot)
Palpable Pulse Location (Foot)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpable Pulse Location (Ankle)
Palpable Pulse Location (Ankle)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Ankle, Foot, Peripheral Pulses and Venous Drainage of the Lower Limb
- The foot is composed of: 7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsal bones, and 14 phalanges.
- The ankle joint is a synovial joint involving the talus of the foot and the distal ends of the tibia and fibula.
- The ankle allows hinge-like dorsiflexion and plantarflexion.
- The articular surface is covered by hyaline cartilage; the talus is wider anteriorly than posteriorly, contributing to stability during dorsiflexion. Medial and lateral ligaments stabilize the joint.
- The lateral ligament of the ankle consists of three separate ligaments: anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular ligaments.
- The medial (deltoid) ligament is strong, large, and triangular, composed of four separate ligaments.
- Ankle sprains occur when ankle ligaments are stretched (but not ruptured), ranging from mild to severe. Inversion sprains are more common, stretching lateral ligaments (anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular). Eversion sprains are less common.
- Pott's fracture-bimalleolar ankle fracture involves the forcible eversion of the foot, pulling on the medial malleolus. The talus moves laterally, causing fractures of the lateral malleolus and possibly the fibula superior to the inferior tibiofibular joint.
- Pilon fracture involves multiple fractures of the tibia, often from high axial forces. Fixation is usually required.
- Tarsal joints include the subtalar (allows gliding and rotation, crucial for inversion), talocalcaneonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints; midtarsal/inter/transverse tarsal joint (combined talocalcaneonavicular and calcaneocuboid). Movement includes inversion and eversion.
- The tarsal tunnel is between the tarsal bones and the flexor retinaculum on the medial side of the ankle.
- Movements at the ankle include dorsiflexion (moving the top of the foot toward the leg), plantarflexion (moving the sole of the foot away from the leg), inversion (directing the sole of the foot medially), and eversion (directing the sole of the foot laterally).
- The arches of the foot (longitudinal and transverse) absorb and distribute weight, with the medial longitudinal arch involving the calcaneus, talus, navicular, three cuneiforms, and the first three metatarsals; the lateral part involves the calcaneus, cuboid, and the last two metatarsals. The transverse arch connects the tarsals and metatarsals. These arches are maintained by ligaments and muscles.
- The plantar ligaments(calcaneocuboid, calcaneonavicular) are strong and crucial for maintaining the arches of the foot, particularly the medial longitudinal arch.
- The sole of the foot has thick skin, plantar fascia, and plantar nerves. Plantar fascia divides into slips which encircle flexor muscles. This structure is important for supporting the foot's arches.
- Peripheral pulses assessed at the midinguinal point, behind the medial malleolus, and using Doppler ultrasound.
- Superficial veins include the small saphenous vein (lateral side of dorsal venous arch) and the great saphenous vein (medial side of dorsal venous arch). Both drain into the popliteal and femoral veins, respectively. Deep veins accompany arteries. Perforating veins connect deep and superficial veins in the leg.
- Nerves include tibial, common fibular, superficial fibular, deep fibular, and saphenous branches; crucial for sensation, movement, and reflexes in the lower limb. Nerves originate primarily from the sacral plexus.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.