Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following amino acids is a precursor of cysteine?
Which of the following amino acids is a precursor of cysteine?
- Tyrosine (correct)
- Phenylalanine
- Arginine
- Histidine
Which metabolic defect is characterized by an inability to fully metabolize phenylalanine?
Which metabolic defect is characterized by an inability to fully metabolize phenylalanine?
- Alkaptonuria
- Albinism
- Homocystinuria
- Phenylketonuria (correct)
Which of the following amino acids is primarily classified as glucogenic?
Which of the following amino acids is primarily classified as glucogenic?
- Isoleucine
- Histidine (correct)
- Lysine
- Leucine
What is a primary characteristic of ketogenic amino acids?
What is a primary characteristic of ketogenic amino acids?
Which of the following is NOT associated with defects in amino acid metabolism?
Which of the following is NOT associated with defects in amino acid metabolism?
The removal of the alpha-amino group in amino acid metabolism is primarily involved in which process?
The removal of the alpha-amino group in amino acid metabolism is primarily involved in which process?
Which metabolic condition is most directly linked to a deficiency in the enzyme responsible for converting methionine to homocysteine?
Which metabolic condition is most directly linked to a deficiency in the enzyme responsible for converting methionine to homocysteine?
Phenylalanine is primarily involved in the synthesis of which precursor amino acid?
Phenylalanine is primarily involved in the synthesis of which precursor amino acid?
In patients with phenylketonuria, why is the dietary restriction of phenylalanine crucial?
In patients with phenylketonuria, why is the dietary restriction of phenylalanine crucial?
What is the significance of tyrosine in the diet of individuals with phenylketonuria?
What is the significance of tyrosine in the diet of individuals with phenylketonuria?
Which of the following statements concerning amino acid catabolism is correct?
Which of the following statements concerning amino acid catabolism is correct?
What dietary intervention is recommended for children diagnosed with classic phenylketonuria?
What dietary intervention is recommended for children diagnosed with classic phenylketonuria?
Which statement accurately describes a metabolic defect related to phenylketonuria?
Which statement accurately describes a metabolic defect related to phenylketonuria?
Which amino acid category is primarily associated with the production of ketone bodies?
Which amino acid category is primarily associated with the production of ketone bodies?
What is the primary result of defects in the enzymes responsible for amino acid metabolism?
What is the primary result of defects in the enzymes responsible for amino acid metabolism?
Which of the following substances is directly involved in the metabolism of oxaloacetate?
Which of the following substances is directly involved in the metabolism of oxaloacetate?
Which metabolic pathway do glucogenic amino acids primarily support?
Which metabolic pathway do glucogenic amino acids primarily support?
What is one characteristic of metabolic defects related to amino metabolism?
What is one characteristic of metabolic defects related to amino metabolism?
Which amino acid is typically categorized as both ketogenic and glucogenic?
Which amino acid is typically categorized as both ketogenic and glucogenic?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of succinyl CoA in metabolic pathways?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of succinyl CoA in metabolic pathways?
What defines a ketogenic amino acid in contrast to a glucogenic amino acid?
What defines a ketogenic amino acid in contrast to a glucogenic amino acid?
Metabolic defects in which of the following amino acid pathways are known to cause urea cycle disorders?
Metabolic defects in which of the following amino acid pathways are known to cause urea cycle disorders?
Which amino acid is most commonly considered to have solely a glucogenic function?
Which amino acid is most commonly considered to have solely a glucogenic function?
What is the primary consequence of amino acid degradation?
What is the primary consequence of amino acid degradation?
Which of the following amino acids are classified as essential?
Which of the following amino acids are classified as essential?
Which intermediate product is NOT formed from amino acid degradation?
Which intermediate product is NOT formed from amino acid degradation?
What is the primary function of glucogenic amino acids?
What is the primary function of glucogenic amino acids?
Which of the following is true regarding metabolic defects in amino acid metabolism?
Which of the following is true regarding metabolic defects in amino acid metabolism?
Which of the following amino acids is primarily ketogenic?
Which of the following amino acids is primarily ketogenic?
What process occurs after the removal of the a-amino group in amino acid degradation?
What process occurs after the removal of the a-amino group in amino acid degradation?
Which product during amino acid degradation contributes to energy production through the TCA cycle?
Which product during amino acid degradation contributes to energy production through the TCA cycle?
Which of the following statements correctly reflects the nature of essential amino acids?
Which of the following statements correctly reflects the nature of essential amino acids?
Which metabolic pathway do ketogenic amino acids primarily enter?
Which metabolic pathway do ketogenic amino acids primarily enter?
What is likely a consequence of a deficiency in dihydropteridine reductase?
What is likely a consequence of a deficiency in dihydropteridine reductase?
Which vitamin is NOT associated with the enzymatic reactions involving aromatic amino acid hydroxylases?
Which vitamin is NOT associated with the enzymatic reactions involving aromatic amino acid hydroxylases?
What compound is used in the screening of newborns for metabolic disorders?
What compound is used in the screening of newborns for metabolic disorders?
Which of the following is true regarding the metabolic defect in phenylketonuria (PKU)?
Which of the following is true regarding the metabolic defect in phenylketonuria (PKU)?
What type of amino acids can lead to the production of ketone bodies upon degradation?
What type of amino acids can lead to the production of ketone bodies upon degradation?
Which amino acid is a direct precursor to serotonin?
Which amino acid is a direct precursor to serotonin?
What is the primary compound produced from the hydroxylation of phenylalanine?
What is the primary compound produced from the hydroxylation of phenylalanine?
Which of the following statements about amino acid metabolism is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about amino acid metabolism is incorrect?
Which statement is true about the effects of dihydropteridine reductase deficiency?
Which statement is true about the effects of dihydropteridine reductase deficiency?
What is a potential clinical outcome when treating hyperphenylalaninemia?
What is a potential clinical outcome when treating hyperphenylalaninemia?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by a defect in the metabolism of tyrosine?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by a defect in the metabolism of tyrosine?
Homocystinuria is primarily linked to a deficiency in the metabolism of which amino acid?
Homocystinuria is primarily linked to a deficiency in the metabolism of which amino acid?
Which condition is characterized by an accumulation of homogentisic acid due to a defect in the metabolism of phenylalanine?
Which condition is characterized by an accumulation of homogentisic acid due to a defect in the metabolism of phenylalanine?
Which amino acid serves as a precursor to histamine?
Which amino acid serves as a precursor to histamine?
What is the primary metabolic defect associated with methylmalonic acidemia?
What is the primary metabolic defect associated with methylmalonic acidemia?
What is the significance of intermediates produced during amino acid catabolism?
What is the significance of intermediates produced during amino acid catabolism?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between amino acid catabolism and the TCA cycle?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between amino acid catabolism and the TCA cycle?
Which biochemical process follows the removal of the alpha-amino group in amino acid degradation?
Which biochemical process follows the removal of the alpha-amino group in amino acid degradation?
Which of the following statements about ketogenic amino acids is correct?
Which of the following statements about ketogenic amino acids is correct?
What is a likely consequence of defects in metabolic pathways of amino acid catabolism?
What is a likely consequence of defects in metabolic pathways of amino acid catabolism?
Which compound is most critical in the catabolism of both glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids?
Which compound is most critical in the catabolism of both glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids?
Which metabolic pathway can be directly affected by dietary restrictions caused by metabolic disorders?
Which metabolic pathway can be directly affected by dietary restrictions caused by metabolic disorders?
What is the primary reason for screening newborns for the possibility of phenylketonuria?
What is the primary reason for screening newborns for the possibility of phenylketonuria?
Why is prenatal diagnosis of classic PKU complicated?
Why is prenatal diagnosis of classic PKU complicated?
What dietary intervention is crucial for managing phenylketonuria?
What dietary intervention is crucial for managing phenylketonuria?
How is blood phenylalanine level managed in patients with phenylketonuria?
How is blood phenylalanine level managed in patients with phenylketonuria?
What developmental issues can arise from high blood phenylalanine levels in a mother during pregnancy?
What developmental issues can arise from high blood phenylalanine levels in a mother during pregnancy?
What is a metabolic characteristic of classic phenylketonuria in newborns?
What is a metabolic characteristic of classic phenylketonuria in newborns?
Which of the following symptoms is characteristic of Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)?
Which of the following symptoms is characteristic of Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)?
What consequence arises from excessive dietary phenylalanine in untreated individuals with PKU?
What consequence arises from excessive dietary phenylalanine in untreated individuals with PKU?
Which factor is key to the timing of newborn screening for PKU?
Which factor is key to the timing of newborn screening for PKU?
In the context of MSUD, what is the consequence of delayed treatment?
In the context of MSUD, what is the consequence of delayed treatment?
What is the inheritance pattern of Maple Syrup Urine Disease?
What is the inheritance pattern of Maple Syrup Urine Disease?
What is one of the primary challenges in providing treatment for individuals with PKU?
What is one of the primary challenges in providing treatment for individuals with PKU?
Which of the following statements correctly reflects the nature of phenylketonuria metabolism?
Which of the following statements correctly reflects the nature of phenylketonuria metabolism?
Which enzyme complex is deficient in individuals with classic MSUD?
Which enzyme complex is deficient in individuals with classic MSUD?
Among the following, what is a common clinical presentation in an infant with MSUD?
Among the following, what is a common clinical presentation in an infant with MSUD?
What dietary intervention is crucial for mothers with high blood phenylalanine levels prior to conception?
What dietary intervention is crucial for mothers with high blood phenylalanine levels prior to conception?
What is the major toxic effect of elevated levels of BCKD substrates in MSUD?
What is the major toxic effect of elevated levels of BCKD substrates in MSUD?
What is a primary feature of the classic neonatal-onset form of MSUD?
What is a primary feature of the classic neonatal-onset form of MSUD?
Which of the following amino acids accumulates significantly in the blood of MSUD patients?
Which of the following amino acids accumulates significantly in the blood of MSUD patients?
What is one of the key symptoms of alkaptonuria?
What is one of the key symptoms of alkaptonuria?
Which type of dietary modification is effective in managing levels of homogentisic acid?
Which type of dietary modification is effective in managing levels of homogentisic acid?
What does the term 'ochronosis' refer to in the context of alkaptonuria?
What does the term 'ochronosis' refer to in the context of alkaptonuria?
Why are infants typically asymptomatic in alkaptonuria?
Why are infants typically asymptomatic in alkaptonuria?
What distinguishes glucogenic amino acids from ketogenic amino acids?
What distinguishes glucogenic amino acids from ketogenic amino acids?
What is the primary characteristic of the urine in patients with alkaptonuria after standing?
What is the primary characteristic of the urine in patients with alkaptonuria after standing?
What form of arthritis is commonly associated with alkaptonuria?
What form of arthritis is commonly associated with alkaptonuria?
Which amino acids are involved in the metabolic pathway of tyrosine?
Which amino acids are involved in the metabolic pathway of tyrosine?
What is a common clinical finding in elderly patients with alkaptonuria?
What is a common clinical finding in elderly patients with alkaptonuria?
Match the following amino acids with their associated metabolic processes:
Match the following amino acids with their associated metabolic processes:
Match the following amino acids to their products in metabolism:
Match the following amino acids to their products in metabolism:
Match the following amino acids to their role in the urea cycle:
Match the following amino acids to their role in the urea cycle:
Match the amino acids with their pathways leading to a-ketoglutarate:
Match the amino acids with their pathways leading to a-ketoglutarate:
Match the following amino acids with their clinical significance:
Match the following amino acids with their clinical significance:
Match the following components of phenylketonuria (PKU) with their descriptions:
Match the following components of phenylketonuria (PKU) with their descriptions:
Match the following dietary components with their relevance in PKU management:
Match the following dietary components with their relevance in PKU management:
Match the following statements regarding PKU with their correct implications:
Match the following statements regarding PKU with their correct implications:
Match the following types of PKU with their characteristics:
Match the following types of PKU with their characteristics:
Match the following consequences of untreated PKU with their outcomes:
Match the following consequences of untreated PKU with their outcomes:
Flashcards
Amino Acid Metabolism
Amino Acid Metabolism
The process of breaking down amino acids for energy or to synthesize other molecules.
Clinically Important Amino Acids
Clinically Important Amino Acids
Amino acids whose metabolic disorders can cause illnesses.
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine
An amino acid that's a precursor to tyrosine and involved in methyl group formation.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tyrosine
Tyrosine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Removal of amino group
Removal of amino group
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino acid catabolism
Amino acid catabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Metabolism Defects
Amino Acid Metabolism Defects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ketogenic Pathways
Ketogenic Pathways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucogenic Pathways
Glucogenic Pathways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metabolic Defects
Metabolic Defects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Breakdown
Amino Acid Breakdown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperphenylalaninemia
Hyperphenylalaninemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Catecholamines
Catecholamines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino acid degradation
Amino acid degradation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon skeletons
Carbon skeletons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucogenic amino acids
Glucogenic amino acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ketogenic amino acids
Ketogenic amino acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Essential amino acids
Essential amino acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonessential amino acids
Nonessential amino acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metabolic pathways
Metabolic pathways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate products
Intermediate products
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Essential amino acid
Essential amino acid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tyrosine (in PKU)
Tyrosine (in PKU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary treatment (PKU)
Dietary treatment (PKU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Early PKU treatment
Early PKU treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylalanine restriction
Phenylalanine restriction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alanine (metabolic)
Alanine (metabolic)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ketogenic amino acid
Ketogenic amino acid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Screening Time
PKU Screening Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Diagnosis Confirmation
PKU Diagnosis Confirmation
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Cause (Prenatal)
PKU Cause (Prenatal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Treatment Principle
PKU Treatment Principle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylalanine and Essential Amino Acids
Phenylalanine and Essential Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
High Maternal Phenylalanine
High Maternal Phenylalanine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
BCKD Deficiency
BCKD Deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
MSUD Symptoms
MSUD Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
MSUD Treatment Importance
MSUD Treatment Importance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homogentisic Aciduria
Homogentisic Aciduria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arthritis (in Alkaptonuria)
Arthritis (in Alkaptonuria)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ochronosis
Ochronosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucogenic Amino Acids
Glucogenic Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ketogenic Amino Acids
Ketogenic Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Treatment (Alkaptonuria)
Dietary Treatment (Alkaptonuria)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Metabolism
Amino Acid Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinically Important Amino Acids
Clinically Important Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Catabolism
Amino Acid Catabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Removal of Amino Group
Removal of Amino Group
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asparagine's role in cancer cells
Asparagine's role in cancer cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asparaginase's function
Asparaginase's function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glutamine breakdown
Glutamine breakdown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glutamate conversion
Glutamate conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proline breakdown pathway
Proline breakdown pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arginine breakdown
Arginine breakdown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ornithine's conversion
Ornithine's conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Screening Time
PKU Screening Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Diagnosis Confirmation
PKU Diagnosis Confirmation
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Cause (Prenatal)
PKU Cause (Prenatal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
PKU Treatment Principle
PKU Treatment Principle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenylalanine and Essential Amino Acids
Phenylalanine and Essential Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Phenylalanine Levels
Normal Phenylalanine Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Feeding and Screening
Protein Feeding and Screening
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
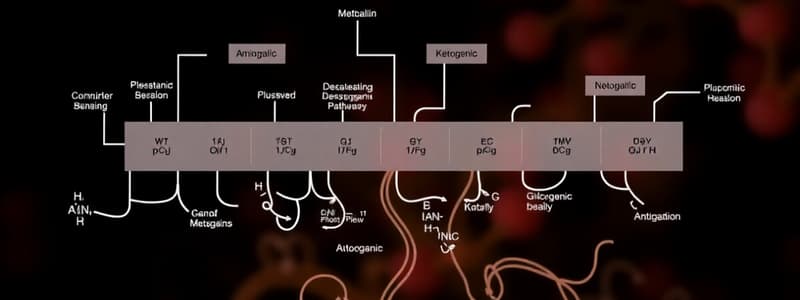
Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
- Amino acid degradation removes the α-amino group, catabolizes the resulting α-keto acids (carbon skeletons)
- Pathways converge to form seven intermediate products (oxaloacetate, pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, fumarate, succinyl CoA, acetyl CoA, acetoacetate)
- These enter intermediate metabolism, producing glucose, ketone bodies, lipids, or energy through TCA cycle oxidation to CO2
- Nonessential amino acids can be synthesized from metabolic intermediates or from essential amino acids
- Essential amino acids must be obtained from the diet for protein synthesis
- Genetic defects in amino acid pathways can cause disease
Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids
- Amino acids are classified as glucogenic, ketogenic, or both based on their catabolism to seven intermediate products
- Glucogenic: Catabolism produces pyruvate or TCA cycle intermediates, able to produce glucose in the liver and kidney
- Ketogenic: Catabolism yields acetoacetate or precursors (acetyl CoA, acetoacetyl CoA), cannot produce glucose
- Leucine and lysine are exclusively ketogenic
- Amino acid catabolism pathways are organized based on the seven intermediate products they produce
Amino Acid Carbon Skeleton Catabolism
- Pathways of amino acid catabolism organized by the intermediate they produce (oxaloacetate, etc.)
- Asparagine: Hydrolyzed by asparaginase to ammonia and aspartate, then transaminated to oxaloacetate
- Glutamine: Hydrolyzed to glutamate and ammonia by glutaminase, converted to α-ketoglutarate via transamination or oxidative deamination
- Proline: Oxidized to glutamate, then transaminated or oxidatively deaminated to α-ketoglutarate
- Arginine: Hydrolyzed to ornithine, then subsequently converted to α-ketoglutarate with glutamate semialdehyde as an intermediate
- Histidine: Oxidatively deaminated to urocanic acid, then N-formiminoglutamate that donates its formimino group to THF
Amino acids that form Pyruvate
- Alanine loses its amino group via transamination to form pyruvate
- Serine can be converted to glycine, or pyruvate
- Glycine can be deaminated to glyoxylate, which is oxidized to oxalate or transaminated to glycine
- Cysteine: Desulfurization yields pyruvate
- Threonine is converted to pyruvate
Amino Acids that form Fumarate
- Phenylalanine produces tyrosine via hydroxylation
- Phenylalanine and tyrosine catabolism merges, producing fumarate and acetoacetate
- Inherited deficiencies in phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism lead to diseases like PKU, tyrosinemia, and albinism
Amino Acids that form Succinyl CoA (Methionine)
- Methionine forms S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a methyl group donor
- Methionine catabolism results in homocysteine (Hcy)
- Hcy can be remethylated to methionine or enter the transsulfuration pathway to form cysteine
Other Amino Acids that form Succinyl CoA
- Valine, isoleucine, and threonine catabolism produce succinyl CoA
- Valine and isoleucine are branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)
- Their catabolism generates propionyl CoA, converted to methylmalonyl CoA and then succinyl CoA
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
-
Single-gene disorders are a subset of inborn errors, caused by mutations
-
Mutations typically lead to abnormal proteins, often enzymes
-
Disorders result in intellectual disability or developmental issues due to metabolite accumulation
-
Phenylketonuria (PKU): Deficiency in phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
-
Elevated phenylalanine levels cause intellectual disability, developmental delay, and other complications
-
Treatment involves dietary restrictions, restricting phenylalanine and supplementing with tyrosine
-
Maple syrup urine disease: Deficiency in branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKD)
-
Accumulation of branched-chain amino acids and α-keto acids, leading to toxic effects
-
Treatment involves dietary restrictions for the amino acids to prevent neurologic complications
-
Albinism: Defect in tyrosine metabolism, resulting in reduced melanin
- Reduced melanin leads to reduced pigmentation in skin, hair, and eyes
- Increased risk of skin cancer
-
Homocystinuria: Defects in homocysteine metabolism
- High homocysteine levels and low cysteine levels
- Symptoms include lens dislocation, skeletal abnormalities, intellectual disability, and thrombosis risk
- Treatment involves methionine restriction and supplementation with B12 and folate
-
Alkaptonuria: Deficiency in homogentisic acid oxidase
- Accumulation of homogentisic acid causes dark urine and joint problems (arthritis)
- Deposition of black pigment ('ochronosis') in cartilage and connective tissue
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.