Podcast
Questions and Answers
The vestibule is located in the inner ear, anterior to the cochlea and posterior to the semicircular canals.
The vestibule is located in the inner ear, anterior to the cochlea and posterior to the semicircular canals.
True (A)
The recessus sphæricus is located on the medial wall of the vestibule, anterior to the crista vestibuli.
The recessus sphæricus is located on the medial wall of the vestibule, anterior to the crista vestibuli.
True (A)
The fossa cochlearis, located inferior to the recessus sphæricus, is perforated by filaments of the vestibular nerve.
The fossa cochlearis, located inferior to the recessus sphæricus, is perforated by filaments of the vestibular nerve.
False (B)
The recessus ellipticus, on the roof of the vestibule, contains an opening for the vestibular aqueduct and openings for nerves to the semicircular canals.
The recessus ellipticus, on the roof of the vestibule, contains an opening for the vestibular aqueduct and openings for nerves to the semicircular canals.
The saccule is situated within the recessus sphæricus and is connected anteriorly to the cochlear duct.
The saccule is situated within the recessus sphæricus and is connected anteriorly to the cochlear duct.
The utricle is continuous with the semicircular ducts and situated within the recessus ellipticus.
The utricle is continuous with the semicircular ducts and situated within the recessus ellipticus.
The semicircular ducts within the canals are identical in size to the bony canals they are contained within.
The semicircular ducts within the canals are identical in size to the bony canals they are contained within.
The membranous structures within the vestibular apparatus are filled with perilymph and surrounded by endolymph.
The membranous structures within the vestibular apparatus are filled with perilymph and surrounded by endolymph.
The utricle detects movement in the anteroposterior axis.
The utricle detects movement in the anteroposterior axis.
Ampullary crests are characterized by their location at the $ampulla$ and are covered by an otolithic membrane.
Ampullary crests are characterized by their location at the $ampulla$ and are covered by an otolithic membrane.
The endolymph movement inside the ampullary crest deflects the central core of the cupula, causing bending of the cilia.
The endolymph movement inside the ampullary crest deflects the central core of the cupula, causing bending of the cilia.
When stereocilia move towards the kinocilium, a hyperpolarization is triggered.
When stereocilia move towards the kinocilium, a hyperpolarization is triggered.
Hair cells in the vestibular apparatus have only one type of receptor.
Hair cells in the vestibular apparatus have only one type of receptor.
Maculae in the saccule and utricle differ in their orientation; the saccule is oriented horizontally, and the utricle vertically.
Maculae in the saccule and utricle differ in their orientation; the saccule is oriented horizontally, and the utricle vertically.
The posterior semicircular canal on one side is parallel to the anterior semicircular canal on the opposite side to form a functional couple.
The posterior semicircular canal on one side is parallel to the anterior semicircular canal on the opposite side to form a functional couple.
The vestibular apparatus primarily detects linear acceleration.
The vestibular apparatus primarily detects linear acceleration.
The cranial nerve VIII is comprised of the vestibular nerve and the optic nerve.
The cranial nerve VIII is comprised of the vestibular nerve and the optic nerve.
The inferior branch of the vestibular nerve collects information entirely from the utricle and the superior semicircular canal.
The inferior branch of the vestibular nerve collects information entirely from the utricle and the superior semicircular canal.
The inner layer of the vestibular apparatus is composed of simple cuboidal epithelium.
The inner layer of the vestibular apparatus is composed of simple cuboidal epithelium.
The vestibular apparatus is part of the auditory system.
The vestibular apparatus is part of the auditory system.
The vestibular apparatus relies solely on hair cells to detect movement.
The vestibular apparatus relies solely on hair cells to detect movement.
Type 1 sensory cells are less discriminative due to their smaller afferent fibers.
Type 1 sensory cells are less discriminative due to their smaller afferent fibers.
The vestibular apparatus is solely responsible for detecting gravity.
The vestibular apparatus is solely responsible for detecting gravity.
All type 1 fibers within a macula or crest share the same polarization.
All type 1 fibers within a macula or crest share the same polarization.
Type II sensory cells, unlike type 1, possess ordinary boutons and receive both afferent and efferent signals.
Type II sensory cells, unlike type 1, possess ordinary boutons and receive both afferent and efferent signals.
The vestibular nerve comprises approximately one-fourth of the cochlear nerve's size.
The vestibular nerve comprises approximately one-fourth of the cochlear nerve's size.
The macula is capable of detecting a constant, continuous acceleration of the head.
The macula is capable of detecting a constant, continuous acceleration of the head.
Fibers originating from the semicircular canals project exclusively to the superior vestibular nucleus.
Fibers originating from the semicircular canals project exclusively to the superior vestibular nucleus.
The utricle is responsible for detecting vertical accelerations, while the saccule detects horizontal accelerations.
The utricle is responsible for detecting vertical accelerations, while the saccule detects horizontal accelerations.
The lateral vestibular nucleus receives input from the utricle and saccule, but not the ampullary crests.
The lateral vestibular nucleus receives input from the utricle and saccule, but not the ampullary crests.
The continuous discharge frequency of maculae sensory cells is altered by the bending of cilia embedded within the otolithic membrane.
The continuous discharge frequency of maculae sensory cells is altered by the bending of cilia embedded within the otolithic membrane.
When stereocilia tilt in the same direction as the kinocilium, it leads to a hyperpolarization of the sensory cell.
When stereocilia tilt in the same direction as the kinocilium, it leads to a hyperpolarization of the sensory cell.
Fibers from the vestibular organs projecting to the cerebellum exclusively form the juxtarestiform body.
Fibers from the vestibular organs projecting to the cerebellum exclusively form the juxtarestiform body.
The striola within the macula, formed by supporting cells, serves as a landmark for identifying the midline and the orientation of kinocilia in type 1 sensory receptors.
The striola within the macula, formed by supporting cells, serves as a landmark for identifying the midline and the orientation of kinocilia in type 1 sensory receptors.
All juxtarestiform body fibers are ipsilateral, meaning they connect to the same side of the cerebellum.
All juxtarestiform body fibers are ipsilateral, meaning they connect to the same side of the cerebellum.
The ampullary crest is responsible for detecting linear acceleration of the head, similar to the macula.
The ampullary crest is responsible for detecting linear acceleration of the head, similar to the macula.
The superior and lateral vestibular nuclei contribute the majority of fibers ascending to the cortex.
The superior and lateral vestibular nuclei contribute the majority of fibers ascending to the cortex.
Fibers from these nuclei primarily enter the ventral-posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus.
Fibers from these nuclei primarily enter the ventral-posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus.
The semicircular ducts can provide a continuous sensation of movement, unlike the macula which only senses the beginning and end of the head tilt.
The semicircular ducts can provide a continuous sensation of movement, unlike the macula which only senses the beginning and end of the head tilt.
Vestibulo-ocular reflexes are primarily mediated by connections between vestibular nuclei and cranial nerves III, IV, and VI.
Vestibulo-ocular reflexes are primarily mediated by connections between vestibular nuclei and cranial nerves III, IV, and VI.
The orientation of the semicircular ducts within the three spatial axes allows for an understanding of head position, even without visual cues.
The orientation of the semicircular ducts within the three spatial axes allows for an understanding of head position, even without visual cues.
The medial vestibulospinal tract, originating from the medial vestibular nucleus, is responsible for maintaining posture by descending to the level of the mid-thoracic region.
The medial vestibulospinal tract, originating from the medial vestibular nucleus, is responsible for maintaining posture by descending to the level of the mid-thoracic region.
The information reaching the primary somatosensory cortex regarding head position is solely conveyed via ascending pathways.
The information reaching the primary somatosensory cortex regarding head position is solely conveyed via ascending pathways.
Flashcards
The vestibule
The vestibule
The central part of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, connecting to cochlea and semicircular canals.
Vestibular system
Vestibular system
The combined structure of the vestibule and semicircular canals responsible for balance.
Recessus sphæricus
Recessus sphæricus
A small, circular depression in the vestibule for nerve passage to the saccule.
Crista vestibuli
Crista vestibuli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fossa cochlearis
Fossa cochlearis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saccule
Saccule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Utricle
Utricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endolymph
Endolymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia in Ampullary Crest
Cilia in Ampullary Crest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cupula and Endolymph
Cupula and Endolymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stereocilia Deflection
Stereocilia Deflection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Coupling of Semicircular Canals
Functional Coupling of Semicircular Canals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular Nerve Structure
Vestibular Nerve Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type 1 fibers
Type 1 fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II sensory cells
Type II sensory cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macula
Macula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otolithic membrane
Otolithic membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excitatory polarization
Excitatory polarization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperpolarization
Hyperpolarization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ampullary crest
Ampullary crest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cupula
Cupula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular apparatus
Vestibular apparatus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hair cells
Hair cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Connective tissue
Connective tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Auditory Meatus
Internal Auditory Meatus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular Nerve
Vestibular Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular Nuclei
Vestibular Nuclei
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior Vestibular Nucleus
Superior Vestibular Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Vestibular Nucleus
Lateral Vestibular Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Juxtarestiform Body
Juxtarestiform Body
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ascending Tract
Ascending Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thalamus
Thalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Vestibulospinal Tract
Medial Vestibulospinal Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibulo-Ocular Reflexes
Vestibulo-Ocular Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
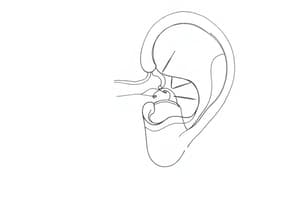
The Vestibule
- The vestibule is the central part of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear.
- It's continuous with the cochlea anteriorly and three semicircular canals posteriorly.
- The vestibule and semicircular canals are called the vestibular system.
- On the medial wall, there are depressions including the recessus sphæricus, which is perforated for nerve passage to the saccule.
- A crista vestibuli ridge follows behind this depression.
- The fossa cochlearis, perforated for cochlear nerve filaments, lies inferior to the recessus sphaericus.
- A transversely oval recessus ellipticus lies above, separated from the recessus sphæricus by the crista vestibuli.
- Openings for the vestibular aqueduct and nerves to semicircular canals are also present here.
The Internal Ear Membranous Portion
- The membranous portion of the semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle has three layers.
- The outer layer is dense connective tissue.
- The intermediate layer contains blood vessels.
- The inner layer faces the endolymph and is simple squamous epithelium, specialized for receptors.
Receptors
- Vestibular receptors are organized in two ways.
- Ampullary crests in the semicircular canals are enlargements where receptor cells are located, covered by a gelatinous cupula.
- Maculae in the utricle and saccule are enlarged laminae or plaques covered by an otolithic membrane (containing otoliths).
- Maculae are often called otolithic organs, and they are oriented differently—horizontal in the utricle, vertical in the saccule.
- Both ampullary crests and maculae have supporting cells for nourishment and ion maintenance within the endolymph.
Hair Cells
- Hair cells, similar to those in the cochlear duct, are covered by stereocilia.
- Kinocilium is present.
- Two types of hair cells:
- Type 1 sensory cells have larger afferent fibers, all with the kinocilium oriented in the same direction within a macula or crest.
- Type 2 sensory cells have ordinary boutons, receiving both afferents and efferents, showing varied polarities.
Macula Function
- Maculae detect linear acceleration.
- Utricular maculae detect horizontal acceleration, and saccular maculae detect vertical acceleration.
- Bending of cilia, trapped within the otolithic membrane, due to head movement is detected as a signal.
Otolith Mechanism
- The maculae continuously discharge, with their frequency modified by cilia bending in the otolithic membrane.
- Movement of endolymph due to head inclination moves the otolithic membrane.
- Bending stereocilia toward the kinocilium causes depolarization, while bending away causes hyperpolarization.
Ampullary Crest
- Ampullary crests respond to angular acceleration, activated by head movement.
- The semicircular ducts provide a continuous feedback of head movement, unlike maculae.
- Cells immersed in a cupula are bent by endolymph movement; this bend, in turn, deflects cilia and changes the polarization of hair cells.
Functional Coupling
- Vestibular pathway information is combined from both ears.
- The labyrinth's orientation helps establish a clear functional pathway with coupled semicircular canals.
Vestibular Nerve
- The vestibular nerve (part of cranial nerve VIII) has two branches.
- The superior branch collects utricle and superior/lateral semicircular canals.
- The inferior branch collects saccule and posterior semicircular canals.
- The vestibular nerve exits through the internal acoustic meatus, along with the cochlear nerve.
Vestibular Nuclei
- Information from ampullary crests and maculae reaches different vestibular nuclei.
- Fibers from semicircular canals mainly go to the superior and rostral portions of the medial vestibular nucleus.
- Fibers from utricle and saccule mainly go to the lateral vestibular nucleus but a minor component goes to the inferior vestibular nucleus.
- Some fibers also go directly to the cerebellum (juxtarestiform body), enabling unconscious postural control.
Ascending Tracts
- Most vestibular fibers project to thalamus (ventral-posterior lateral nucleus).
- Ascending fibers from the superior and lateral nuclei travel via the medial longitudinal fasciculus.
- Signals reach primary somatosensory cortex (areas 2v and 3a).
Descending Tracts
- Vestibular nuclei provide descending pathways for posture control, such as the medial vestibulospinal tract (originating from the medial vestibular nucleus) and the lateral vestibulospinal tract (originating from the lateral vestibular nucleus).
- Connections to spinal cord ensure appropriate muscle responses for maintaining balance, correcting head position during movement.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.