Podcast
Questions and Answers
Why is it important to fast the patient?
Why is it important to fast the patient?
- To improve the visualization of the pancreas
- To ensure the patient's comfort during the examination
- To minimize artefacts during the examination (correct)
- To reduce reverberation from the anterior abdominal wall
What is the recommended probe frequency for gallbladder examination?
What is the recommended probe frequency for gallbladder examination?
- 5-MHz
- 7-MHz
- 10-MHz
- 3-MHz (correct)
What is the primary tool for assessing the structure of the biliary tree?
What is the primary tool for assessing the structure of the biliary tree?
- CT cholangiography
- MRI
- Ultrasound (correct)
- Nuclear medicine
What is Caroli's disease?
What is Caroli's disease?
What is the common anatomic variation in the biliary tree?
What is the common anatomic variation in the biliary tree?
What is the recommended patient position for imaging the common bile duct?
What is the recommended patient position for imaging the common bile duct?
What is the name of the duct that joins the CBD?
What is the name of the duct that joins the CBD?
What is the site where the CBD enters the duodenum?
What is the site where the CBD enters the duodenum?
What can be used to move anatomy out from beneath the ribs?
What can be used to move anatomy out from beneath the ribs?
What is the purpose of assessing the pancreas during gallbladder examination?
What is the purpose of assessing the pancreas during gallbladder examination?
What is the purpose of cannulating the CBD during cholecystectomy surgery?
What is the purpose of cannulating the CBD during cholecystectomy surgery?
What can cause obstruction in the bile duct?
What can cause obstruction in the bile duct?
What is the term for the inflammation of the bile ducts?
What is the term for the inflammation of the bile ducts?
Why is it important to measure the diameter of the extrahepatic bile duct?
Why is it important to measure the diameter of the extrahepatic bile duct?
What is the term for the presence of a stone in the CBD?
What is the term for the presence of a stone in the CBD?
What is the function of the Sphincter of Oddi?
What is the function of the Sphincter of Oddi?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
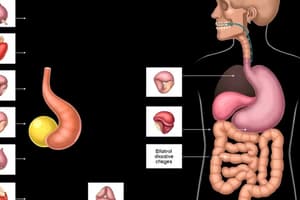
Anatomy of the Biliary Tree
- The biliary tree originates from canaliculi at hepatocytes, merging to form the right and left hepatic ducts, which join at porta hepatis to form the Common Hepatic Duct (CHD).
- The Common Bile Duct (CBD) is formed by the junction of the cystic duct with the CHD.
- The CBD traverses through the head of the pancreas, entering the duodenum at the Ampulla of Vater through the Sphincter of Oddi.
- The pancreatic duct joins the CBD before it drains into the duodenum.
Variations in Anatomy
- A common anatomic variation is to have an extrahepatic junction of the right/left hepatic ducts, occurring in 20% of people.
- Another variation is for the right hepatic duct to join the cystic duct rather than merge with the left hepatic duct.
Ultrasound and Scan Protocol
- Ultrasound is the primary tool for assessing the structure of the biliary tree.
- Scan protocol involves using a curvi-linear probe, with adjustments for patient habitus, and good colour/power/Doppler capabilities.
- Patient preparation involves fasting, and the patient may need to be positioned supine, erect, or left decubitus during the scan.
Limitations and Applications
- Limitations of ultrasound include non-fasted patients and large habitus patients.
- Ultrasound is useful for assessing obstruction, cholangitis, choledochal cysts, cholangioma, and guiding injections, aspirations, or biopsies.
Pathology
- Obstruction can be due to intraductal (calculus, sludge, tumor) or extraductal (tumor extrinsic compression, tumor invasion, collection) causes.
- Cholangitis and Caroli's disease are other pathologies that can be assessed with ultrasound.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.