Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary location of gray matter in the spinal cord?
What is the primary location of gray matter in the spinal cord?
- Deep in the cerebrum
- Spread throughout the spinal cord
- Outside, forming a layer
- Inside, forming an 'H' shape (correct)
What is the main function of the neurons in the cerebral cortex?
What is the main function of the neurons in the cerebral cortex?
- Sensory functions
- Motor functions
- Cognition, emotion, and consciousness (correct)
- Automatic functions
What is the primary component of white matter in the CNS?
What is the primary component of white matter in the CNS?
- Dendrites
- Glial cells
- Myelinated axons (correct)
- Neuron somas
What is the term for collections of axons traveling together in the CNS?
What is the term for collections of axons traveling together in the CNS?
What is the main characteristic that distinguishes gray matter from white matter?
What is the main characteristic that distinguishes gray matter from white matter?
What is the term for areas of gray matter deep in the brain?
What is the term for areas of gray matter deep in the brain?
What is the main function of neurons in the CNS that participate in automatic functions?
What is the main function of neurons in the CNS that participate in automatic functions?
Where are the neuron somas primarily located in the cerebral cortex?
Where are the neuron somas primarily located in the cerebral cortex?
What is the term for the outer layer of gray matter in the cerebellum?
What is the term for the outer layer of gray matter in the cerebellum?
What is the primary location of white matter in the brain?
What is the primary location of white matter in the brain?
Which of the following is a characteristic of tracts in the CNS?
Which of the following is a characteristic of tracts in the CNS?
What is the term for areas of gray matter deep in the brain that contain many neuron somas?
What is the term for areas of gray matter deep in the brain that contain many neuron somas?
What is the main function of neurons in the CNS that participate in sensory functions?
What is the main function of neurons in the CNS that participate in sensory functions?
What is the significance of the gray matter in the CNS?
What is the significance of the gray matter in the CNS?
Which part of the brain contains neurons participating in higher functions such as cognition and emotion?
Which part of the brain contains neurons participating in higher functions such as cognition and emotion?
What is the characteristic of white matter in the CNS?
What is the characteristic of white matter in the CNS?
What is the main difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS?
What is the main difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS?
What is the function of the CNS?
What is the function of the CNS?
Study Notes
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- Gray matter in the CNS contains most of the neuron somas.
- White matter in the CNS is composed of myelinated axons.
Spinal Cord
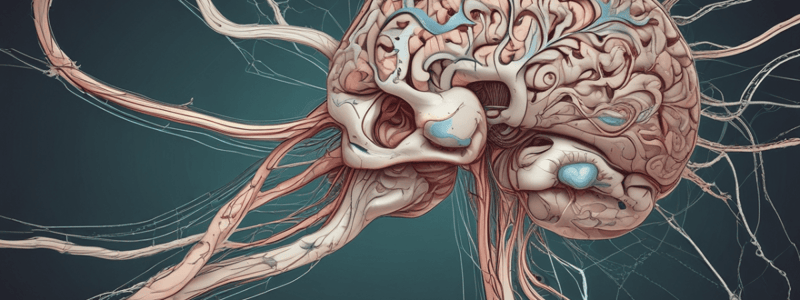
- Gray matter in the spinal cord is mostly located on the inside, forming an "H" shape or butterfly shape.
- White matter in the spinal cord is mostly located on the outside.
- Gray matter contains neuron somas, giving it a different color from the white matter.
Brain
- Gray matter in the brain is mostly located on the outside, forming a layer called the cortex.
- The cortex covering the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex, and the cortex covering the cerebellum is called the cerebellar cortex.
- Gray matter on the outside of the brain contains most of the neuron somas.
- White matter in the brain is mostly located on the inside, deep in the cerebrum and brain stem.
Gray Matter
- Gray matter contains neuron somas.
- Areas of gray matter deep in the brain are called nuclei.
- Nuclei contain lots of neuron somas.
White Matter
- White matter is composed of myelinated axons.
- Collections of axons traveling together in the CNS are called tracts.
- Tracts can have many axons carrying similar information from one part of the CNS to another.
Functions of the CNS
- The CNS has neurons involved in motor, sensory, and automatic functions.
- The CNS also has neurons participating in higher functions such as cognition, emotion, and consciousness, particularly in the cerebral cortex.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Spinal Cord
- Gray matter is located internally, forming an "H" or butterfly shape.
- White matter is located externally.
- Gray matter contains neuron somas, giving it a different color from white matter.
Brain
- Gray matter is located externally, forming a layer called the cortex.
- Cerebral cortex covers the cerebrum.
- Cerebellar cortex covers the cerebellum.
- External gray matter contains most neuron somas.
- White matter is located internally, deep in the cerebrum and brain stem.
Gray Matter
- Contains neuron somas.
- Deep areas of gray matter are called nuclei.
- Nuclei contain many neuron somas.
White Matter
- Composed of myelinated axons.
- Collections of axons are called tracts.
- Tracts carry similar information from one part of the CNS to another.
Functions of the CNS
- Involved in motor, sensory, and automatic functions.
- Participates in higher functions like cognition, emotion, and consciousness, particularly in the cerebral cortex.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Spinal Cord
- Gray matter is located internally, forming an "H" or butterfly shape.
- White matter is located externally.
- Gray matter contains neuron somas, giving it a different color from white matter.
Brain
- Gray matter is located externally, forming a layer called the cortex.
- Cerebral cortex covers the cerebrum.
- Cerebellar cortex covers the cerebellum.
- External gray matter contains most neuron somas.
- White matter is located internally, deep in the cerebrum and brain stem.
Gray Matter
- Contains neuron somas.
- Deep areas of gray matter are called nuclei.
- Nuclei contain many neuron somas.
White Matter
- Composed of myelinated axons.
- Collections of axons are called tracts.
- Tracts carry similar information from one part of the CNS to another.
Functions of the CNS
- Involved in motor, sensory, and automatic functions.
- Participates in higher functions like cognition, emotion, and consciousness, particularly in the cerebral cortex.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Spinal Cord
- Gray matter is located internally, forming an "H" or butterfly shape.
- White matter is located externally.
- Gray matter contains neuron somas, giving it a different color from white matter.
Brain
- Gray matter is located externally, forming a layer called the cortex.
- Cerebral cortex covers the cerebrum.
- Cerebellar cortex covers the cerebellum.
- External gray matter contains most neuron somas.
- White matter is located internally, deep in the cerebrum and brain stem.
Gray Matter
- Contains neuron somas.
- Deep areas of gray matter are called nuclei.
- Nuclei contain many neuron somas.
White Matter
- Composed of myelinated axons.
- Collections of axons are called tracts.
- Tracts carry similar information from one part of the CNS to another.
Functions of the CNS
- Involved in motor, sensory, and automatic functions.
- Participates in higher functions like cognition, emotion, and consciousness, particularly in the cerebral cortex.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the structure and composition of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, and their gray and white matter.