Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where does the cystic duct drain into?
Where does the cystic duct drain into?
- Left hepatic duct
- Common bile duct (CBD) (correct)
- Right hepatic duct
- Pancreatic duct
What is the function of the valves of Heister?
What is the function of the valves of Heister?
- To mix bile with pancreatic juices
- To stimulate contraction of the gallbladder
- To retain bile in the gallbladder (correct)
- To drain bile from the gallbladder
What is the main source of the biliary cholesterol?
What is the main source of the biliary cholesterol?
- Bile salts
- Circulating lipoproteins and hepatic synthesis (correct)
- Hepatic glycogenolysis
- Dietary cholesterol
What is the function of the tight junctions in the biliary tree?
What is the function of the tight junctions in the biliary tree?
What is the fate of the majority of the bile secreted into the bile canaliculi?
What is the fate of the majority of the bile secreted into the bile canaliculi?
What type of bacteria is most commonly found in biliary infections?
What type of bacteria is most commonly found in biliary infections?
What is the purpose of prophylactic antibiotics in biliary interventions?
What is the purpose of prophylactic antibiotics in biliary interventions?
What type of antibiotics is recommended for prophylaxis in most patients undergoing biliary interventions?
What type of antibiotics is recommended for prophylaxis in most patients undergoing biliary interventions?
What is the main function of bile salts in the gallbladder?
What is the main function of bile salts in the gallbladder?
What is the process that occurs in the gallbladder to increase the concentrations of bile solutes and calcium?
What is the process that occurs in the gallbladder to increase the concentrations of bile solutes and calcium?
What is the main function of the sphincter of Oddi?
What is the main function of the sphincter of Oddi?
What is the indication for antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
What is the indication for antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
What is the effect of cholecystokinin on the sphincter of Oddi?
What is the effect of cholecystokinin on the sphincter of Oddi?
What is the role of glycoproteins in the biliary system?
What is the role of glycoproteins in the biliary system?
What is the effect of a high tonic contraction of the sphincter of Oddi in the fasting state?
What is the effect of a high tonic contraction of the sphincter of Oddi in the fasting state?
What is the maximum amount of bile that the gallbladder can store?
What is the maximum amount of bile that the gallbladder can store?
What is the primary reason for observing patients with mild symptoms of gallstones?
What is the primary reason for observing patients with mild symptoms of gallstones?
What induces the secretion of cholecystokinin from duodenal epithelial cells?
What induces the secretion of cholecystokinin from duodenal epithelial cells?
What is the significance of a level of bilirubin above 5 mg/dL in the skin?
What is the significance of a level of bilirubin above 5 mg/dL in the skin?
What is the significance of a positive sign in cholecystectomy?
What is the significance of a positive sign in cholecystectomy?
What is the limitation of plain radiographs in the evaluation of biliary tree disease?
What is the limitation of plain radiographs in the evaluation of biliary tree disease?
What is the primary indication for elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
What is the primary indication for elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
What is the most common grading system used to evaluate the severity of cholecystitis?
What is the most common grading system used to evaluate the severity of cholecystitis?
What is the outcome of cholecystectomy in more than 90% of patients?
What is the outcome of cholecystectomy in more than 90% of patients?
What is the term for acute cholecystitis resulting from a blockage of the cystic duct by a stone?
What is the term for acute cholecystitis resulting from a blockage of the cystic duct by a stone?
What is the characteristic of biliary colic in the absence of infection and inflammation?
What is the characteristic of biliary colic in the absence of infection and inflammation?
What is the highest grade of acute cholecystitis according to the AAST EGS guidelines?
What is the highest grade of acute cholecystitis according to the AAST EGS guidelines?
What is indicated when more anatomic delineation is required in biliary disease?
What is indicated when more anatomic delineation is required in biliary disease?
What does the injection of CCK during a HIDA scan document?
What does the injection of CCK during a HIDA scan document?
What is the characteristic feature of acute cholecystitis on a HIDA scan?
What is the characteristic feature of acute cholecystitis on a HIDA scan?
What type of stones are radiographically isodense?
What type of stones are radiographically isodense?
What is the outcome of cholecystectomy in more than 90% of patients?
What is the outcome of cholecystectomy in more than 90% of patients?
What is the term for acute cholecystitis resulting from a blockage of the cystic duct by a stone?
What is the term for acute cholecystitis resulting from a blockage of the cystic duct by a stone?
What is the limitation of plain radiographs in the evaluation of biliary tree disease?
What is the limitation of plain radiographs in the evaluation of biliary tree disease?
What is the sensitivity of transabdominal ultrasonography in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the sensitivity of transabdominal ultrasonography in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the primary indication for removing a cholecystostomy tube?
What is the primary indication for removing a cholecystostomy tube?
What is the use of a HIDA scan in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the use of a HIDA scan in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the significance of a positive Murphy sign in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the significance of a positive Murphy sign in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the role of Tokyo Guidelines in managing gallbladder disorders?
What is the role of Tokyo Guidelines in managing gallbladder disorders?
What is the incidence of CBD stones in patients undergoing biliary imaging?
What is the incidence of CBD stones in patients undergoing biliary imaging?
What is the significance of gallbladder wall thickening in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the significance of gallbladder wall thickening in diagnosing acute cholecystitis?
What is the outcome of delaying cholecystectomy in patients with acute cholecystitis?
What is the outcome of delaying cholecystectomy in patients with acute cholecystitis?
What is the primary use of biliary scintigraphy in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the primary use of biliary scintigraphy in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the significance of failed gallbladder filling 2 hours after injection on a HIDA scan?
What is the significance of failed gallbladder filling 2 hours after injection on a HIDA scan?
What is the advantage of ultrasound in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the advantage of ultrasound in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the role of a HIDA scan in the postoperative setting?
What is the role of a HIDA scan in the postoperative setting?
What is the limitation of computed tomography in the diagnosis of biliary disease?
What is the limitation of computed tomography in the diagnosis of biliary disease?
What is the significance of gallbladder filling on a HIDA scan?
What is the significance of gallbladder filling on a HIDA scan?
What is the primary indication for using a HIDA scan in patients with biliary tract pain?
What is the primary indication for using a HIDA scan in patients with biliary tract pain?
What is the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma?
What is the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma?
What can be identified by ultrasound in many gallbladder diseases?
What can be identified by ultrasound in many gallbladder diseases?
What is seen in ultrasound images of porcelain gallbladder?
What is seen in ultrasound images of porcelain gallbladder?
What is the characteristic feature of acute cholecystitis on ultrasound?
What is the characteristic feature of acute cholecystitis on ultrasound?
What can be seen in ultrasound images of gallstones in the gallbladder neck?
What can be seen in ultrasound images of gallstones in the gallbladder neck?
What is the significance of posterior shadowing in ultrasound images of the gallbladder?
What is the significance of posterior shadowing in ultrasound images of the gallbladder?
What is the diagnostic role of ultrasound in gallbladder diseases?
What is the diagnostic role of ultrasound in gallbladder diseases?
What is the characteristic ultrasound feature of a gallstone in the gallbladder neck?
What is the characteristic ultrasound feature of a gallstone in the gallbladder neck?
What is the ultrasound feature of porcelain gallbladder?
What is the ultrasound feature of porcelain gallbladder?
What type of gallstones are most common in the United States?
What type of gallstones are most common in the United States?
What is the primary reason for increased stone formation in conditions associated with impaired gallbladder emptying?
What is the primary reason for increased stone formation in conditions associated with impaired gallbladder emptying?
What is the term for the temporary blockage of the cystic duct that causes pain?
What is the term for the temporary blockage of the cystic duct that causes pain?
What is the characteristic of pigment stones found in the bile ducts?
What is the characteristic of pigment stones found in the bile ducts?
What percentage of the population is affected by cholelithiasis?
What percentage of the population is affected by cholelithiasis?
What accelerates crystal formation in the gallbladder?
What accelerates crystal formation in the gallbladder?
What is the typical composition of gallstones in the United States?
What is the typical composition of gallstones in the United States?
Why do gallstones become symptomatic?
Why do gallstones become symptomatic?
What is the significance of a dilated bile duct in the presence of gallstones?
What is the significance of a dilated bile duct in the presence of gallstones?
What is the treatment for choledocholithiasis?
What is the treatment for choledocholithiasis?
What is the indication for ERCP in patients undergoing cholecystectomy?
What is the indication for ERCP in patients undergoing cholecystectomy?
What is the presentation of an elderly patient with a sudden mechanical small intestine obstruction?
What is the presentation of an elderly patient with a sudden mechanical small intestine obstruction?
What is the role of MRCP in patients with a likelihood of CBD stones?
What is the role of MRCP in patients with a likelihood of CBD stones?
What is the significance of a computed tomography scan in the diagnosis of biliary disease?
What is the significance of a computed tomography scan in the diagnosis of biliary disease?
What is the outcome of cholecystectomy in patients with choledocholithiasis?
What is the outcome of cholecystectomy in patients with choledocholithiasis?
What is the role of ultrasound in patients with a likelihood of CBD stones?
What is the role of ultrasound in patients with a likelihood of CBD stones?
What is the primary use of ultrasound in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the primary use of ultrasound in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the significance of failed gallbladder filling 2 hours after injection on a HIDA scan?
What is the significance of failed gallbladder filling 2 hours after injection on a HIDA scan?
What is the advantage of ultrasound in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the advantage of ultrasound in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the role of a HIDA scan in the postoperative setting?
What is the role of a HIDA scan in the postoperative setting?
What is the primary indication for using a HIDA scan in patients with biliary tract pain?
What is the primary indication for using a HIDA scan in patients with biliary tract pain?
What is the limitation of computed tomography in the diagnosis of biliary disease?
What is the limitation of computed tomography in the diagnosis of biliary disease?
When is early conversion to open cholecystectomy considered?
When is early conversion to open cholecystectomy considered?
What is the significance of gallbladder filling on a HIDA scan?
What is the significance of gallbladder filling on a HIDA scan?
What is the purpose of a partial cholecystectomy?
What is the purpose of a partial cholecystectomy?
What is the role of biliary scintigraphy in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the role of biliary scintigraphy in the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice?
What is the characteristic of the gallbladder wall in acute cholecystitis?
What is the characteristic of the gallbladder wall in acute cholecystitis?
What is the purpose of a percutaneously placed cholecystostomy tube?
What is the purpose of a percutaneously placed cholecystostomy tube?
What is the indication for a percutaneously placed cholecystostomy tube?
What is the indication for a percutaneously placed cholecystostomy tube?
When is a partial cholecystectomy performed?
When is a partial cholecystectomy performed?
What is the role of ultrasound guidance in cholecystostomy?
What is the role of ultrasound guidance in cholecystostomy?
What is the effect of cholecystostomy?
What is the effect of cholecystostomy?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
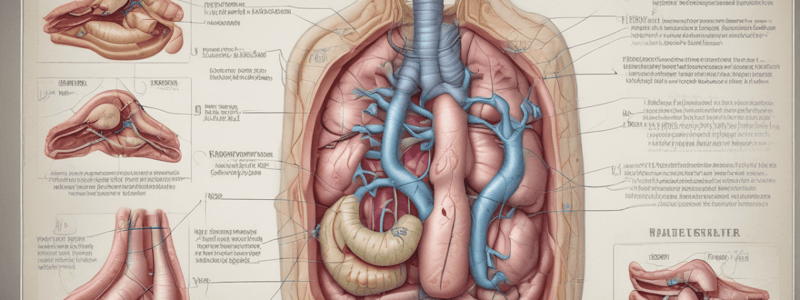
Bile Ducts and Anatomy
- Bile ducts, either intrahepatic or extrahepatic, lie superior to the corresponding portal vein, which in turn are lateral and inferior to the arterial supply.
- The left hepatic duct retains a longer transverse extrahepatic portion and travels under the edge of segment IV before joining the bifurcation.
- The left duct drains segments I, II, III, and IV, with the most distal branch draining segment IVA.
- The ducts draining segment IVB arise further superolateral, and the ducts for segments II and III arise further up the left duct.
- The cystic duct can range from 1 to 5 cm in length and drains at an acute angle into the CBD.
- The CBD is divided into three portions: supraduodenal, retroduodenal, and the pancreatic portion, which is the most inferior portion.
Bile Production and Flow
- Bile components are secreted into the bile canaliculi directly from hepatocytes.
- The secretion of bile components into the bile tree is a major stimulus to bile flow, and the volume of bile flow is an osmotic process.
- Bile salts combine to form spherical pockets, known as micelles, which provide no osmotic activity.
- The cations that are secreted into the bile tree provide osmotic activity.
- The sphincter of Oddi maintains a high tonic contraction, but is inhibited by cholecystokinin.
Enterohepatic Circulation
- Bile salts are secreted into the bile canaliculi directly from hepatocytes.
- The bile salts are then secreted into the bile duct and stored in the gallbladder.
- The passage of fat, protein, and acid into the duodenum induces CCK secretion from duodenal epithelial cells.
- CCK secretion increases the flow of bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum.
Bile Composition
- Bile contains proteins, lipids, and pigments.
- The major lipid components of bile are phospholipids and cholesterol.
- Cholesterol is secreted into the bile duct and serves to excrete cholesterol from the body.
- Glycoproteins are also secreted into the bile duct to help protect the gallbladder from the detergent activity of bile.
Imaging Studies
- Plain radiographs are of limited use in the overall evaluation of biliary tree disease.
- Ultrasound is used to evaluate the biliary tree and diagnose gallstones.
- Endoscopic ultrasound with needle biopsy can be used to diagnose biliary disease.
Infection and Inflammation
- Infection in the absence of obstruction is rare.
- With the presence of stones or obstruction, the likelihood of bacterial infection increases.
- The most common types of bacteria found in biliary infections are Enterobacteriaceae, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter, followed by Enterococcus spp.
- Prophylactic antibiotics should be used in most patients undergoing interventions in the biliary tree, such as ERCP or PTC.
Cholecystectomy
- Cholecystectomy carries a low-risk profile but is not without complications.
- An analysis of risks and benefits is important before undergoing cholecystectomy.
- In more than 90% of patients, cholecystectomy is curative, leaving them symptom-free.
- Elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy is warranted for patients with more severe or recurrent symptoms.
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
- Acute cholecystitis is the result of a blockage of the cystic duct and is called acute calculous cholecystitis when the blockage is by a stone.
- Acute calculous cholecystitis is associated with a higher rate of complications.
- Elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy is warranted for patients with acute calculous cholecystitis.
- There have been multiple grading systems evaluating the severity of cholecystitis, such as the Tokyo Guidelines and the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) Emergency General Surgery (EGS) guidelines.
Biliary Disease Diagnosis
- CT provides superior anatomic information and is indicated when more anatomic delineation is required.
- HIDA scans can determine gallbladder function by documenting physiologic response to injection of CCK.
Gallbladder Function
- HIDA scans can show non-filling of the gallbladder, indicating occlusion of the cystic duct, a characteristic feature of acute cholecystitis.
- Filling of the gallbladder during a HIDA scan essentially eliminates the diagnosis of cholecystitis.
Biliary Scintigraphy
- Hepatic iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan can evaluate the physiologic secretion of bile.
- The scan identifies bile flow and can demonstrate obstruction of the cystic duct, biliary tree, and bile leaks.
- HIDA scan does not provide fine anatomic detail, nor can it identify gallstones.
Computed Tomography
- CT provides superior anatomic information, especially for the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tree and pancreas.
- CT can identify the cause of obstructive jaundice, showing CBD stones or cholangiocarcinoma.
Ultrasound
- Transabdominal ultrasonography is a sensitive, inexpensive, and reliable tool for the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis.
- Ultrasound has a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 95% for diagnosing acute cholecystitis.
- Ultrasound can identify gallstones, pericholecystic fluid, gallbladder wall thickening, and a sonographic Murphy sign.
Choledocholithiasis
- CBD stones, or choledocholithiasis, are generally silent and are seen in up to 10% of patients undergoing biliary imaging.
- Tokyo Guidelines, revised in 2018, predict the severity of gallbladder disorder, prognosis, and rate of conversion or bail-out procedure.
Gallbladder Diseases and Ultrasound
- Ultrasound can identify pathologic changes in many gallbladder diseases, such as gallbladder wall thickening and pericholecystic fluid seen in cholecystitis.
- Gallstones can be identified by ultrasound, with characteristic posterior shadowing stripe under the stone.
- Porcelain gallbladder appears as a curvilinear echogenic focus along the entire gallbladder wall, with posterior shadowing.
Hepatic Iminodiacetic Acid (HIDA) Scan
- HIDA scan can evaluate the physiologic secretion of bile and identify bile flow.
- The scan can demonstrate obstruction of the cystic duct, as seen in acute cholecystitis.
- It can also identify obstruction of the biliary tree and bile leaks, which may be useful in the postoperative setting.
Calculous Biliary Disease
- Cholelithiasis is the most common disease of the gallbladder and biliary tree, affecting 10% to 15% of the population.
- Gallstones are classified into two major subtypes: cholesterol and pigment stones.
- Cholesterol stones account for more than 70% of gallstones in the United States, and pure cholesterol stones account for less than 10%.
- Pigment stones can be divided into black stones, seen in hemolytic conditions and cirrhosis, and brown stones, found in the bile ducts and thought to be secondary to infection.
Natural History
- Gallstones become symptomatic when they obstruct a visceral structure such as a cystic duct.
- However, gallstones often remain asymptomatic, only found incidentally on imaging.
- Biliary colic, caused by temporary blockage of the cystic duct, tends to occur early.
Treatment
- ERCP or CBD exploration is generally the treatment for choledocholithiasis.
- Laparoscopic or open cholecystectomy may be performed, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Percutaneously placed cholecystostomy tube may be considered for patients with acute cholecystitis who have a prohibitively high operative risk.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.