Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the premotor frontal cortex?
What is the primary function of the premotor frontal cortex?
- To control involuntary movements
- To process sensory information
- To regulate emotions
- To plan and organize the sequence of movement (correct)
What is the significance of the gray matter in the brain?
What is the significance of the gray matter in the brain?
- It is responsible for involuntary movements
- It contains neuronal cell bodies (correct)
- It is the outer layer of the brain
- It contains the cerebral spinal fluid
What is the role of the supplementary motor cortex?
What is the role of the supplementary motor cortex?
- To regulate sensory information
- To control voluntary movements
- To process visual information
- To prepare orientation of the body to execute a particular motor task (correct)
How many pairs of spinal nerves are present in the human body?
How many pairs of spinal nerves are present in the human body?
What is the function of the association areas?
What is the function of the association areas?
Where do motor signals exit the spinal cord?
Where do motor signals exit the spinal cord?
Where do sensory signals enter the spinal cord?
Where do sensory signals enter the spinal cord?
What is the significance of the cervical and lumbar intumescences?
What is the significance of the cervical and lumbar intumescences?
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
What is the term for an outward fold in the cerebrum?
What is the term for an outward fold in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the pons?
What is the function of the pons?
What is the term for the pathways in the midbrain that control voluntary movements?
What is the term for the pathways in the midbrain that control voluntary movements?
What is the function of the cerebral cortex?
What is the function of the cerebral cortex?
What is the term for a deep sulcus in the cerebrum?
What is the term for a deep sulcus in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the cerebellum?
What is the function of the cerebellum?
What is the function of the visceral sensory fibers?
What is the function of the visceral sensory fibers?
What is the term for the white, myelinated axons in the cerebrum?
What is the term for the white, myelinated axons in the cerebrum?
What is the primary route of information transmission to the CNS?
What is the primary route of information transmission to the CNS?
Which type of fiber carries motor commands from the CNS to peripheral tissues?
Which type of fiber carries motor commands from the CNS to peripheral tissues?
What is the characteristic of secondary-order neurons?
What is the characteristic of secondary-order neurons?
What is the main function of the dorsal root?
What is the main function of the dorsal root?
What is the difference between somatic sensory and visceral sensory fibers?
What is the difference between somatic sensory and visceral sensory fibers?
Which type of fiber is responsible for controlling skeletal muscle contraction?
Which type of fiber is responsible for controlling skeletal muscle contraction?
What is the function of tertiary-order neurons?
What is the function of tertiary-order neurons?
What is the function of the ventral root?
What is the function of the ventral root?
What is the main function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the main function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the characteristic of quaternary-order neurons?
What is the characteristic of quaternary-order neurons?
What happens to the impulses before they reach the thalamus?
What happens to the impulses before they reach the thalamus?
What is the advantage of grouping neurons by function?
What is the advantage of grouping neurons by function?
What is the main function of the sympathetic trunk?
What is the main function of the sympathetic trunk?
What is the primary function of the neurons in the somatosensory cortex?
What is the primary function of the neurons in the somatosensory cortex?
What is the relationship between secondary and tertiary-order neurons?
What is the relationship between secondary and tertiary-order neurons?
What type of muscle is under involuntary control and includes adipose tissue?
What type of muscle is under involuntary control and includes adipose tissue?
Which of the following is a function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Which of the following is a function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons located?
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons located?
What type of receptor is involved in the auditory and vestibular system?
What type of receptor is involved in the auditory and vestibular system?
How many cranial nerves are there in the human body?
How many cranial nerves are there in the human body?
Where do axons project via cranial and spinal nerves?
Where do axons project via cranial and spinal nerves?
What is the function of primary neurons?
What is the function of primary neurons?
What is the purpose of complex receptors?
What is the purpose of complex receptors?
What type of fibers connect the cerebral cortex with other brain regions?
What type of fibers connect the cerebral cortex with other brain regions?
Which layers of the cerebral cortex are responsible for sending output signals to other brain regions?
Which layers of the cerebral cortex are responsible for sending output signals to other brain regions?
What is the function of the association fibers in the cerebral cortex?
What is the function of the association fibers in the cerebral cortex?
What is the function of the commissural fibers in the cerebral cortex?
What is the function of the commissural fibers in the cerebral cortex?
What is the name of the layer in the cerebral cortex that has a multiform structure?
What is the name of the layer in the cerebral cortex that has a multiform structure?
What is the primary function of the fibers in the cerebral cortex that originate in the thalamus?
What is the primary function of the fibers in the cerebral cortex that originate in the thalamus?
Which of the following regions is divided into the telencephalon and diencephalon?
Which of the following regions is divided into the telencephalon and diencephalon?
Which region is responsible for integrating sensory information?
Which region is responsible for integrating sensory information?
What is the primary function of the cerebellum?
What is the primary function of the cerebellum?
Which region connects the brain to the spinal cord?
Which region connects the brain to the spinal cord?
How many major regions can the CNS be anatomically subdivided into?
How many major regions can the CNS be anatomically subdivided into?
What is the term for the lower part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord?
What is the term for the lower part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord?
What is the function of the spinal cord?
What is the function of the spinal cord?
What is the primary function of the corpus callosum?
What is the primary function of the corpus callosum?
What is the term for the intersection of pathways in the form of an X?
What is the term for the intersection of pathways in the form of an X?
What is the function of the basal nuclei?
What is the function of the basal nuclei?
Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and preparation for movement?
Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and preparation for movement?
What is the role of the thalamus in the basal nuclei?
What is the role of the thalamus in the basal nuclei?
What is the location of the gray matter nuclei of the basal nuclei?
What is the location of the gray matter nuclei of the basal nuclei?
What is the primary component of the gray matter in the cerebrum?
What is the primary component of the gray matter in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the basal nuclei in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the basal nuclei in the cerebrum?
What is the term for a cluster of neurons cell bodies outside the CNS?
What is the term for a cluster of neurons cell bodies outside the CNS?
What is the function of the hippocampus in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the hippocampus in the cerebrum?
What is the term for a cluster of neurons cell bodies inside the CNS?
What is the term for a cluster of neurons cell bodies inside the CNS?
What is the function of the amygdala in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the amygdala in the cerebrum?
What is the composition of the white matter in the cerebrum?
What is the composition of the white matter in the cerebrum?
What is the function of the cerebrum in the central nervous system?
What is the function of the cerebrum in the central nervous system?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
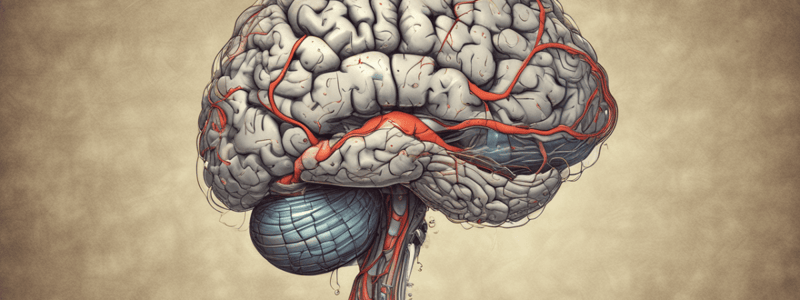
Central Nervous System
- The brain receives and processes sensory information, initiates responses, stores memories, generates thoughts and emotions.
- Cerebrum has two hemispheres: left and right, which are extensively folded, with gyri (outward folds) and sulci (inward folds).
- Functions of the cerebrum include conscious experience of sensation and initiation of voluntary movement.
- Medulla oblongata regulates heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, walking, sleeping, and swallowing.
- Pons influences cortex to maintain consciousness and alertness, and regulates posture, locomotion, and visceral function.
Brainstem
- Midbrain is the location of the brainstem UMN pathways and subconscious posture and voluntary skilled/learned movements.
Cerebellum
- Cerebellum is responsible for premotor frontal cortex, which plans and organizes the sequence of movement.
- Supplementary motor cortex is responsible for preparatory orientation of the body to execute a particular motor task.
- Cerebellum integrates and interprets information, producing a specific learned output.
Spinal Nerves
- There are 36 pairs of spinal nerves that communicate the spinal cord with sensory receptors, muscles, viscera, and vessels.
- Each segment gives rise to paired spinal nerves that exit the vertebral canal via the lateral vertebral foramen of the atlas or via intervertebral foramen.
- Neurons innervating the limbs are confined to cervical and lumbar intumescences.
Peripheral Nervous System
- Sensory/Afferent system brings information to the CNS from receptors in peripheral tissues and organs.
- Motor/Efferent system carries motor commands from CNS to peripheral tissue and systems.
- Visceral Sensory provides information about internal organs, while Somatic Sensory provides information about position, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
- Somatic Motor controls skeletal muscle contraction, while Visceral Motor provides autonomic regulation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, and adipose tissue.
Receptors
- Receptors are of different types, including free nerve endings, complex receptors, and special senses receptors.
Neurons
- Primary (first-order) neurons receive signals and send information to CNS.
- Secondary (second-order) neurons conduct impulses from spinal cord to brainstem to thalamus.
- Tertiary (third-order) neurons conduct impulses from thalamus to primary somatosensory cortex.
- Quaternary (fourth-order) neurons are located in sensory area of cerebral cortex.
Cranial Nerves
- There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves that arrive in the brainstem.
- Individual nerves have specific sensory and/or motor, somatic and/or autonomic functions.
Cerebrum or Telencephalon
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two hemispheres.
- It is composed of the cerebral cortex, white matter, and subcortical structures.
Cerebral Cortex
- The cerebral cortex is a layer of gray matter at the surface of the cerebrum.
- It is divided into 6 separate horizontal layers parallel to the surface of the cortex.
- The layers are:
- I: Molecular
- II: Outer granular (external granular)
- III: Outer pyramidal (external pyramidal)
- IV: Inner granular (internal granular)
- V: Inner pyramidal (internal pyramidal)
- VI: Multiform
- Different distribution of layers according to functional areas.
- Most incoming signals are received in layer IV.
- Most output signals leave the cortex through layers V and VI.
- Layer V sends signals to the brainstem and spinal cord.
- Layer VI sends signals to the thalamus.
- Layers I, II, and III are involved in intracortical association functions.
White Matter
- The white matter is composed of myelinated axons that connect the cerebral cortex with other brain regions.
- It is divided into:
- Projection fibers
- Association fibers
- Commissural fibers
- Projection fibers leave the white matter and terminate in the basal nuclei, brainstem, or spinal cord.
- Association fibers connect regions of the cerebral cortex within one hemisphere.
- Commissural fibers connect the cortices from the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Subcortical Structures
- Basal nuclei (Basal Ganglia) are gray matter nuclei located deep within the white matter of the cerebral hemisphere.
- They include the Caudate nucleus, nucleus accumbens, putamen, globus pallidum, and claustrum.
- The subthalamic nucleus and substancia nigra are also called Basal nuclei.
- Basal nuclei project output via the thalamus into the supplementary and premotor cortices.
- They are involved in planning and preparation for movement.
- They also send output directly to the brainstem.
Brain Regions
- The CNS can be anatomically subdivided into 7 major regions:
-
- Telencephalon or Cerebrum
-
- Diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus)
-
- Cerebellum
-
- Mesencephalon or Midbrain
-
- Pons
-
- Medulla oblongata
-
- Spinal cord
-
Functional Areas
- The brain can be divided into 5 major functional areas:
-
- Cerebrum
-
- Thalamus
-
- Hypothalamus
-
- Cerebellum
-
- Brainstem (Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla)
-
Commissures and Decussations
- A commissure is a place where fibers cross and connect the two cerebral hemispheres.
- Example: Corpus callosum
- A decussation is an intersection of pathways in the form of an X.
- This accounts for why each side of our brain has control over the opposite side of our body.
Basal Nuclei
- Basal nuclei are an accessory motor system that helps execute the initiation and control of movement.
- They are responsible for the cognitive control of motor activity.
- Studies in monkeys show that changes in neuronal activity of the basal nuclei occur prior to the firing of the neuronal activity of the motor cortex and the movement of body parts.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.