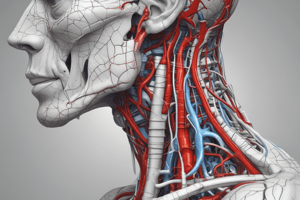
Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which artery arises at the same level as the facial artery?
Which artery arises at the same level as the facial artery?
- Posterior auricular artery
- Occipital artery (correct)
- Maxillary artery
- Ascending pharyngeal artery
Which branch of the External Carotid Artery supplies the middle ear?
Which branch of the External Carotid Artery supplies the middle ear?
- Tonsillar artery
- Posterior tympanic artery (correct)
- Inferior tympanic artery
- Mastoid branch
Which artery passes through the apical part of the parotid gland?
Which artery passes through the apical part of the parotid gland?
- Occipital artery
- Maxillary artery
- Superficial temporal artery
- Posterior auricular artery (correct)
What is the smallest branch of the External Carotid Artery?
What is the smallest branch of the External Carotid Artery?
Which artery is described in relation to the face?
Which artery is described in relation to the face?
Which artery crosses the lateral aspect of the scalp?
Which artery crosses the lateral aspect of the scalp?
In the carotid triangle, which structure lies posteriorly and medially to the ICA?
In the carotid triangle, which structure lies posteriorly and medially to the ICA?
Which nerve crosses the ICA laterally in the parapharyngeal space?
Which nerve crosses the ICA laterally in the parapharyngeal space?
On the right side, which artery does the subclavian artery arise from?
On the right side, which artery does the subclavian artery arise from?
Which structure lies medially to the right subclavian artery?
Which structure lies medially to the right subclavian artery?
Which nerve hooks around the right subclavian artery?
Which nerve hooks around the right subclavian artery?
Which structure lies laterally to the left subclavian artery?
Which structure lies laterally to the left subclavian artery?
What is the name of the sinus that is a tributary of the internal jugular vein?
What is the name of the sinus that is a tributary of the internal jugular vein?
Where is the external jugular vein formed?
Where is the external jugular vein formed?
Which of the following veins may the external jugular vein enter?
Which of the following veins may the external jugular vein enter?
What is the name of the vein that begins below the hyoid bone?
What is the name of the vein that begins below the hyoid bone?
What is the purpose of internal jugular and subclavian veins catheterisations?
What is the purpose of internal jugular and subclavian veins catheterisations?
What is the name of the structure that unites the two anterior jugular veins?
What is the name of the structure that unites the two anterior jugular veins?
What is the point of division of the common carotid artery into external and internal carotid arteries?
What is the point of division of the common carotid artery into external and internal carotid arteries?
Which nerve lies medially to the external carotid artery in the carotid triangle?
Which nerve lies medially to the external carotid artery in the carotid triangle?
What is the relationship of the external carotid artery to the internal carotid artery in the carotid triangle?
What is the relationship of the external carotid artery to the internal carotid artery in the carotid triangle?
What is the number of branches that the external carotid artery gives off?
What is the number of branches that the external carotid artery gives off?
Where does the external carotid artery terminate?
Where does the external carotid artery terminate?
Which structure does the external carotid artery pass through?
Which structure does the external carotid artery pass through?
What is the function of the carotid body located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery?
What is the function of the carotid body located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery?
Which nerve is responsible for the innervation of the carotid sinus and carotid body?
Which nerve is responsible for the innervation of the carotid sinus and carotid body?
At what level does the common carotid artery bifurcate?
At what level does the common carotid artery bifurcate?
What is the origin of the right common carotid artery?
What is the origin of the right common carotid artery?
What is the function of the carotid sinus located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery?
What is the function of the carotid sinus located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery?
What is the significance of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery?
What is the significance of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery?
In the carotid triangle, which structure lies anteriorly to the ICA?
In the carotid triangle, which structure lies anteriorly to the ICA?
What lies behind the ICA in the carotid triangle?
What lies behind the ICA in the carotid triangle?
What is the relationship between the ICA and the ECA in the parapharyngeal space?
What is the relationship between the ICA and the ECA in the parapharyngeal space?
What is the relationship between the right subclavian artery and the jugular vein?
What is the relationship between the right subclavian artery and the jugular vein?
What is the relationship between the left subclavian artery and the thoracic duct?
What is the relationship between the left subclavian artery and the thoracic duct?
What is the relationship between the right recurrent laryngeal nerve and the right subclavian artery?
What is the relationship between the right recurrent laryngeal nerve and the right subclavian artery?
Study Notes
Arteries of the Neck
- Common Carotid Artery (CCA): Divides into External Carotid Artery (ECA) and Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) at bifurcation, with carotid sinus (baroreceptor) and carotid body (chemoreceptor) located at this junction.
- External Carotid Artery (ECA): Anteromedial branch of the CCA, arises at the bifurcation and terminates into the maxillary and superficial temporal arteries. Courses through the parotid gland.
- Internal Carotid Artery (ICA): Lies posteriorly and medially to ECA within the carotid sheath, crossed by the hypoglossal nerve and stylohyoid muscle.
ECA Branches and Relations
- Major Branches: Ascending palatine, tonsillar, submental, pharyngeal, meningeal, inferior tympanic, occipital, posterior auricular.
- Occipital Artery: Arises at the same level as the facial artery, provides branches to neck muscles, mastoid region, and scalp.
- Posterior Auricular Artery: Travels along the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, supplies auricular branches and tympanic artery to the middle ear.
Subclavian Artery
- Origin: Right side from brachiocephalic trunk; left side from the aortic arch.
- Relations: Right subclavian artery is medial to scalenus anterior and behind the jugular vein; left subclavian is behind the left common carotid artery and left vagus nerve.
- Neurovascular Relations: Right recurrent laryngeal nerve and ansa subclavia encircle the right artery; thoracic duct crosses anterior to the left artery.
Jugular Veins
- External Jugular Vein: Forms from the posterior branch of the retromandibular and posterior auricular veins; enters internal jugular, brachiocephalic, or subclavian veins.
- Anterior Jugular Vein: Begins below the hyoid, enters external jugular or subclavian veins, linked by the jugular arch.
Clinical Significance
- Central Venous Catheterization: Internal jugular and subclavian veins are accessed for monitoring central venous pressure and providing parenteral nutrition.
- Anatomical Awareness: Knowledge of arterial and venous relations critical for surgical procedures and interventions in the neck region.
Summary of Veins
- Tributaries of External Jugular Vein: Includes posterior auricular, occipital, suprascapular, and transverse cervical veins.
- Brachiocephalic Veins: Comprised of vertebral vein and deep cervical vein; important for returning blood to the heart from the neck region.
Other Key Associations
- Pharyngeal Space: ICA is separated from ECA by stylopharyngeus muscle and glossopharyngeal nerve; essential for understanding vascular dynamics in surgical contexts.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the relationships and branches of the external carotid artery in the neck region, including the submandibular gland and their connections to the face and pharynx. Test your knowledge of the anatomy of the neck!