Podcast
Questions and Answers
The maximum size of an umbilical hernia is generally reached by _______ of age.
The maximum size of an umbilical hernia is generally reached by _______ of age.
1 month
Diastasis rectus abdominis is a separation _______ wide in the midline.
Diastasis rectus abdominis is a separation _______ wide in the midline.
1 to 4 cm
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can be a problem, especially if the infant is _______ frequently.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can be a problem, especially if the infant is _______ frequently.
vomiting
Peristaltic waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as _______ stenosis.
Peristaltic waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as _______ stenosis.
The abdomen of the young child protrudes slightly, giving a potbellied appearance when the child is standing, sitting, and _______.
The abdomen of the young child protrudes slightly, giving a potbellied appearance when the child is standing, sitting, and _______.
An umbilical hernia in a newborn is common and usually resolves by the age of _______ months.
An umbilical hernia in a newborn is common and usually resolves by the age of _______ months.
_______ waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as paralytic ileus.
_______ waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as paralytic ileus.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can lead to an _______ hernia.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can lead to an _______ hernia.
A potbellied appearance in a child can be caused by a _______ hernia.
A potbellied appearance in a child can be caused by a _______ hernia.
The maximum size of an umbilical hernia is generally reached by _______ of age.
The maximum size of an umbilical hernia is generally reached by _______ of age.
Inspect the umbilical cord of the newborn, counting the number of vessels.Two arteries and one ______ should be present.
Inspect the umbilical cord of the newborn, counting the number of vessels.Two arteries and one ______ should be present.
Any intestinal structure present in the umbilical cord or protruding into the umbilical area and visible through a thick transparent membrane suggests an ______.
Any intestinal structure present in the umbilical cord or protruding into the umbilical area and visible through a thick transparent membrane suggests an ______.
The umbilical stump area should be dry and odorless.Inspect it for discharge, redness, induration, and skin warmth.Once the stump has separated, typically by 2 weeks of age, serous or serosanguineous discharge may indicate a granuloma when no other signs of infection are present.Inspect all folds of skin in the umbilicus for a nodule of granulomatous tissue.If drainage persists after cord separation, consider the possibility of a patent ______ cyst or remnant.
The umbilical stump area should be dry and odorless.Inspect it for discharge, redness, induration, and skin warmth.Once the stump has separated, typically by 2 weeks of age, serous or serosanguineous discharge may indicate a granuloma when no other signs of infection are present.Inspect all folds of skin in the umbilicus for a nodule of granulomatous tissue.If drainage persists after cord separation, consider the possibility of a patent ______ cyst or remnant.
Note any protrusion through the umbilicus or rectus abdominis muscles when the infant strains.The umbilicus is usually inverted.A small ______ (i.e., the protrusion of omentum and intestine through the umbilical opening, forming a visible and palpable bulge) is a common finding in infants.
Note any protrusion through the umbilicus or rectus abdominis muscles when the infant strains.The umbilicus is usually inverted.A small ______ (i.e., the protrusion of omentum and intestine through the umbilical opening, forming a visible and palpable bulge) is a common finding in infants.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can be a problem, especially if the infant is ______ frequently.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can be a problem, especially if the infant is ______ frequently.
The alimentary tract runs from the mouth to the _______
The alimentary tract runs from the mouth to the _______
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can lead to an _______ hernia
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can lead to an _______ hernia
An umbilical hernia in a newborn is common and usually resolves by the age of _______ months
An umbilical hernia in a newborn is common and usually resolves by the age of _______ months
Diastasis rectus abdominis is a separation _______ wide in the midline
Diastasis rectus abdominis is a separation _______ wide in the midline
A potbellied appearance in a child can be caused by a _______ hernia
A potbellied appearance in a child can be caused by a _______ hernia
Diuretics, distention, deficiency of potassium may cause a paralytic ileus known as intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Other common causes include narcotics and hypothyroidism. Ask the patient to take a deep breath and hold it. The contour should remain smooth and symmetric. This maneuver lowers the diaphragm and compresses the organs of the abdominal cavity, which may cause previously unseen bulges or masses to appear. Next, ask the patient to raise his or her head from the table. This contracts the rectus abdominis muscles, which produces muscle prominence in thin or athletic adults. This clinical scenario is suggestive of a potential _______ as a cause of paralytic ileus.
Diuretics, distention, deficiency of potassium may cause a paralytic ileus known as intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Other common causes include narcotics and hypothyroidism. Ask the patient to take a deep breath and hold it. The contour should remain smooth and symmetric. This maneuver lowers the diaphragm and compresses the organs of the abdominal cavity, which may cause previously unseen bulges or masses to appear. Next, ask the patient to raise his or her head from the table. This contracts the rectus abdominis muscles, which produces muscle prominence in thin or athletic adults. This clinical scenario is suggestive of a potential _______ as a cause of paralytic ileus.
Abdomen distended with no particular pain, hypoactive or absent bowel sounds, and no masses palpable. Patient on diuretics for hypertension. Consider hypokalemia as a cause of paralytic ileus. Narcotics and hypothyroidism are other common causes. This presentation highlights the importance of considering electrolyte imbalances in the differential diagnosis of _______.
Abdomen distended with no particular pain, hypoactive or absent bowel sounds, and no masses palpable. Patient on diuretics for hypertension. Consider hypokalemia as a cause of paralytic ileus. Narcotics and hypothyroidism are other common causes. This presentation highlights the importance of considering electrolyte imbalances in the differential diagnosis of _______.
Asymmetric distention or protrusion of the abdomen may indicate various conditions, including hernia, tumor, cysts, bowel obstruction, muscle or soft tissue hematoma, or enlargement of abdominal organs. This clinical finding suggests a potential _______ as one of the differential diagnoses.
Asymmetric distention or protrusion of the abdomen may indicate various conditions, including hernia, tumor, cysts, bowel obstruction, muscle or soft tissue hematoma, or enlargement of abdominal organs. This clinical finding suggests a potential _______ as one of the differential diagnoses.
Distention of the upper half of the abdomen, above the umbilicus, can be due to various causes like tumor, pancreatic cyst, or gastric dilation. In such cases, consider the possibility of an _______ as a contributing factor.
Distention of the upper half of the abdomen, above the umbilicus, can be due to various causes like tumor, pancreatic cyst, or gastric dilation. In such cases, consider the possibility of an _______ as a contributing factor.
The maximum size of an _______ is generally reached by adulthood. Surgical intervention may be necessary if the hernia becomes symptomatic or increases in size beyond a certain threshold.
The maximum size of an _______ is generally reached by adulthood. Surgical intervention may be necessary if the hernia becomes symptomatic or increases in size beyond a certain threshold.
An incisional hernia is caused by a defect in the abdominal musculature that develops after a surgical incision, resulting in a protrusion in the area of the surgical scar. Protrusion of the navel indicates an ______ hernia.
An incisional hernia is caused by a defect in the abdominal musculature that develops after a surgical incision, resulting in a protrusion in the area of the surgical scar. Protrusion of the navel indicates an ______ hernia.
The adult type develops during pregnancy, in long-standing ascites, or when intrathoracic pressure is repeatedly increased, as occurs in chronic respiratory disease. Hernias may also occur in the midline of the epigastrium due to small fascial defects in the linea alba. This type of hernia contains a bit of fat and is felt as a small, tender nodule. Most hernias are reducible, meaning that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into place. If not, the hernia is nonreducible or incarcerated (blood supply to the protruded contents may become obstructed and require immediate surgery). In addition to hernias, separation of the rectus abdominis muscles (i.e., diastasis recti) may become apparent when the patient raises his or her head from the table. ______ occurs more often in pregnancy and the postpartum period.
The adult type develops during pregnancy, in long-standing ascites, or when intrathoracic pressure is repeatedly increased, as occurs in chronic respiratory disease. Hernias may also occur in the midline of the epigastrium due to small fascial defects in the linea alba. This type of hernia contains a bit of fat and is felt as a small, tender nodule. Most hernias are reducible, meaning that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into place. If not, the hernia is nonreducible or incarcerated (blood supply to the protruded contents may become obstructed and require immediate surgery). In addition to hernias, separation of the rectus abdominis muscles (i.e., diastasis recti) may become apparent when the patient raises his or her head from the table. ______ occurs more often in pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Superficial abdominal wall masses may become visible. If a hernia is present, the increased abdominal pressure may cause it to protrude. An ______ hernia is caused by a defect in the abdominal musculature that develops after a surgical incision, resulting in a protrusion in the area of the surgical scar.
Superficial abdominal wall masses may become visible. If a hernia is present, the increased abdominal pressure may cause it to protrude. An ______ hernia is caused by a defect in the abdominal musculature that develops after a surgical incision, resulting in a protrusion in the area of the surgical scar.
Hernias may also occur in the midline of the epigastrium due to small fascial defects in the linea alba. This type of hernia contains a bit of fat and is felt as a small, tender nodule. Most hernias are reducible, meaning that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into place. If not, the hernia is nonreducible or incarcerated (blood supply to the protruded contents may become obstructed and require immediate surgery). In addition to hernias, separation of the rectus abdominis muscles (i.e., diastasis recti) may become apparent when the patient raises his or her head from the table. Diastasis recti occurs more often in pregnancy and the postpartum period. The condition is of little clinical significance. Movement. With the patient’s head again resting on the table, inspect the abdomen for movement. Smooth, even movement should occur with respiration. ______ of the navel indicates an umbilical hernia.
Hernias may also occur in the midline of the epigastrium due to small fascial defects in the linea alba. This type of hernia contains a bit of fat and is felt as a small, tender nodule. Most hernias are reducible, meaning that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into place. If not, the hernia is nonreducible or incarcerated (blood supply to the protruded contents may become obstructed and require immediate surgery). In addition to hernias, separation of the rectus abdominis muscles (i.e., diastasis recti) may become apparent when the patient raises his or her head from the table. Diastasis recti occurs more often in pregnancy and the postpartum period. The condition is of little clinical significance. Movement. With the patient’s head again resting on the table, inspect the abdomen for movement. Smooth, even movement should occur with respiration. ______ of the navel indicates an umbilical hernia.
The adult type develops during pregnancy, in long-standing ascites, or when intrathoracic pressure is repeatedly increased, as occurs in chronic respiratory disease. Hernias may also occur in the midline of the epigastrium due to small fascial defects in the linea alba. This type of hernia contains a bit of fat and is felt as a small, tender nodule. Most hernias are reducible, meaning that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into place. If not, the hernia is nonreducible or incarcerated (blood supply to the protruded contents may become obstructed and require immediate surgery). In addition to hernias, separation of the rectus abdominis muscles (i.e., diastasis recti) may become apparent when the patient raises his or her head from the table. Diastasis recti occurs more often in pregnancy and the postpartum period. The condition is of little clinical significance. Movement. With the patient’s head again resting on the table, inspect the abdomen for movement. Smooth, even movement should occur with respiration. An ______ hernia is caused by a defect in the abdominal musculature that develops after a surgical incision, resulting in a protrusion in the area of the surgical scar.
The adult type develops during pregnancy, in long-standing ascites, or when intrathoracic pressure is repeatedly increased, as occurs in chronic respiratory disease. Hernias may also occur in the midline of the epigastrium due to small fascial defects in the linea alba. This type of hernia contains a bit of fat and is felt as a small, tender nodule. Most hernias are reducible, meaning that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into place. If not, the hernia is nonreducible or incarcerated (blood supply to the protruded contents may become obstructed and require immediate surgery). In addition to hernias, separation of the rectus abdominis muscles (i.e., diastasis recti) may become apparent when the patient raises his or her head from the table. Diastasis recti occurs more often in pregnancy and the postpartum period. The condition is of little clinical significance. Movement. With the patient’s head again resting on the table, inspect the abdomen for movement. Smooth, even movement should occur with respiration. An ______ hernia is caused by a defect in the abdominal musculature that develops after a surgical incision, resulting in a protrusion in the area of the surgical scar.
A potbellied appearance in a child can be caused by a _______ hernia.
A potbellied appearance in a child can be caused by a _______ hernia.
_______ waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as paralytic ileus.
_______ waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as paralytic ileus.
Diastasis rectus abdominis is a separation _______ wide in the midline.
Diastasis rectus abdominis is a separation _______ wide in the midline.
The abdomen of the young child protrudes slightly, giving a potbellied appearance when the child is standing, sitting, and _______.
The abdomen of the young child protrudes slightly, giving a potbellied appearance when the child is standing, sitting, and _______.
The maximum size of an umbilical hernia is generally reached by _______ of age.
The maximum size of an umbilical hernia is generally reached by _______ of age.
Peristaltic waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as _______ stenosis.
Peristaltic waves may sometimes be seen in thin, malnourished infants, suggesting an intestinal obstruction such as _______ stenosis.
An umbilical hernia in a newborn is common and usually resolves by the age of _______ months.
An umbilical hernia in a newborn is common and usually resolves by the age of _______ months.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can be a problem, especially if the infant is _______ frequently.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can be a problem, especially if the infant is _______ frequently.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can lead to an _______ hernia.
Herniation through the rectus abdominis muscles can lead to an _______ hernia.
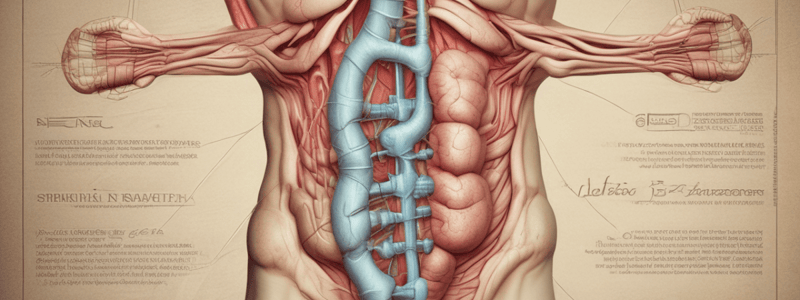
The ileocecal valve between the ileum and large intestine prevents backward flow of fecal material. The small intestine completes digestion through the action of pancreatic enzymes, bile, and several other enzymes. Nutrients are absorbed through the mucosa of the small intestine. The functional surface area of the small intestine is increased by its circular folds and villi. The large intestine begins at the cecum, a blind pouch about 2 to 3 inches long. The ileal contents empty into the cecum through the ileocecal valve, and the vermiform appendix extends from the base of the cecum. The ascending colon rises from the cecum along the right posterior abdominal wall to the undersurface of the liver. Rectus sheath Liver A Gallbladder Liver Hepatic Falciform Celiac duct ligament trunk Left adrenal gland Cystic duct Right kidney Common bile duct Duodenum Inferior vena cava Stomach Ascending colon Transverse colon Small intestine Descending colon Cecum Sigmoid colon Appendix Bladder B Gallbladder Spleen Spleen Pancreas Left kidney Superior mesenteric artery and vein Abdominal aorta Promontory C FIG. 18.1 Anatomic structures of the abdominal cavity.
The ileocecal valve between the ileum and large intestine prevents backward flow of fecal material. The small intestine completes digestion through the action of pancreatic enzymes, bile, and several other enzymes. Nutrients are absorbed through the mucosa of the small intestine. The functional surface area of the small intestine is increased by its circular folds and villi. The large intestine begins at the cecum, a blind pouch about 2 to 3 inches long. The ileal contents empty into the cecum through the ileocecal valve, and the vermiform appendix extends from the base of the cecum. The ascending colon rises from the cecum along the right posterior abdominal wall to the undersurface of the liver. Rectus sheath Liver A Gallbladder Liver Hepatic Falciform Celiac duct ligament trunk Left adrenal gland Cystic duct Right kidney Common bile duct Duodenum Inferior vena cava Stomach Ascending colon Transverse colon Small intestine Descending colon Cecum Sigmoid colon Appendix Bladder B Gallbladder Spleen Spleen Pancreas Left kidney Superior mesenteric artery and vein Abdominal aorta Promontory C FIG. 18.1 Anatomic structures of the abdominal cavity.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying