Podcast
Questions and Answers
Associe cada estrutura anatômica do rim com a sua descrição correta:
Associe cada estrutura anatômica do rim com a sua descrição correta:
Cápsula renal = Camada protetora que envolve os rins Córtex renal = Camada externa do rim que contém os néfrons Medula renal = Região do rim composta por pirâmides renais Papila renal = Ponto central de cada pirâmide renal
Relacione os tipos de artérias presentes no suprimento sanguíneo renal com as suas funções:
Relacione os tipos de artérias presentes no suprimento sanguíneo renal com as suas funções:
Artérias renais = Principais artérias que alimentam os rins Artérias interlobares = Ramos das artérias renais que se conectam às arcuadas Artérias arqueadas = Responsáveis por fornecer sangue para as artérias interlobulares Artérias interlobulares = Artérias que suprem sangue aos néfrons
Combine as seguintes estruturas do rim com as suas localizações anatômicas:
Combine as seguintes estruturas do rim com as suas localizações anatômicas:
Néfrons = Localizados no córtex renal Pelvis renal = Cavidade em forma de funil que coleta a urina Pirâmides renais = Parte da medula renal Arcuate arteries = Divisões das artérias renais
Emparelhe as seguintes partes do rim com as suas funções fisiológicas:
Emparelhe as seguintes partes do rim com as suas funções fisiológicas:
Relacione os seguintes componentes do néfron com suas descrições correspondentes:
Relacione os seguintes componentes do néfron com suas descrições correspondentes:
Correlacione os tipos de néfrons com suas localizações específicas no rim:
Correlacione os tipos de néfrons com suas localizações específicas no rim:
Combine as estruturas relacionadas ao suprimento sanguíneo renal com suas funções:
Combine as estruturas relacionadas ao suprimento sanguíneo renal com suas funções:
Relacione as zonas da medula renal com suas funções específicas:
Relacione as zonas da medula renal com suas funções específicas:
Combine os seguintes termos relacionados ao córtex renal com suas características correspondentes:
Combine os seguintes termos relacionados ao córtex renal com suas características correspondentes:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Renal Anatomy: Exploring the Structure and Function of the Kidney
The kidney, a vital organ in the human body, plays a central role in maintaining homeostasis by filtering waste products, regulating electrolyte balance, and producing urine. To comprehend its functions, it's essential to understand the kidney's anatomical structure, which we'll explore in detail below.
Kidney Structure
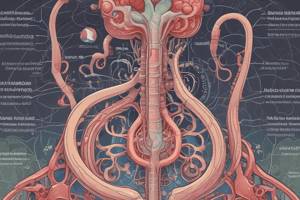
Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist, positioned on either side of the spine in the upper abdomen, just below the rib cage. They're enclosed in a protective capsule called the renal capsule. The outer layer of the kidney is called the renal cortex, which contains the nephrons, tiny functional units of the kidney. The renal cortex is followed by the renal medulla, composed of cone-shaped structures called renal pyramids. The central point of each pyramid is called the papilla, which projects into the renal pelvis, a funnel-shaped cavity collecting urine.
Renal Blood Supply
The kidneys receive a generous blood supply, ensuring their ability to perform their essential functions. Two major arteries feed the kidneys: the renal arteries, which branch off from the abdominal aorta. The renal arteries further divide into smaller branches called interlobar arteries. These branches then form the arcuate arteries, which supply blood to the interlobular arteries. These arteries branch off into the afferent arterioles, which lead to the glomerulus, the beginning of the nephron.
Renal Pelvis
The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped cavity located at the center of the kidney. It receives urine from the renal calyces and collects it before passing it through the ureter, a muscular tube that carries urine to the bladder. The renal pelvis's shape and location provide a large surface area for the collection of urine, preventing backflow and ensuring efficient urine drainage from the kidney.
Nephrons
The functional units of the kidney, nephrons, are responsible for filtering waste products, regulating electrolyte balance, and producing urine. There are two types of nephrons: cortical nephrons, primarily found in the outer cortex, and juxtamedbranous nephrons, located deeper in the cortex. Both types of nephrons share a similar structure, composed of a glomerulus (a network of blood capillaries surrounded by a Bowman's capsule), a tubule (consisting of the proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle, and the distal convoluted tubule), and the collecting duct. The nephron's structure enables it to filter waste, reabsorb essential nutrients, and regulate the concentration and composition of urine.
Renal Cortex and Medulla
The renal cortex and medulla are two distinct layers within the kidney. The renal cortex is the outer layer and contains the nephrons, while the renal medulla lies beneath the cortex and contains the renal pyramids and loops of Henle. The renal medulla is further divided into several zones of varying oxygen concentrations and acid-base balance. These zones enable the kidney to actively reabsorb and concentrate urine.
Understanding the structure and function of these components is essential to comprehend the complex processes and functions of the kidney. By studying renal anatomy, we can appreciate how the kidney plays a central role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.