Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following structures is located on the posterior aspect of the scapula?
Which of the following structures is located on the posterior aspect of the scapula?
- Subscapular fossa
- Glenoid fossa
- Coracoid process
- Spine of scapula (correct)
Which of the following bones is part of the shoulder girdle?
Which of the following bones is part of the shoulder girdle?
- Radius
- Humerus
- Clavicle (correct)
- Ulna
What is the correct order of the three major regions of the upper limb, starting from the shoulder?
What is the correct order of the three major regions of the upper limb, starting from the shoulder?
- Arm, Forearm, Hand (correct)
- Forearm, Arm, Hand
- Shoulder, Arm, Hand
- Arm, Hand, Forearm
Which of the following features is located on the scapula?
Which of the following features is located on the scapula?
Which set of bones is located in the forearm?
Which set of bones is located in the forearm?
Which term describes a structure located closer to the midline of the body?
Which term describes a structure located closer to the midline of the body?
A surgeon makes an incision described as 'superficial'. What depth is the incision?
A surgeon makes an incision described as 'superficial'. What depth is the incision?
When comparing the radius to the humerus, which statement accurately describes their relative positions?
When comparing the radius to the humerus, which statement accurately describes their relative positions?
A patient complains of pain radiating down their arm towards their hand. Which term best describes the location of the pain relative to the shoulder?
A patient complains of pain radiating down their arm towards their hand. Which term best describes the location of the pain relative to the shoulder?
If a doctor is examining a structure on the back of a patient, which directional term would they most likely use?
If a doctor is examining a structure on the back of a patient, which directional term would they most likely use?
Which of the following features is located on the humerus?
Which of the following features is located on the humerus?
Which carpal bone is located most medially?
Which carpal bone is located most medially?
Which joint allows for the greatest range of motion in the upper limb?
Which joint allows for the greatest range of motion in the upper limb?
What type of synovial joint is the radiocarpal joint, and what movements does it facilitate?
What type of synovial joint is the radiocarpal joint, and what movements does it facilitate?
Which combination of bones articulates to form the elbow joint?
Which combination of bones articulates to form the elbow joint?
Flashcards
Superior
Superior
Towards the head.
Inferior
Inferior
Towards the feet.
Anterior (Ventral)
Anterior (Ventral)
Towards the front.
Medial
Medial
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral
Lateral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pectoral Girdle
Pectoral Girdle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arm bone
Arm bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Forearm bones
Forearm bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bones of Wrist & Hand
Bones of Wrist & Hand
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scapula
Scapula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humerus Head
Humerus Head
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interosseous Membrane
Interosseous Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glenohumeral Joint
Glenohumeral Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elbow Joint
Elbow Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiocarpal Joint
Radiocarpal Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Upper Limb Gross Anatomy is being taught as part of the UM1010 Musculoskeletal Block
Learning Outcomes
- Identify the bones of the upper limb and their prominent bony features
- Describe the structure of the joints of the upper limb
- Summarize the muscle compartments of the upper limb and their actions
- Outline the neurovascular distribution of the upper limb
Lecture Structure
- The bones and joints of the upper limb will be looked at
- The musculature of the upper limb will be considered
- The neurovascular supply to the upper limb will be outlined
Terminology Recap
- Superior: Towards the head
- Inferior: Towards the feet
- Anterior or Ventral: To the front
- Posterior or Dorsal: To the back
- Medial: Closer to the midline
- Lateral: Further away from the midline
- Proximal: Closer to the trunk
- Distal: Further away from the trunk
- Superficial: Closer to the surface of the body
- Deep: Closer to the center of the body
Gross Anatomy of the Upper Limb: Part 1, Bones and Joints
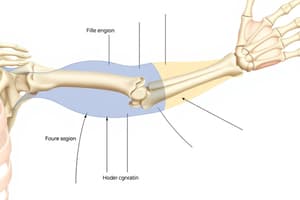
- The regions of the upper limb are based on the positions of its major joints and component bones
- The upper limb regions are the shoulder, arm, forearm, wrist, and hand
Bones of the Upper Limb
- Shoulder: Scapula, Clavicle, and the proximal end of the humerus
- Arm: Humerus
- Forearm: Radius and Ulna
- Wrist & Hand: Carpal bones, Metacarpals, and Phalanges
Scapula
- The Scapula has 2 surfaces, 3 borders, and 3 angles
- It includes the subscapular fossa, spine of the scapula, supraspinous fossa, infraspinous fossa, acromion, coracoid process, glenoid fossa, and suprascapular notch
Humerus
- The humerus features the head, anatomical neck, surgical neck, greater and lesser tubercles, intertubercular groove, radial groove, medial and lateral epicondyles, capitulum, trochlea, radial, coronoid & olecranon fossa
Radius & Ulna
- Radius and Ulna bones are joined by the interosseous membrane
- Radius features the radial head, neck of the radium, radial tuberosity, and styloid process of radius
- Ulna features the olecranon process, trochlear notch, and coronoid process, ulnar tuberosity, and styloid process
Bones of the Wrist and Hand
- Bones of the wrist and hand include the Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Hamate, Capitate, Trapezoid, Trapezium, Metacarpals and Phalanges
Joints of the Upper Limb
- Shoulder & Arm: Scapulothoracic Joint, Sternoclavicular Joint, Acromioclavicular Joint, Glenohumeral Joint
- Elbow & Forearm: Humeroulnar Joint, Humeroradial Joint, Proximal and Distal Radioulnar Joint
- Wrist & Hand: Radiocarpal Joint, Carpometacarpal Joints, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Interphalangeal Joints
Glenohumeral Joint
- This is a ball and sock type of synovial joint
- It is the articulation between the head of humerus and glenoid fossa
- It is the most mobile large joint of the body
- Movements include flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal and external rotation, and circumduction
- It is strengthened by ligaments and muscles
Elbow Joint
- This is a hinge type of synovial joint and is freely moveable in a single axis
- Articulation exits between the trochlea and capitulum of the humerus with the proximal heads of ulna and radius
- Movements include flexion and extension
- It is strengthened by ligaments and muscles surrounding it
Radiocarpal Joint
- A condyloid type of synovial joint
- Articulation between the distal raduis and the carpal bones. Bones include the scaphoid, luntate and triquetrum.
- It's moveable in two axis.
- Movements include flexion, extension, abduction and adduction
- Strengthed by ligaments and muscles surrounding it.
Gross Anatomy of the Upper Limb: Part 2, The Musculature of the Upper Limb
- Muscles to be Discussed
Year 1 Muscles
- Deltoid: A thick triangular muscle, it is responsible for a variety of arm movements at the shoulder joint
- Muscles of the Anterior and Posterior Arm
- Muscles of the Anterior and Posterior Forearm
Year 2 Muscles
- Shoulder Muscles
- Muscles of Scapulothoracic Movement
- Hand Muscles
Deltoid
- The deltoid muscle abducts the shoulder
- meaning it will have to run over the top of the glenohumeral joint – it also helps with flexion and extension of the shoulder.
- Attaches onto the spine and acromion of the scapula and the clavicle medially and ends at the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus inferolaterally
Anterior Arm Muscles
- All are innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve
- Includes the Coracobrachialis, Biceps brachii, and Brachialis muscles
Coracobrachialis
- Attaches from the coracoid process of scapula to the humeral shaft
- Functions to flex the shoulder
Brachialis
- Attaches from the distal humerus to the coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna
- Functions to flex at the elbow
Biceps Brachii
- Has two heads
- The short head attaches from the coracoid process of the scapula whereas the long head attaches from the supraglenoid tubercle above the glenoid fossa
- Both heads converge and attach onto the radial tuberosit
- It functions to flex the shoulder and flex the elbow
Posterior Arm
- The posterior arm is innervated by the radial nerve
Triceps Brachii Muscle
- Has 3 heads
- The long head attaches from the infraglenoid tubercle below the shoulder joint
- The medial head attaches from the posterior humerus below the radial groove
- The lateral head attaches from the posterior humerus above the radial groove
- All the heads converge and attach onto the olecranon of the ulna
- The triceps brachii mainly functions to extend the elbow in active extension; the long head can also extend the shoulder
Anterior Forearm
- Can be broken down into Superficial, Intermediate, and Deep layers
Anterior Forearm: Superficial Layer
- Includes the Pronator teres, Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus and Flexor carpi ulnaris muscles
Anterior Forearm: Intermediate Layer
- Consists of the Flexor digitorium superficialis muscle
Anterior Forearm: Deep Layer
- Includes the Flexor digitorum profundus, Flexor pollicis longus, and Pronator quadratus
Anterior Forearm Muscles Function
- Pronator teres: pronates the forearm
- Flexor carpi radialis: abduction of wrist
- Flexor carpi ulnaris: adduction of wrist
- Flexors carpi radialis and ulnaris muscles: together flex the wrist
- Palmaris longus: weak flexion
- Flexor digitorum superficialis: flexion of the wrist but mainly flexion at the proximal interphalangeal joint
- -Flexor digitorum profundus*: flexion of the wrist, but mainly distal interphalangeal joint
- Flexor pollicis longus: flexion of the thumb
- Pronator quadratus: pronates the forearm
- All the muscles are innervated by the median nerve, except for the flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnar half of flexor digitorum profundus, which are innervated by the ulnar nerve
Posterior Forearm
- Can be broken down into Superficial and Deep layers
Posterior Forearm: Superficial Layer
- Includes the Brachioradialis, Extensor carpi, radialis longus, Extensor carpi radialis brevis, Extensor digitorum, Extensor digiti minimi, Extensor carpi ulnaris, and Anconeus
Posterior Forearm: Deep Layer
- Includes the Supinator, Abductor pollicis longus, Extensor pollicis brevis, Extensor pollicis longus, and Extensor indicis
- The posterior arm, is innervated by the radial nerve
Posterior Forearm: Superficial Layer Muscle Function
- Brachioradialis: elbow flexion; stabilizes the elbow
- Extensor carpi radialis longus: wrist abduction
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis: wrist abduction
- Extensor carpi ulnaris: wrist adduction
- Extensors carpi radialis and ulnaris muscles: work together for wrist extension
- Extensor digitorum: extension of digits 2-5
- Extensor digiti minimi: extension of digit 5 (pinky)
Posterior Forearm: Deep Layer Muscle Function
- Supinator: supination
- Abductor pollicis longus: abduction of the thumb and wrist
- Extensor pollicis brevis: extension of the thumb
- Extensor pollicis longus: extension of thumb
- Extensor indicis: extension of digit 2 (index)
Anatomical Spaces in the Upper Limb
- Axilla, Cubital Fossa and Carpal Tunnel.
Gross Anatomy of the Upper Limb: Part III, Neurovascular Supply of the Upper Limb
- Discussing network of nerves from the anterior rami of cervical spinal nerve C5 to C8, and T1
Brachial Plexus Structure
- Roots > Trunks > Divisions > Cords > Terminal Branches
- All these components innervate the upper limb.
Motor Innervation in the Upper Limb
- Axillary: deltoid muscle and teres minor
- Radial: all muscles found in posterior compartment
- Musculocutaneous: all muscles found in anterior compartment of the arm
- Median: muscles in anterior forearm
- Ulnar: two muscles in forearm; intrinsic muscles of the hand
Sensory Innervation in the Upper Limb
- Axillary: skin of superolateral arm
- Radial: posterior and inferoltateral arm
- Musculocutaneous: lateral aspect of forearm
- Median: palmar skin
- Ulnar: skin of hand
Blood Supply of Upper Limb
- Subclavian artery
- Axillary artery
- Brachial Artery
- Radial and ulnar arteries
- Deep and superficial palmar arch
Venous Drainage of the Upper Limb
- Deep Venous -Deep venous arch of palm -Ulnar and radial vein -Brachial Vein -Axillar Vein -Subclavian Vein
- Superficial Venous -Superficial Venous arch of palm -Cephalic vein of forearm -Basilic vein of forearm.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge of anatomical terms and the skeletal structure of the upper limb. This quiz covers the posterior scapula, shoulder girdle bones, upper limb regions, and directional terms. It also includes questions about the humerus and carpal bones.