Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the biceps brachii muscle?
What is the primary function of the biceps brachii muscle?
- Rotating the ankle and the wrist
- Flexing the elbow and the shoulder (correct)
- Flexing the knee and the hip
- Extending the elbow and the shoulder
Which part of the upper limb contains the triceps brachii muscle?
Which part of the upper limb contains the triceps brachii muscle?
- Shoulder joint
- Forearm
- Anterior compartment of the upper arm
- Posterior compartment of the upper arm (correct)
Where does the coracobrachialis muscle originate from?
Where does the coracobrachialis muscle originate from?
- Supraglenoid tubercle
- Radial tuberosity
- Coracoid process of the scapula (correct)
- Deltoid tubercle
What is the function of the coracobrachialis muscle?
What is the function of the coracobrachialis muscle?
Which muscle resides in the posterior compartment of the upper arm?
Which muscle resides in the posterior compartment of the upper arm?
What are the primary functions of the upper arm?
What are the primary functions of the upper arm?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Arm: Structure and Functions
The arm, also known as the upper limb, is the external appendage of the upper torso in vertebrates, consisting of two parts: the upper arm and the forearm. It plays a crucial role in providing support, maintaining balance, and performing various tasks such as grasping objects, manipulating tools, and engaging in activities of daily living.
Upper Arm
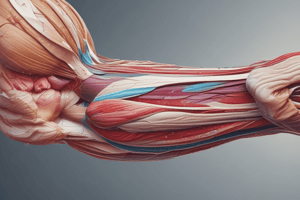
The upper arm is situated between the shoulder joint and the elbow joint. It contains four muscles, each residing in one of its two compartments. The anterior compartment houses three muscles: biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, and brachialis, whereas the posterior compartment contains the triceps brachii muscle.
Biceps Brachii
The two-headed biceps brachii muscle is primarily responsible for flexing the elbow and the shoulder, as well as supinating the forearm. Its primary attachment sites include the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula and the coracoid process of the scapula, while its distal attachment is made via the bicipital aponeurosis into the radial tuberosity and the fascia of the forearm.
Coracobrachialis
The coracobrachialis muscle lies deep within the arm, originating from the coracoid process of the scapula. It passes through the axilla and attaches to the medial side of the humeral shaft, just below the deltoid tubercle. This muscle contributes to flexion at the shoulder joint and weak adduction of the upper limb.
Brachialis
The brachialis muscle, located deeper than the other muscles in the anterior compartment, is responsible for flexing the elbow joint. It originates from the medial and lateral surfaces of the humeral shaft and inserts onto the ulnar tuberosity, right next to the elbow joint.
Posterior Compartment
The posterior compartment of the arm houses the triceps brachii muscle, which consists of three heads: long head, lateral head, and medial head. The long and lateral heads originate from their respective attachments on the scapula and humerus, while the medial head is attached to the inferior aspect of the humeral shaft. These heads converge towards the elbow joint, where they insert onto the olecranon of the ulna, allowing extension of the elbow.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.