Podcast
Questions and Answers
The superior border of the kidneys typically lies at which vertebral level?
The superior border of the kidneys typically lies at which vertebral level?
- 3rd lumbar
- 10th thoracic (correct)
- 12th thoracic
- 5th lumbar
Which term describes the concave region of the kidney where blood vessels and the ureter connect?
Which term describes the concave region of the kidney where blood vessels and the ureter connect?
- Renal pyramid
- Renal cortex
- Hilum (correct)
- Renal medulla
What is the primary function of the renal pelvis?
What is the primary function of the renal pelvis?
- Hormone production
- Collecting area for urine
- Filtration of blood (correct)
- Regulation of blood pressure
Which of the following is a major function of the kidneys?
Which of the following is a major function of the kidneys?
Erythropoietin release by the kidneys stimulates what process?
Erythropoietin release by the kidneys stimulates what process?
What is the destination of blood carried by the afferent arterioles?
What is the destination of blood carried by the afferent arterioles?
What is the primary function of the efferent arterioles?
What is the primary function of the efferent arterioles?
Which of the following structures is found in the renal medulla?
Which of the following structures is found in the renal medulla?
The main filtering units of the kidney are located in which region?
The main filtering units of the kidney are located in which region?
What are the two main components of a nephron?
What are the two main components of a nephron?
Which of the following is the filtering unit within the nephron?
Which of the following is the filtering unit within the nephron?
Which structure collects filtrate from the glomerulus?
Which structure collects filtrate from the glomerulus?
What specialized cells are sensitive to changes in sodium, potassium, and chloride levels in the distal convoluted tubule?
What specialized cells are sensitive to changes in sodium, potassium, and chloride levels in the distal convoluted tubule?
Which type of cells are baroreceptors that respond to changes in blood pressure?
Which type of cells are baroreceptors that respond to changes in blood pressure?
The afferent arteriole has a larger diameter than the efferent arteriole. How is this important in glomerular filtration?
The afferent arteriole has a larger diameter than the efferent arteriole. How is this important in glomerular filtration?
What effect does vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole have on GFR?
What effect does vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole have on GFR?
Vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole will have what impact on GFR?
Vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole will have what impact on GFR?
How does a DECREASE in plasma protein affect GFR?
How does a DECREASE in plasma protein affect GFR?
Which of the following scenarios is most likely to DECREASE GFR?
Which of the following scenarios is most likely to DECREASE GFR?
What two processes occur after glomerular filtration?
What two processes occur after glomerular filtration?
What percentage of filtered sodium and water is typically reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
What percentage of filtered sodium and water is typically reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
By the time the filtrate goes through the loop of Henle and the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) approximately what % of the filtered fluid is reabsorbed?
By the time the filtrate goes through the loop of Henle and the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) approximately what % of the filtered fluid is reabsorbed?
What is the role of tubular secretion in urine formation?
What is the role of tubular secretion in urine formation?
If blood pressure drops, what is the immediate response by the juxtaglomerular cells?
If blood pressure drops, what is the immediate response by the juxtaglomerular cells?
In the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS), where is renin released?
In the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS), where is renin released?
In the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS), where is angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) manufactured?
In the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS), where is angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) manufactured?
What is the primary effect of aldosterone on the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the primary effect of aldosterone on the distal convoluted tubule?
ACE inhibitors, used to treat hypertension, have which common side effect?
ACE inhibitors, used to treat hypertension, have which common side effect?
What is the effect of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) on the collecting duct?
What is the effect of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) on the collecting duct?
Diabetes insipidus occurs due to inadequate secretion of which hormone?
Diabetes insipidus occurs due to inadequate secretion of which hormone?
How does caffeine affect sodium reabsorption in the renal tubules?
How does caffeine affect sodium reabsorption in the renal tubules?
Approximately what percentage of urine is comprised of water?
Approximately what percentage of urine is comprised of water?
What does the urine specific gravity reflect?
What does the urine specific gravity reflect?
What is a possible indication if a patient's urine output is consistently less than 30 milliliters per hour?
What is a possible indication if a patient's urine output is consistently less than 30 milliliters per hour?
After urine forms in the nephron, through which series of structures does the urine travel?
After urine forms in the nephron, through which series of structures does the urine travel?
Which of the following is a common component of renal stones?
Which of the following is a common component of renal stones?
What name is given to inflammation of the urinary bladder?
What name is given to inflammation of the urinary bladder?
Which region on the floor of the bladder is a triangular region with 3 openings? (two ureters and one urethra)
Which region on the floor of the bladder is a triangular region with 3 openings? (two ureters and one urethra)
What process is defined as the voiding or urination reflex that causes urine to leave the bladder?
What process is defined as the voiding or urination reflex that causes urine to leave the bladder?
Costovertebral Angle (CVA) tenderness can indicate:
Costovertebral Angle (CVA) tenderness can indicate:
A researcher is studying the impact of a novel drug on kidney function. After administering the drug, they observe a significant decrease in the production of erythropoietin. Which of the following is the MOST likely consequence of this drug's effect?
A researcher is studying the impact of a novel drug on kidney function. After administering the drug, they observe a significant decrease in the production of erythropoietin. Which of the following is the MOST likely consequence of this drug's effect?
Which of the following describes the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column?
Which of the following describes the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column?
The kidneys are described as being retroperitoneal. What does this mean?
The kidneys are described as being retroperitoneal. What does this mean?
What is the main function of the kidneys?
What is the main function of the kidneys?
The renal arteries branch directly from which major blood vessel?
The renal arteries branch directly from which major blood vessel?
What type of blood do the efferent arterioles carry?
What type of blood do the efferent arterioles carry?
Which action would result in decreased GFR?
Which action would result in decreased GFR?
How does an obstruction in the glomerulus affect GFR?
How does an obstruction in the glomerulus affect GFR?
Which of the following conditions would likely increase GFR?
Which of the following conditions would likely increase GFR?
Approximately what percentage of sodium and water is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Approximately what percentage of sodium and water is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
What is the primary role of tubular secretion?
What is the primary role of tubular secretion?
What is the immediate response of juxtaglomerular cells to a drop in blood pressure?
What is the immediate response of juxtaglomerular cells to a drop in blood pressure?
Which of the following is a common side effect of ACE inhibitors?
Which of the following is a common side effect of ACE inhibitors?
What is the primary effect of caffeine on the kidneys?
What is the primary effect of caffeine on the kidneys?
What does the specific gravity of urine indicate?
What does the specific gravity of urine indicate?
What is the most likely sequence urine follows after it forms in the nephron?
What is the most likely sequence urine follows after it forms in the nephron?
Which substance is most commonly found in renal stones?
Which substance is most commonly found in renal stones?
What is the correct medical term for inflammation of the urinary bladder?
What is the correct medical term for inflammation of the urinary bladder?
What is the trigone of the urinary bladder?
What is the trigone of the urinary bladder?
What triggers the micturition reflex?
What triggers the micturition reflex?
If a patient presents with Costovertebral Angle (CVA) tenderness, which condition is most likely?
If a patient presents with Costovertebral Angle (CVA) tenderness, which condition is most likely?
A pharmaceutical company is developing a new diuretic drug. Ideally, which part of the nephron should this drug target to have the greatest impact on water reabsorption?
A pharmaceutical company is developing a new diuretic drug. Ideally, which part of the nephron should this drug target to have the greatest impact on water reabsorption?
In a patient with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia leads to glucose in the urine that subsequently impairs water reabsorption. Which part of the nephron is most directly affected in this scenario?
In a patient with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia leads to glucose in the urine that subsequently impairs water reabsorption. Which part of the nephron is most directly affected in this scenario?
A patient is prescribed a medication that increases the permeability of the collecting duct to urea. What is the likely intended effect of this medication on urine concentration and overall kidney function?
A patient is prescribed a medication that increases the permeability of the collecting duct to urea. What is the likely intended effect of this medication on urine concentration and overall kidney function?
A patient exhibits symptoms of hyperaldosteronism (excessive aldosterone secretion). Which set of electrolyte imbalances is MOST likely to be observed in this patient's blood work?
A patient exhibits symptoms of hyperaldosteronism (excessive aldosterone secretion). Which set of electrolyte imbalances is MOST likely to be observed in this patient's blood work?
If you were to block the action of the Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, what direct effect would this have on the kidney's ability to concentrate urine?
If you were to block the action of the Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, what direct effect would this have on the kidney's ability to concentrate urine?
Imagine a scenario where the liver suddenly stops producing angiotensinogen. What would be the MOST immediate and direct consequence of this condition on the body's regulatory mechanisms?
Imagine a scenario where the liver suddenly stops producing angiotensinogen. What would be the MOST immediate and direct consequence of this condition on the body's regulatory mechanisms?
Flashcards
Kidney Location
Kidney Location
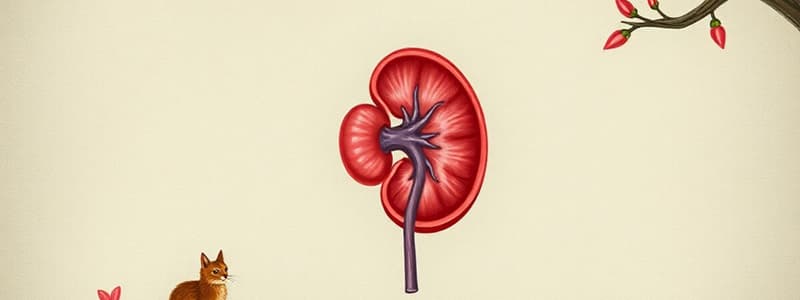
Located on either side of the vertebral column, superior border at the 12th thoracic vertebrae. Lie retroperitoneal.
Kidney Hilum
Kidney Hilum
Concave region of the kidney where vessels, nerves, and ureters enter and leave.
Renal Pelvis
Renal Pelvis
Funnel-shaped collecting area in the medial body of the kidney.
Renal Cortex
Renal Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Medulla
Renal Medulla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Arteries
Renal Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Arterioles
Efferent Arterioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron Loop
Nephron Loop
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macula Densa
Macula Densa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Juxtaglomerular Cells
Juxtaglomerular Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration Pressure
Filtration Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Afferent Arteriole Vasoconstriction Outcome
Afferent Arteriole Vasoconstriction Outcome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Arteriole Vasoconstriction Outcome
Efferent Arteriole Vasoconstriction Outcome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Colloid Osmotic Pressure Impact
Colloid Osmotic Pressure Impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renin-Angiotensin...
Renin-Angiotensin...
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anti-diuretic Hormone(ADH)
Anti-diuretic Hormone(ADH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH and Alcohol
ADH and Alcohol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caffeine effect on kidneys
Caffeine effect on kidneys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Composition
Urine Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Flowpath Formation
Urine Flowpath Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureters
Ureters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Stones(Nephrolithiasis)
Renal Stones(Nephrolithiasis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder
Urinary Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethritis
Urethritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micturition
Micturition
Signup and view all the flashcards
CVA Tenderness
CVA Tenderness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Anatomy and Physiology of the Kidney
- Kidneys lie on either side of the vertebral column.
- The superior border is located at the 12th thoracic vertebrae.
- The Costovertebral angle (CVA) is on the posterior side.
- Kidneys are retroperitoneal, located behind the peritoneum.
- Connective and adipose tissue hold the kidneys in place and protect them.
- Major anatomical landmarks include the hilum and renal pelvis.
- The hilum is a concave region where vessels, nerves, and ureters enter and leave the kidney.
- The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped collecting area in the medial body of the kidney.
- The two major divisions of the kidneys are the renal medulla and the renal cortex.
- The renal medulla houses the collecting ducts of renal tubules.
- The renal cortex houses the main filtering units of the kidneys.
- Main function is to regulate the volume, composition, and pH of body fluids.
- This is achieved through removing and excreting metabolic wastes from the blood.
- Controlling the rate of red blood cell (RBC) production via erythropoietin.
- Regulation of blood pressure.
- Regulation of calcium absorption by activating vitamin D.
- Renal blood vessels consist of renal arteries which arise from the abdominal aorta and branch several times.
- The final branches are afferent arterioles, which carry blood to the nephron.
- Efferent arterioles carry blood away from the nephron.
- These become peritubular capillaries.
- Venous return occurs from the renal veins into the inferior vena cava.
Nephrons
- Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney.
- Two components of nephrons: renal corpuscle and renal tubule.
- The renal corpuscle contains the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule (glomerular capsule).
- The glomerulus is comprised of afferent and efferent arterioles and acts as a filtering unit within the nephron.
- Bowman's capsule (glomerular capsule) is a glove-like structure over the glomerulus that collects filtrate.
- The renal tubule consists of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), nephron loop, and distal convoluted tubule (DCT).
- The PCT is the highly coiled, proximal portion of the renal tubule leaving the glomerulus.
- The nephron loop has a descending limb (PCT dips down toward renal pelvis) and an ascending limb (returns toward corpuscle).
- The Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a shorter and straighter coiled tubule after the loop.
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
- Includes the macula densa and juxtaglomerular cells.
- The macula densa consists of epithelial cells in the DCT.
- These cells are sensitive to [Na+], [K+], and [Cl-] in the DCT.
- Decreasing levels of these electrolytes stimulate renin secretion.
- Juxtaglomerular cells are located in the wall of the afferent arteriole.
- They are near the attachment to the glomerulus.
- They are baroreceptors sensitive to blood pressure.
- Act as a key structure for renin secretion.
Urine Formation
- Glomerular filtration occurs when the glomerulus filters out water and small dissolved particles.
- Filtration pressure is maintained via hydrostatic blood pressure.
- Filtration is affected by extreme changes in blood pressure.
- Afferent arteriole has a larger diameter than the efferent arteriole, allowing blood to back up in the glomerulus.
- Several factors affect glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Afferent arteriole pressure.
- Vasoconstriction results in decreased GFR, decreasing blood flow to the glomerulus.
- Low blood volume will result in decreased filtration and an increase in blood volume.
- Vasodilation increases GFR.
- Efferent arteriole pressure.
- Vasoconstriction here results in increased GFR.
- The same amount of blood is coming into the glomerulus but is slower to come out.
- Colloid Osmotic Pressure.
- Decreased plasma protein in vessels (aka colloid pressure) increases GFR by decreasing fluid pulled back into the vessels.
- Increase in plasma protein pressure decreases GFR as more fluid is pulled back into the vessels)
- Change in surface area of glomerulus.
- Obstructions or damage to the glomerulus can affect GFR.
- Renal disease, overuse of NSAIDs, scarring, etc can affect GFR.
- Net filtration = force favoring filtration - the forces opposing filtration.
- Filtration pressure is normally positive but various disease conditions and medications can affect it.
- NSAIDs, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and lupus erythematous.
- Most filtrate is reabsorbed because of colloid osmotic pressure of the plasma.
- Tubular reabsorption involves water, electrolytes, and glucose.
- Location is important when considering where certain HTN medications have their effects.
- The PCT reabsorbs 70% of filtered Na+, other ions, and water.
- By the time the filtrate goes through the loop and DCT, 97-99% is reabsorbed.
- Tubular secretion involves H+ and toxins from the blood directly into the tubule.
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
- Greatly affects the glomerular filtration rate.
- Juxtaglomerular cells monitor BP, if BP drops→ renin is secreted.
- Renin reacts with a circulating plasma protein angiotensinogen.
- Stored and released in the liver Renin + angiotensinogen → angiotensin I.
- Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II by ACE in the lungs.
- Angiotensin II works at the adrenal gland to secrete aldosterone.
- Aldosterone stimulates sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule.
- This conserves sodium and water increasing circulatory volume → rise in BP.
- ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are common medications working to control hypertension.
- A common side effect of ACE inhibitors is a cough.
Effects of ADH and Caffeine on Urine Formation
- Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH):
- Secreted by the posterior pituitary gland.
- ADH controls water reabsorption at DCT and collecting duct by increasing ADH secretion.
- Greater water reabsorption raises BP.
- Without ADH, the DCT/collecting duct is relatively impermeable to water.
- Urine becomes more concentrated.
- Inadequate secretion of ADH →Diabetes Insipidus
- Grain alcohol blocks the release of ADH from the posterior pituitary.
- Caffeine inhibits proximal tubular sodium reabsorption.
- Less Na+ reabsorbed resulting in = more Na+ and water in the renal tubule.
Urine Composition
- At rest, the kidneys receive ≈ 25% of cardiac output.
- Glomerular filtration occurs at ≈ 180 liters a day (45 gallons).
- The majority of fluid through the kidneys is reabsorbed.
- ≈ 95% of urine is water with small amounts of urea/electrolytes.
- Composition varies based on dietary activities and disease.
- Urea gives urine its typical color as a by-product of protein catabolism.
- Urine specific gravity reflects the relative concentration of solutes in the urine.
- Normal urine output is 50-60 mls/hr, < 30 mls/hr may indicate kidney failure.
Elimination of Urine
- After formation in the nephron urine drains from the collecting ducts.
- Goes to the minor calyces → major calyces → renal pelvis → ipsilateral ureter.
- Ureters are Muscular tubes ≈ 25cm long Peristaltic waves move urine from renal pelvis to urinary bladder.
- Renal stones (nephrolithiasis) are a common cause of pain and obstruction.
- This is caused by the precipitation of solutes out of solution; the majority of stones are calcium-oxalate.
- The Urinary bladder is a hollow, distensible muscular organ within the pelvic cavity.
- The trigone, a triangular region on the floor of the bladder, has 3 openings includes two ureters coming in and one urethra going out.
- Cystitis is bladder inflammation, often caused by bacterial infection, certain drugs, radiation therapy, potential irritants, and even anxiety.
- The urethra is a tube conveying urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
- Females: ≈ 4 cm long
- Males: ≈ 20 cm long
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra, often caused by from sexually transmitted diseases/infections
Micturition
- The voiding or urination reflex causes urine to leave the bladder.
- The urinary bladder distends with urine.
- Stretch receptors in the bladder stimulate micturition reflex in the sacral nerves.
- Detrusor muscle within the bladder contracts and is accompanied by a sense of urgency.
- Internal pressure increases, contractions intensify and force the internal sphincter open.
- Another reflex allows the external urethral sphincter (under conscious control) to relax and urine is then excreted through the urethra.
Urinary System Physical Exam
- The physical exam is limited to costovertebral angle tenderness.
- Palpation of the kidneys is extremely difficult to elicit findings and is not performed in this course.
- Most evaluation is through laboratory testing, including:
- Urinalysis as a will perform UA dipstick in disorders block.
- Metabolic panels which measure BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) and Cr (Creatinine).
- Costovertebral angle tenderness is measured by:
- Placing palm flat over CVA and strike with other fist; repeat bilaterally.
- It's important to assess for pain.
- In patients with suspected renal colic or pyelonephritis pain is elicited due to inflammation of the renal capsule.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
The kidneys regulate body fluids by removing metabolic wastes from the blood. The major anatomical landmarks include the hilum and renal pelvis. The two divisions of the kidneys are the renal medulla and the renal cortex. The renal cortex houses the main filtering units of the kidneys.