Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is flexion in anatomical movement?
What is flexion in anatomical movement?
- Bending a joint so the angle between the two bones decreases. (correct)
- Rotating a limb away from the midline of the body.
- Moving a limb towards the midline of the body.
- Straightening a joint so the angle between bones increases.
Which of the following describes adduction?
Which of the following describes adduction?
- Rotating the shoulder or hip outward.
- Lifting the arm or leg sideways.
- Moving a limb toward the midline of the body. (correct)
- Moving a limb away from the midline of the body.
What is the primary action involved in circumduction?
What is the primary action involved in circumduction?
- Bending a joint to decrease the angle.
- Rotating a limb inward.
- A circular movement encompassing flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. (correct)
- Moving a body part downwards.
Which movement is defined as dorsiflexion?
Which movement is defined as dorsiflexion?
In anatomical terms, what does elevation refer to?
In anatomical terms, what does elevation refer to?
Which of these describes the stride position?
Which of these describes the stride position?
What does internal rotation of a limb involve?
What does internal rotation of a limb involve?
What is the function of the standing position in human posture?
What is the function of the standing position in human posture?
What is the primary symptom of a contusion?
What is the primary symptom of a contusion?
Which activity is most likely associated with lower-extremity sprains and strains?
Which activity is most likely associated with lower-extremity sprains and strains?
What should be done as first aid for a fracture?
What should be done as first aid for a fracture?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typically associated with concussions?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typically associated with concussions?
What type of injury are tendonitis and stress fractures examples of?
What type of injury are tendonitis and stress fractures examples of?
Which item is NOT considered a basic supply in a sports first aid kit?
Which item is NOT considered a basic supply in a sports first aid kit?
What is the role of elastic bandages in a sports first aid kit?
What is the role of elastic bandages in a sports first aid kit?
Which of the following items is essential for performing CPR?
Which of the following items is essential for performing CPR?
What position involves lying on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the ground?
What position involves lying on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the ground?
Which principle emphasizes the need for exercise to be customized for each individual's unique characteristics?
Which principle emphasizes the need for exercise to be customized for each individual's unique characteristics?
What does the acronym F.I.T.T. stand for in the context of progressive overload?
What does the acronym F.I.T.T. stand for in the context of progressive overload?
Which principle states that exercise should be done at regular intervals to adapt efficiently?
Which principle states that exercise should be done at regular intervals to adapt efficiently?
In the context of progressive overload, what does 'overload' refer to?
In the context of progressive overload, what does 'overload' refer to?
What adaptation occurs as a result of performing exercise based on specific goals and needs?
What adaptation occurs as a result of performing exercise based on specific goals and needs?
How often is it recommended to exercise to achieve the benefits of the principle of regularity?
How often is it recommended to exercise to achieve the benefits of the principle of regularity?
Which of the following best describes the principle of progression?
Which of the following best describes the principle of progression?
What does the principle of reversibility imply about training effects?
What does the principle of reversibility imply about training effects?
Which of the following practices aligns with the principle of variation & adaptation?
Which of the following practices aligns with the principle of variation & adaptation?
Why is rest and recovery crucial in a training regimen?
Why is rest and recovery crucial in a training regimen?
What is a key feature of the principle of periodization?
What is a key feature of the principle of periodization?
Which of the following statements about the FITT formula is correct?
Which of the following statements about the FITT formula is correct?
What does exercising consistently help to maintain?
What does exercising consistently help to maintain?
What consequence can arise from inadequate rest and recovery?
What consequence can arise from inadequate rest and recovery?
How can one prevent reaching a training plateau according to the content?
How can one prevent reaching a training plateau according to the content?
What is the primary purpose of exercise regression?
What is the primary purpose of exercise regression?
Which of the following is a key reason to implement exercise regression?
Which of the following is a key reason to implement exercise regression?
What method of regression involves using tools to assist in performing an exercise?
What method of regression involves using tools to assist in performing an exercise?
Which regression method focuses on performing exercises with less than full range of movement?
Which regression method focuses on performing exercises with less than full range of movement?
When is exercise regression particularly beneficial?
When is exercise regression particularly beneficial?
What does modifying a movement pattern in exercise regression typically involve?
What does modifying a movement pattern in exercise regression typically involve?
Why is gradually building strength and skill important in exercise?
Why is gradually building strength and skill important in exercise?
Slowing down the tempo of an exercise helps in which of the following aspects?
Slowing down the tempo of an exercise helps in which of the following aspects?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
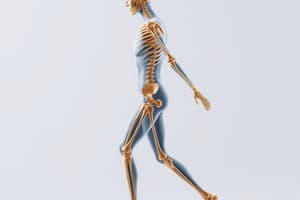
Anatomical Movement
- Flexion: Decreases the angle between two bones. Example: Bending the elbow or knee.
- Extension: Increases the angle between two bones. Example: Straightening the elbow or knee.
- Abduction: Moving a limb away from the body's midline. Example: Lifting the arm or leg sideways.
- Adduction: Moving a limb towards the body's midline. Example: Bringing the arm or leg back to the body's side.
- Internal (Medial) Rotation: Rotating a limb towards the body's midline. Example: Rotating the shoulder or hip inward.
- External (Lateral) Rotation: Rotating a limb away from the body's midline. Example: Rotating the shoulder or hip outward.
- Circumduction: Circular movement involving flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. Example: Moving the arm or leg in a circular motion.
- Pronation: Rotating the forearm so the palm faces downwards.
- Supination: Rotating the forearm so the palm faces upwards.
- Dorsiflexion: Lifting the foot upwards towards the shin.
- Plantarflexion: Pointing the toes downwards, away from the shin.
- Inversion: Turning the sole of the foot inward, towards the midline.
- Eversion: Turning the sole of the foot outward, away from the midline.
- Elevation: Moving a body part upwards. Example: Shrugging the shoulders.
- Depression: Moving a body part downwards. Example: Lowering the shoulders.
- Protraction: Moving a body part forward. Example: Moving the shoulder blades forward.
- Retraction: Moving body part backward. Example: Pulling the shoulder blades back.
Standing Positions
- Standing Position: Upright posture, supported by feet. Feet together or parallel, arms hang naturally, body balanced over feet, core engaged.
- Stride Position: Feet positioned about one foot apart. One foot forward, one foot back, body upright, weight evenly distributed, arms at sides or on hips.
- Long Sitting Position: Body fully extended, toes pointed up, arms relaxed, core engaged to support lower back.
- Hook Lying Position: Lying on back, knees bent, feet flat on ground. Feet close to buttocks, knees bent, arms overhead or at sides, core muscles engaged.
Principles of Training
- Principle of Progressive Overload: To improve fitness and strength, increase load/demand on the body. This occurs by gradually increasing the stress: frequency, intensity, duration, or type of exercise.
- Principle of Individualization: Exercise programs should be tailored to individual characteristics (physical abilities, potential, psychology, body type, age, gender, strength, athletic background, daily stress, health, and nutrition).
- Principle of Regularity: Consistent exercise (3–5 times per week) allows the body to adapt efficiently.
- Principle of Specificity: Exercise should target specific goals and needs. Exercises should resemble the desired activity.
- Principle of Reversibility: "Use it or lose it." Training effects are reversed with breaks in exercise.
- Principle of Variation & Adaptation: To avoid plateaus, exercise routine needs variation. This also helps increase motivation, compliance, and reduces injury risks.
- Principle of Rest & Recovery: Rest allows the body to repair and remove wastes. Optimal rest is 24–48 hours post-training. Alternating strenuous and easier days is beneficial.
- Principle of Periodization: Long-term training plan with variations over time. Focuses on achieving peak performance at specific times.
Exercise Regression
- Why It's Important: Prevents injury, builds a foundation, accommodates individual differences, and creates a gradual learning process.
- Methods of Regression:
- Reducing Load: Lowering weight or using body weight.
- Assistance: Using resistance bands, machines, or external support.
- Limiting Range of Motion: Performing partial repetitions.
- Modifying the Movement Pattern: Simplifying complex movements.
- Slower Tempo: Performing movements slowly.
Common PE Class Injuries
- Lower-Extremity Sprains and Strains: 23% of PE-related injuries. Common in running, basketball, and soccer. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving.
- Upper-Extremity Injuries: Sprains, strains, and fractures. 14% of injuries in PE classes. Occur during activities like gymnastics or volleyball. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Fractures: Common in arms, legs, and wrists. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and visible deformity.
- Concussions: Result from falls or collisions. Symptoms include headache, confusion, dizziness, and nausea.
- Overuse Injuries: Tendonitis or stress fractures due to repetitive activities. Symptoms include gradual onset of pain, swelling, and tenderness.
Essential Sports First Aid Kit Items
- Basic Supplies: Emergency cards, CPR mask, surgical gloves, safety pins, disposable instant cold packs, elastic bandages.
- Wound Care Items: Sterile gauze pads, adhesive bandages, antiseptic wipes, antibiotic ointment, roll gauze, alcohol wipes.
- Instruments: Bandage scissors, tweezers, tape and tape under wrap.
- Miscellaneous: Sunscreen, hand sanitizer, petroleum jelly.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.