Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the cochlea in the ear?
What is the function of the cochlea in the ear?
- Detection of sound (correct)
- Maintaining body balance
- Transmitting sound waves to the brain
- Producing ear wax
What is the role of the pinna in the external ear?
What is the role of the pinna in the external ear?
- Producing ear wax
- Collecting and amplifying sound waves (correct)
- Equalizing air pressure
- Maintaining body balance
What is the function of the vestibular apparatus?
What is the function of the vestibular apparatus?
- Maintaining body balance (correct)
- Producing ear wax
- Amplifying sound waves
- Detection of sound
How much does the middle ear amplify sound waves?
How much does the middle ear amplify sound waves?
What are the three ossicles in the middle ear?
What are the three ossicles in the middle ear?
What is the function of the tensor tympani muscle?
What is the function of the tensor tympani muscle?
What is the function of the auditory tube?
What is the function of the auditory tube?
Where does the ear canal end?
Where does the ear canal end?
What is the function of the three bones of the middle ear?
What is the function of the three bones of the middle ear?
What happens when the staples vibrate against the oval window?
What happens when the staples vibrate against the oval window?
What is the function of the hair cells in the cochlear duct?
What is the function of the hair cells in the cochlear duct?
What happens when the basilar membrane moves upwards?
What happens when the basilar membrane moves upwards?
What is the result of the entry of K+ ions into the hair cell?
What is the result of the entry of K+ ions into the hair cell?
What happens when the basilar membrane moves in the opposite direction?
What happens when the basilar membrane moves in the opposite direction?
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
What is the final destination of the auditory pathway?
What is the final destination of the auditory pathway?
What is the primary function of the stapedius muscle?
What is the primary function of the stapedius muscle?
Which part of the inner ear is responsible for balance?
Which part of the inner ear is responsible for balance?
What is the range of sound frequencies that the human ear can detect?
What is the range of sound frequencies that the human ear can detect?
What is the name of the membrane that separates the middle ear from the inner ear?
What is the name of the membrane that separates the middle ear from the inner ear?
What is the function of the hair cells in the spiral organ of Corti?
What is the function of the hair cells in the spiral organ of Corti?
What is the name of the bony structure that houses the inner ear?
What is the name of the bony structure that houses the inner ear?
What is the mechanism by which sound waves are transmitted to the inner ear?
What is the mechanism by which sound waves are transmitted to the inner ear?
What is the name of the nerve that transmits auditory information from the inner ear to the brain?
What is the name of the nerve that transmits auditory information from the inner ear to the brain?
The cochlear nucleus receives information from which side of the body?
The cochlear nucleus receives information from which side of the body?
What is the function of the superior olivary nucleus?
What is the function of the superior olivary nucleus?
What is the function of the vestibule?
What is the function of the vestibule?
Where do fibers carrying auditory information from the inferior colliculus project to?
Where do fibers carrying auditory information from the inferior colliculus project to?
What type of acceleration is monitored by the semicircular canals?
What type of acceleration is monitored by the semicircular canals?
Where are the maculae (static equilibrium receptors) located?
Where are the maculae (static equilibrium receptors) located?
What happens to hearing in cases of supranuclear lesions?
What happens to hearing in cases of supranuclear lesions?
What is the final destination of auditory information in the brain?
What is the final destination of auditory information in the brain?
What is the function of the otolithic membrane?
What is the function of the otolithic membrane?
What is the primary function of the utricle and saccule?
What is the primary function of the utricle and saccule?
What happens to otoliths when the head is tilted?
What happens to otoliths when the head is tilted?
What is the purpose of the crista ampullaris?
What is the purpose of the crista ampullaris?
What is the gel-like structure that the hair cells are embedded in within the crista ampullaris?
What is the gel-like structure that the hair cells are embedded in within the crista ampullaris?
What is the function of the semicircular ducts?
What is the function of the semicircular ducts?
What is the direction of one of the semicircular ducts?
What is the direction of one of the semicircular ducts?
What is the role of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
What is the role of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Functions of the Ear
- The ear has two main functions: hearing (detection of sound) and equilibrium (maintenance of body balance)
- Hearing involves the detection of sound waves by the cochlea
- Equilibrium involves the maintenance of body balance by the vestibule and semicircular canals
Parts of the Ear
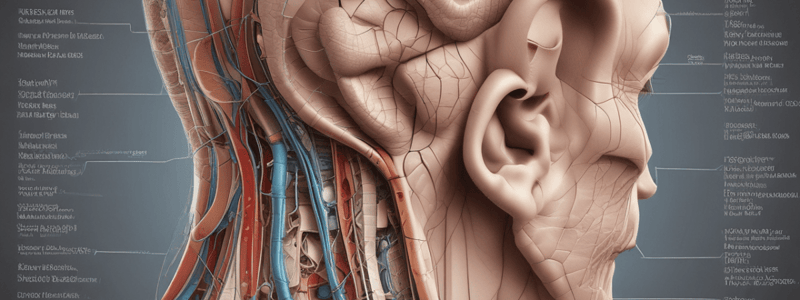
- The ear consists of three main regions: external ear, middle ear, and inner ear
- The external ear (outer ear) collects sound waves and channels them down the ear canal
- The middle ear transmits sound waves to the inner ear, amplifying sound energy
- The inner ear consists of two sensory systems: cochlea (hearing) and vestibular apparatus (balance)
External Ear
- Plays a role in sound localization
- Amplifies sound by approximately 5-6 dB
- Pinna (auricle) collects sound waves and channels them down the ear canal
- Ceruminous (wax) glands produce ear wax, trapping foreign particles and preventing them from entering the ear
- Ends at the tympanic membrane (eardrum), which vibrates when sound waves hit it and transmits the sound waves to the middle ear
Middle Ear
- Contains three ossicles (smallest bones): malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup)
- Ossicles are connected to each other and transmit sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
- Amplifies sound waves by 22 times
- The auditory tube (Eustachian tube) connects the middle ear with the throat (nasopharynx), helping to equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane during yawning or swallowing
Muscles of the Middle Ear
- Two muscles: tensor tympani and stapedius
- Tensor tympani muscle:
- Contracts in response to loud sounds, pulling the tympanic membrane inward and restricting its freedom of movement
- Protects the ear from loud noise or trauma
- Stapedius muscle:
- Smallest muscle in the body
- Contracts in response to loud sounds, damping the ossicular chain vibration and limiting potential damage
Inner Ear
- Most complex portion of the ear
- A maze of bony chambers within the temporal bone
- Consists of three parts: semicircular canals (balance), vestibule (balance), and cochlea (hearing)
Hearing (Audition)
- Hearing is the transduction of sound waves into electrical signals
- Spiral organ of Corti is housed within the cochlear duct and contains hair cells (hearing receptors)
- Hair cells convert sound waves into nerve impulses, transmitted via the auditory nerves to the brain for perception and interpretation as sound
- Cochlea encodes auditory stimuli for frequencies between 20 and 20,000 Hz
Mechanism of Hearing
- Sound waves in the ear canal strike the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and become vibrations
- Vibrations of the stapes against the oval window are converted into fluid waves within the vestibular duct
- Fluid waves push on the membranes of the cochlear duct, activating the sensory hair cell receptors
- Activated hair cells stimulate the auditory nerve, transmitting the signal to the brain for perception and interpretation as sound
Auditory Pathway
- The nerve impulse travels along the vestibulocochlear nerve, synapsing with neurons in the cochlear nuclei of the medulla
- From the cochlear nucleus, some fibers synapse at the ipsilateral superior olivary nuclei, while most fibers decussate to the contralateral superior olivary nuclei
- Fibers from superior olivary nuclei project upwards through the lateral lemniscus to reach the inferior colliculus nucleus
- Axons carrying auditory information project to the medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, then to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex for interpretation as hearing
Physiology of Balance: Vestibular Apparatus
- The vestibular apparatus consists of the vestibule (monitoring static equilibrium) and the semicircular canals (monitoring dynamic equilibrium)
- The vestibule is responsible for monitoring static equilibrium, detecting changes in position of the head in space with respect to the pull of gravity
- The semicircular canals are responsible for monitoring dynamic equilibrium, detecting angular or rotatory movements of the head
Vestibule: Utricle and Saccule
- Maculae (static equilibrium receptors) are located within the membranous sacs of the vestibule (utricle and saccule)
- Each macula is a patch of hair cells with stereocilia embedded in the otolithic membrane (a viscous gel containing calcium crystals called otoliths)
- When the head tilts, otoliths roll in response to the pull of gravity, creating a pull on the otolithic membrane and bending of macula hair cells
- The hair cells become activated and send impulses along the vestibulocochlear nerve to the brain stem and cerebellum, informing it of the head position in space
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.