Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following ligaments is NOT labelled in the diagram?
Which of the following ligaments is NOT labelled in the diagram?
- Gastrohepatic ligament
- Phrenicocolic ligament (correct)
- Gastrophrenic ligament
- Splenorenal ligament
Which part of the duodenum is intraperitoneal?
Which part of the duodenum is intraperitoneal?
- Fourth part
- Second part
- Third part
- First part (correct)
Which of the following structures is usually intraperitoneal but sometimes retroperitoneal?
Which of the following structures is usually intraperitoneal but sometimes retroperitoneal?
- Ascending colon
- Caecum (correct)
- Rectum
- Descending colon
What is the term for the folds of peritoneum that connect organs to the posterior abdominal wall?
What is the term for the folds of peritoneum that connect organs to the posterior abdominal wall?
Which of the following organs is NOT retroperitoneal?
Which of the following organs is NOT retroperitoneal?
What is the term for the peritoneal fold that connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
What is the term for the peritoneal fold that connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
Which of the following structures is NOT a retroperitoneal organ?
Which of the following structures is NOT a retroperitoneal organ?
What is the term for the peritoneal fold that connects the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall?
What is the term for the peritoneal fold that connects the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall?
What is a characteristic of the segmental arteries of the kidney?
What is a characteristic of the segmental arteries of the kidney?
What is a consequence of ligation of any branch of a segmental artery?
What is a consequence of ligation of any branch of a segmental artery?
Which of the following nerve(s) may be affected by an enlarged psoas muscle?
Which of the following nerve(s) may be affected by an enlarged psoas muscle?
What is a feature of aberrant renal arteries?
What is a feature of aberrant renal arteries?
What is a characteristic of interlobar veins?
What is a characteristic of interlobar veins?
What is the primary cause of psoas abscess in patients with haemophilia?
What is the primary cause of psoas abscess in patients with haemophilia?
How does pus from a psoas abscess typically manifest itself clinically?
How does pus from a psoas abscess typically manifest itself clinically?
What is the drainage pattern of the left gonadal vein?
What is the drainage pattern of the left gonadal vein?
Which of the following is NOT a typical branch of the lumbar plexus?
Which of the following is NOT a typical branch of the lumbar plexus?
What is the principal lymphatic drainage of the left kidney?
What is the principal lymphatic drainage of the left kidney?
What is the consequence of blockage of the left renal vein?
What is the consequence of blockage of the left renal vein?
What is the most common reason for psoas abscess formation?
What is the most common reason for psoas abscess formation?
What is the termination point of the renal veins?
What is the termination point of the renal veins?
What is the typical presentation of a psoas abscess in a patient with lumbar tuberculosis?
What is the typical presentation of a psoas abscess in a patient with lumbar tuberculosis?
Which nerve is responsible for providing sensation to the anterior thigh?
Which nerve is responsible for providing sensation to the anterior thigh?
Which of the following nerves is NOT directly related to the abdomen?
Which of the following nerves is NOT directly related to the abdomen?
What anatomical structure lies anterior to the isthmus in the case of a horseshoe kidney?
What anatomical structure lies anterior to the isthmus in the case of a horseshoe kidney?
Which of the following characteristics is true about the positioning of the kidneys?
Which of the following characteristics is true about the positioning of the kidneys?
How often does horseshoe kidney occur in births?
How often does horseshoe kidney occur in births?
What anatomical feature is the primary reason the right kidney is lower than the left kidney?
What anatomical feature is the primary reason the right kidney is lower than the left kidney?
What is the relative position of the ureters in relation to the psoas major muscle?
What is the relative position of the ureters in relation to the psoas major muscle?
Which of the following best describes the tilt of the kidneys?
Which of the following best describes the tilt of the kidneys?
What is a common outcome if the isthmus of a horseshoe kidney cannot ascend properly?
What is a common outcome if the isthmus of a horseshoe kidney cannot ascend properly?
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding kidney protection?
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding kidney protection?
What muscle is the middle part of the kidney primarily associated with?
What muscle is the middle part of the kidney primarily associated with?
Where do the renal vessels enter and exit the kidneys?
Where do the renal vessels enter and exit the kidneys?
Which of the following organs is located posterior to the parietal peritoneum?
Which of the following organs is located posterior to the parietal peritoneum?
Which muscle is located medially to the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter?
Which muscle is located medially to the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter?
What anatomical relation do the kidneys have concerning the diaphragm?
What anatomical relation do the kidneys have concerning the diaphragm?
Which structures lie anterior to the renal veins?
Which structures lie anterior to the renal veins?
What surrounds the kidneys in the abdominal cavity?
What surrounds the kidneys in the abdominal cavity?
What movement do the kidneys perform during respiration?
What movement do the kidneys perform during respiration?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
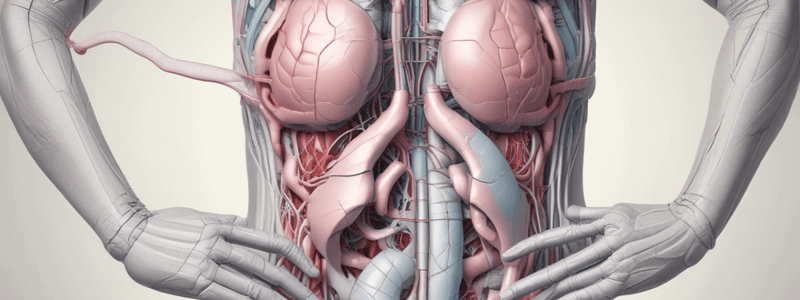
Peritoneum and Ligaments
- The peritoneum folds forward from the posterior abdominal wall to form ligaments and mesenteries.
- Principal ligaments include the gastrophrenic, gastrohepatic, and splenorenal ligaments, positioned from superior to inferior.
- Key mesenteries are the transverse mesocolon, the mesentery, and the sigmoid mesocolon.
Retroperitoneal Organs
- Retroperitoneal organs include the suprarenal glands, kidneys, pancreas, ascending colon, descending colon, and rectum.
- The first part of the duodenum is intraperitoneal; however, the rest is retroperitoneal.
- The caecum is typically intraperitoneal but can occasionally be retroperitoneal.
Psoas Abscess
- Psoas abscess can occur from infections or conditions like tuberculosis, leading to pus collection in the psoas sheath.
- Symptoms include swelling near the thigh and lower abdomen, hip flexion, and significant pain.
Lumbar Plexus
- Formed from the anterior rami of L1-L4, often with contributions from T12.
- Key branches include iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, lateral femoral cutaneous, femoral, and obturator nerves.
- Iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, and genitofemoral nerves are particularly relevant to abdominal concerns.
Kidney and Ureter Positioning
- Kidneys are located retroperitoneally, extending from T12 to L3 vertebrae.
- The right kidney's upper part reaches the 12th rib, while the left reaches the 11th rib, influenced by the liver's position.
- Ureters descend along the posterior wall, anterior to the psoas major muscle.
Relationship to Muscles and Diaphragm
- Kidneys relate to the diaphragm, with movement during respiration.
- Positioned against abdominal wall muscles: laterally on transversus abdominis, medially on psoas major, and on quadratus lumborum in the middle.
Renal Anatomy and Blood Supply
- Renal artery divides into segmental arteries, supplying specific kidney segments with no anastomosis, critical for surgeries.
- Accessory renal arteries can directly enter the kidney substance at poles.
- Renal veins aggregate into two main veins leading to the inferior vena cava; the left renal vein drains the left gonadal vein.
Lymphatic Drainage
- Principal lymphatic drainage of the left kidney occurs via left para-aortic lymph nodes.
- Right kidney drains to inter-aortocaval and paracaval lymph nodes.
- Lymphatic pathways are critical as they can influence pathology or metastasis in related organs.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.