Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of inserting an ET-tube during the maintenance phase of anesthesia?
What is the primary purpose of inserting an ET-tube during the maintenance phase of anesthesia?
- To administer intravenous fluids to the patient
- To monitor the heart rate and blood pressure
- To provide an unobstructed route for administering oxygen and inhalation agents (correct)
- To facilitate the patient's recovery by enhancing anesthesia
Why is the cuff of the ET-tube inflated after insertion?
Why is the cuff of the ET-tube inflated after insertion?
- To facilitate the administration of medication directly into the airway
- To prevent the leakage of gases and secure the airway (correct)
- To minimize the pressure on the vocal cords
- To allow for easier removal of the tube later
What potential complication can arise if intubation is attempted before the patient reaches stage III anesthesia?
What potential complication can arise if intubation is attempted before the patient reaches stage III anesthesia?
- Prolonged recovery time from anesthesia
- Laryngospasm or bronchospasm (correct)
- Severe hypotension during surgery
- Inability to ventilate the patient properly
What role does the muscle relaxing agent play in the intubation procedure?
What role does the muscle relaxing agent play in the intubation procedure?
Which anatomical structures need to be illuminated for proper intubation?
Which anatomical structures need to be illuminated for proper intubation?
What is a critical responsibility of the anesthetist during the intubation process?
What is a critical responsibility of the anesthetist during the intubation process?
What is meant by 'securing the airway' in the context of intubation?
What is meant by 'securing the airway' in the context of intubation?
In cases where oral intubation is not possible, which method is recommended?
In cases where oral intubation is not possible, which method is recommended?
What stage of anesthesia does the patient re-enter after the effects of the anesthetic wear off?
What stage of anesthesia does the patient re-enter after the effects of the anesthetic wear off?
What is the primary reason for gently restraining the patient emerging from anesthesia?
What is the primary reason for gently restraining the patient emerging from anesthesia?
What is the primary action taken by the anesthetist once the patient begins breathing spontaneously?
What is the primary action taken by the anesthetist once the patient begins breathing spontaneously?
Why is it important to have suction equipment available during the patient's emergence from anesthesia?
Why is it important to have suction equipment available during the patient's emergence from anesthesia?
What can result from rapid movements after anesthesia?
What can result from rapid movements after anesthesia?
What should be done with drainage containers during the transport of the patient to the recovery room?
What should be done with drainage containers during the transport of the patient to the recovery room?
What is the purpose of covering the patient with a warm blanket after anesthesia?
What is the purpose of covering the patient with a warm blanket after anesthesia?
Which role typically accompanies the anesthetist and patient during their transport to the recovery room?
Which role typically accompanies the anesthetist and patient during their transport to the recovery room?
What is the primary focus during the maintenance phase of general anesthesia?
What is the primary focus during the maintenance phase of general anesthesia?
What should be a priority when positioning an anesthetized patient?
What should be a priority when positioning an anesthetized patient?
How should blood loss be monitored in infants during surgery?
How should blood loss be monitored in infants during surgery?
What role does the circulator play when additional anesthesia supplies are required?
What role does the circulator play when additional anesthesia supplies are required?
When starting an invasive line, what is an important preparation step?
When starting an invasive line, what is an important preparation step?
What is the first action taken during the emergence phase of general anesthesia?
What is the first action taken during the emergence phase of general anesthesia?
If reversal agents are used during emergence from anesthesia, what should also be tested?
If reversal agents are used during emergence from anesthesia, what should also be tested?
Why is it essential to monitor wound or urinary-bladder drainage devices during surgery?
Why is it essential to monitor wound or urinary-bladder drainage devices during surgery?
What must the circulator do if blood has not been typed and cross-matched for the patient?
What must the circulator do if blood has not been typed and cross-matched for the patient?
When is it critical for the circulator to assist with emergency resuscitative procedures?
When is it critical for the circulator to assist with emergency resuscitative procedures?
What should be done before inserting the ET-tube if the patient is suspected to have a full stomach?
What should be done before inserting the ET-tube if the patient is suspected to have a full stomach?
What is the purpose of applying pressure to the cricoid cartilage during intubation?
What is the purpose of applying pressure to the cricoid cartilage during intubation?
When is cricoid pressure released during the rapid sequence induction?
When is cricoid pressure released during the rapid sequence induction?
What should be done if the ET-tube is improperly positioned during intubation?
What should be done if the ET-tube is improperly positioned during intubation?
What should the anesthetist check after inserting the ET-tube to confirm its correct position?
What should the anesthetist check after inserting the ET-tube to confirm its correct position?
What role does the stylet play in the intubation process?
What role does the stylet play in the intubation process?
How can the anesthetist confirm that the ET-tube is in the correct position during intubation?
How can the anesthetist confirm that the ET-tube is in the correct position during intubation?
What is a critical action during a 'crash' or rapid sequence induction?
What is a critical action during a 'crash' or rapid sequence induction?
Which ET-tube modification may be used specifically for laser procedures?
Which ET-tube modification may be used specifically for laser procedures?
What should be communicated regarding the volume of air needed for an ET-tube cuff?
What should be communicated regarding the volume of air needed for an ET-tube cuff?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
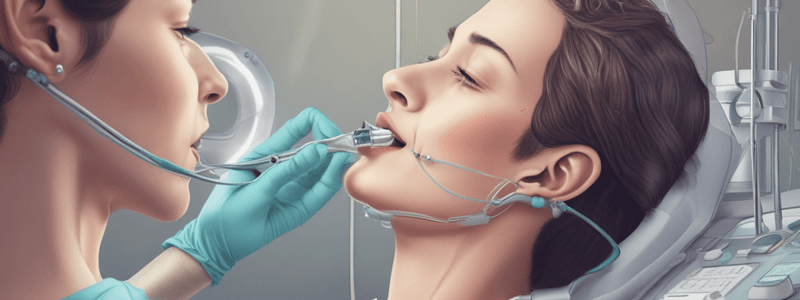
Endotracheal Intubation Procedure
- Involves inserting an endotracheal (ET) tube into the trachea for oxygen and inhalation agents during anesthesia.
- A laryngoscope is used for exposure and illumination of the throat and larynx.
- The ET-tube is positioned roughly 1/2 inch below the vocal cords; nasal intubation may be required in some cases.
- Cuff inflation secures the airway, preventing aspiration during surgery.
- Difficult intubation can lead to complications like laryngospasm or bronchospasm.
- Intubation is not performed until the patient reaches stage III of anesthesia; muscle relaxants are generally administered beforehand.
Assisting the Anesthetist with Intubation
- Pass necessary items swiftly, such as laryngotracheal anesthesia syringe and ET-tube.
- Apply directed pressure to the cricoid cartilage to assist in visualization of vocal cords and reduce aspiration risk.
- Carefully remove the stylet when instructed; ensure ET-tube remains stationary.
- Inflate the ET-tube cuff with the correct volume of air as guided by the anesthetist.
- Confirm ET-tube placement by monitoring chest rise and breath sounds, using a capnograph to detect CO2 presence.
- If the ET-tube enters the esophagus, it must be removed and reinserted.
Crash or Rapid Sequence Induction
- Employed for patients with a full stomach to reduce aspiration risks during anesthesia.
- Administer oxygen for 3-5 minutes pre-induction; firm cricoid pressure applied during muscle relaxant administration.
- Manual ventilation is generally avoided before intubation unless absolutely necessary.
- Post-intubation, the anesthetist confirms ET-tube position before releasing cricoid pressure.
Maintaining Anesthesia (Phase II)
- Patient remains in stage III (surgical plane) for the duration of surgery.
- Positioning is crucial: requires consent from the anesthetist to avoid injury or pressure sores.
- Monitor blood and body fluid loss, including measuring blood loss and fluid output.
- Retrieve and provide additional anesthesia supplies and assist in blood transfusions if required.
- Assist with starting and monitoring invasive lines, like CVP or arterial monitoring.
Emergence from General Anesthesia (Phase III)
- Emergence phase details the patient's awakening process as anesthetic agents decrease.
- 100% oxygen is administered as muscle relaxants may require reversal.
- Patients may experience restlessness and should be gently restrained to prevent injuries.
- Extubation occurs once patients breathe spontaneously and normal reflexes return.
- After extubation, patients are monitored for stability and transported to the postanesthesia care unit.
- Suction equipment should remain available for reintubation emergencies.
- Provide warmth to the patient post-anesthesia, as they may be sensitive to temperature changes.
Assisting During Emergence
- Support the anesthetist by staying nearby and offering reassurance or hands-on assistance as needed.
- Prepare for potential reintubation and assist with patient transport preparations post-extubation.
- Ensure all medical equipment, including drains and catheters, is secured prior to transport.
- Monitor and measure contents of drainage containers for the anesthetist.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.