Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the urinary system also called?
What is the urinary system also called?
- Circulatory system
- Respiratory system
- Excretory system (correct)
- Nervous system
What are the four main components of the urinary system?
What are the four main components of the urinary system?
- Kidneys, urinary bladder, urethra, and adrenal gland
- Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra (correct)
- Kidneys, ureters, pancreas, and urethra
- Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and liver
What is the function of the kidneys in the urinary system?
What is the function of the kidneys in the urinary system?
- Only hormonal production
- Only excretion of waste products
- Only filtration of blood
- Excretion of waste products, hormonal production, and regulatory functions (correct)
What is the approximate weight of a single kidney in adults?
What is the approximate weight of a single kidney in adults?
What is the outermost layer of tissue that covers the kidney?
What is the outermost layer of tissue that covers the kidney?
What is the function of the renal pelvis?
What is the function of the renal pelvis?
What is the middle portion of the kidney?
What is the middle portion of the kidney?
What is the function of the apex of each renal pyramid?
What is the function of the apex of each renal pyramid?
What is the name of the smooth muscle layer in the wall of the bladder?
What is the name of the smooth muscle layer in the wall of the bladder?
What is the length of the male urethra?
What is the length of the male urethra?
What is the main component of urine?
What is the main component of urine?
What is the pH range of urine?
What is the pH range of urine?
What is the minimum amount of urine excreted per day?
What is the minimum amount of urine excreted per day?
What is the process of emptying the bladder?
What is the process of emptying the bladder?
What is the main function of the renal cortex?
What is the main function of the renal cortex?
What is the structural and functional unit of the kidney?
What is the structural and functional unit of the kidney?
What is the purpose of the renal artery?
What is the purpose of the renal artery?
What is the function of the loop of Henle?
What is the function of the loop of Henle?
How many liters of blood are filtered by the kidney every day?
How many liters of blood are filtered by the kidney every day?
What is the function of the ureter?
What is the function of the ureter?
What is the approximate capacity of the urinary bladder?
What is the approximate capacity of the urinary bladder?
What is the function of the rugae in the urinary bladder?
What is the function of the rugae in the urinary bladder?
Study Notes
Urinary System
- The urinary system is also known as the excretory system, as it removes waste products from the blood and eliminates them from the body.
- The urinary system consists of four main components: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Functions of the Urinary System
- Excretion of waste products
- Hormonal production (renin-angiotensin and erythropoietin)
- Regulatory functions:
- Artery blood pressure
- Water and electrolytes balance
- Acid-base balance
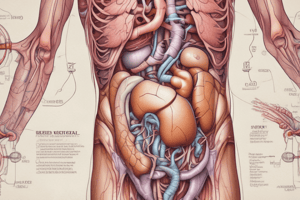
Kidney
- External anatomy:
- Pair of reddish-brown, bean-shaped organs located in the posterior wall of the abdomen region
- Approximately 12-cm long, 6-cm wide, and 2.5-cm thick in adults
- One in each side of the vertebral column, capped by the adrenal gland
- Covering and supporting layers:
- Renal capsule: innermost, tough, fibrous layer
- Adipose capsule: middle layer composed of fat, providing a protective cushion
- Renal fascia: outer subserous membrane, connective tissue layer
- Internal anatomy:
- Sagittal section reveals three distinct regions: pelvis, medulla, and cortex
- Renal pelvis: large collecting space within the kidney, formed from the expanded upper portion of the ureters
- Renal medulla: middle portion of the kidney, consisting of 8-18 renal pyramids
- Renal cortex: outermost portion of the kidney, divided into two regions: outer cortical and inner-juxta medullary region
Nephron
- The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney
- Each kidney contains approximately 1 million nephrons
- Components of a nephron:
- Renal corpuscle: consisting of Bowman's capsule and glomerular capillaries
- Tubular system: consisting of proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting system
Functions of the Kidney
- Elimination of waste products
- Regulation of total body water balance
- Control of acid-base balance
- Blood filtration: approximately 1700 liters of blood per day
- Tubular reabsorption
- Control of the chemical composition of the blood and other body fluids
- Tubular secretion
Ureter
- Pair of narrow, thick-walled muscular tubes, each approximately 25-30 cm in length
- Attach to each kidney and transport urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder
- Layers of the ureter:
- Tunica mucosa: innermost layer
- Tunica muscularis: middle layer, composed of smooth muscle
- Tunica Adventitia: outer layer
Urinary Bladder
- Hollow muscular organ that collects urine from the ureters and stores it
- Located below the peritoneum and behind the pubic bones
- Capacity: approximately 300-400 mL
- Smooth muscle layer in the wall of the bladder: called the detrusor muscle
Urethra
- Tube of smooth muscle lined with a mucosal layer, joining the bladder at its inferior surface and transporting urine outside the body during urination
- Female urethra: approximately 3-5 cm long
- Male urethra: approximately 17-20 cm long, consisting of three segments:
- Prostatic urethra: approximately 3-4 cm long, extending through the prostate gland
- Membranous urethra: short segment, passing through the urogenital diaphragm
- Spongy urethra: approximately 15 cm long
Urine and Urination
- Composition of urine varies depending on diet, exercise, water consumption, and other factors
- Main components of urine: water, urea, chloride, potassium, sodium, creatinine, phosphate, sulfate, uric acid, protein, glucose, and casts
- pH of urine: 5.0 to 8.0 (mostly acidic)
- Volume and concentration of urine controlled by:
- Antidiuretic hormone
- Aldosterone
- Threnin-angiotensin mechanism
- Urination is controlled by the nervous system and is the process of emptying the bladder.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Learn about the urinary system, also known as the excretory system, and its functions including excretion, hormonal production, and regulation of blood pressure.