Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where is the pancreas anatomically located in relation to the stomach?
Where is the pancreas anatomically located in relation to the stomach?
- Above and to the left of the stomach
- In front of the stomach
- To the right side of the stomach
- Below and behind the stomach (correct)
What is the duodenum in relation to the pancreas?
What is the duodenum in relation to the pancreas?
- The pancreas is completely separate from the duodenum
- The pancreas wraps around the duodenum (correct)
- The duodenum is the part of the pancreas
- The duodenum sits above the pancreas
In which compartment does the pancreas reside?
In which compartment does the pancreas reside?
- Retroperitoneum (correct)
- Subperitoneum
- Intraperitoneum
- Peritoneum
What distinguishes the retroperitoneum from the peritoneum?
What distinguishes the retroperitoneum from the peritoneum?
What is a significant function of the pancreas?
What is a significant function of the pancreas?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the pancreas and the peritoneum?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the pancreas and the peritoneum?
What is the primary function of the exocrine pancreas?
What is the primary function of the exocrine pancreas?
Which enzyme released by the exocrine pancreas is responsible for breaking down starch?
Which enzyme released by the exocrine pancreas is responsible for breaking down starch?
What types of macromolecules can the enzymes released by the pancreas digest?
What types of macromolecules can the enzymes released by the pancreas digest?
What defines the pancreas as unique compared to organs like the liver or kidney?
What defines the pancreas as unique compared to organs like the liver or kidney?
Which vessels are mentioned to run through the abdomen near the pancreas?
Which vessels are mentioned to run through the abdomen near the pancreas?
What is the role of lipase in the digestive process?
What is the role of lipase in the digestive process?
Why do surgeons need to be cautious when operating near the pancreas?
Why do surgeons need to be cautious when operating near the pancreas?
What nickname do many physicians give to the pancreas and why?
What nickname do many physicians give to the pancreas and why?
When are the pancreatic enzymes released into the digestive system?
When are the pancreatic enzymes released into the digestive system?
Which component from the exocrine pancreas mainly helps to neutralize gastric acid?
Which component from the exocrine pancreas mainly helps to neutralize gastric acid?
What type of organ is the pancreas classified as?
What type of organ is the pancreas classified as?
Which of the following statements about the pancreas is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about the pancreas is incorrect?
What characterizes a monoglyceride?
What characterizes a monoglyceride?
What is the function of lipase in digestion?
What is the function of lipase in digestion?
What role does enteropeptidase play in digestion?
What role does enteropeptidase play in digestion?
What is a zymogen?
What is a zymogen?
What occurs immediately after trypsin is activated?
What occurs immediately after trypsin is activated?
What causes the danger associated with the pancreas when damaged?
What causes the danger associated with the pancreas when damaged?
Which of the following enzymes is a proteolytic enzyme released by the exocrine pancreas?
Which of the following enzymes is a proteolytic enzyme released by the exocrine pancreas?
How does trypsin impact protein digestion in the duodenum?
How does trypsin impact protein digestion in the duodenum?
What is produced when a triglyceride is broken down?
What is produced when a triglyceride is broken down?
What happens to trypsinogen at the duodenum?
What happens to trypsinogen at the duodenum?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
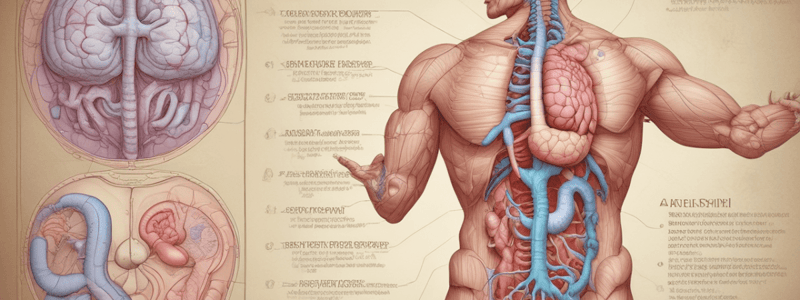
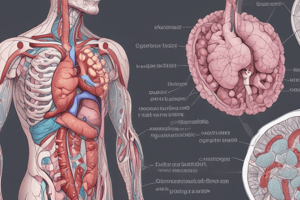
Pancreas Overview
- Located beneath and behind the stomach, hugging the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
- Sits in the retroperitoneum, which is the space behind the peritoneum, unlike other organs that are within the peritoneum.
- Surrounded by important blood vessels: abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava.
Functions and Characteristics
- Releases powerful enzymes that aid in digestion of macromolecules.
- Unencapsulated, consisting of a slurry of cells, complicating surgeries due to potential enzyme release.
- Known as “lion of the abdomen” due to its critical role and the potency of its enzymes.
Exocrine Function
- The exocrine pancreas releases salts and enzymes into the duodenum to aid digestion.
- Four main roles:
- Neutralization: Releases bicarbonate to neutralize gastric acid from the stomach.
- Carbohydrate breakdown: Produces amylase, which breaks down starches into simpler carbohydrates (glucose monomers, disaccharides).
- Lipid breakdown: Releases lipase to digest triglycerides into free fatty acids, monoglycerides, and diglycerides.
- Protein breakdown: Secretes proteolytic enzymes (trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen) that become active in the duodenum.
Proteolytic Enzymes Activation
- Inactive forms (zymogens) need activation typically involving breaking a bond:
- Trypsinogen is converted to active trypsin by the enzyme enteropeptidase in the duodenum.
- Trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin, which also digests proteins.
- If activated improperly (e.g., due to injury), these enzymes can damage surrounding tissues, highlighting the pancreas's precarious nature.
Summary
- The pancreas is crucial for digestion, releasing enzymes to break down carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, while its anatomical placement and lack of encapsulation present unique challenges and risks in medical contexts.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.