Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the factory default voltage mode of the power supply?
What is the factory default voltage mode of the power supply?
- 110V
- 120V
- 240V
- 220V (correct)
Filament should be inserted into the hotend before preheating.
Filament should be inserted into the hotend before preheating.
False (B)
What is the recommended temperature range for filament to flow through the hotend?
What is the recommended temperature range for filament to flow through the hotend?
180-190°C
It is important to ensure there are no tied or _______ on the filament reel.
It is important to ensure there are no tied or _______ on the filament reel.
Match the following components with their corresponding functions:
Match the following components with their corresponding functions:
Which of the following steps should be performed during filament installation?
Which of the following steps should be performed during filament installation?
Customers should use tweezers to insert the filament into the hotend.
Customers should use tweezers to insert the filament into the hotend.
What is indicated by the temperature reaching over 180-190°C during printing?
What is indicated by the temperature reaching over 180-190°C during printing?
What should be done to ensure easier feeding of filament into the extruder?
What should be done to ensure easier feeding of filament into the extruder?
The DMSCREATE DP-X 3D printer can resume printing after a power outage only if it was printing online.
The DMSCREATE DP-X 3D printer can resume printing after a power outage only if it was printing online.
What should you measure to ensure the correct flow of filament?
What should you measure to ensure the correct flow of filament?
To remove excessive filament at the nozzle, you should use __________ before resuming print.
To remove excessive filament at the nozzle, you should use __________ before resuming print.
Which of the following could cause the first layer not to adhere to the heat bed?
Which of the following could cause the first layer not to adhere to the heat bed?
Match the symptoms with their potential causes in 3D printing.
Match the symptoms with their potential causes in 3D printing.
What is a potential solution if the nozzle is too close to the heat bed?
What is a potential solution if the nozzle is too close to the heat bed?
Teflon tubing should be completely straight and untangled for proper extrusion.
Teflon tubing should be completely straight and untangled for proper extrusion.
What can cause gaps or hollows on the top layer during printing?
What can cause gaps or hollows on the top layer during printing?
A print head moving too slowly can cause layer shifting or lost steps.
A print head moving too slowly can cause layer shifting or lost steps.
What should be checked if filament is not extruding during printing?
What should be checked if filament is not extruding during printing?
If the printing temperature is too high, it can cause the model to __________.
If the printing temperature is too high, it can cause the model to __________.
What is the purpose of adjusting the nuts under the platform during leveling?
What is the purpose of adjusting the nuts under the platform during leveling?
Match the issues with their possible causes:
Match the issues with their possible causes:
Loosening the Z adjustable nut will raise the nozzle closer to the platform.
Loosening the Z adjustable nut will raise the nozzle closer to the platform.
Which setting should be adjusted if the fill value is set too low?
Which setting should be adjusted if the fill value is set too low?
What file extensions can be loaded into Cura?
What file extensions can be loaded into Cura?
To minimize adhesion issues during printing, always use the ______ option after rotating the model.
To minimize adhesion issues during printing, always use the ______ option after rotating the model.
Increasing withdrawal speed can alleviate wire drawing issues.
Increasing withdrawal speed can alleviate wire drawing issues.
Match the following actions in Cura with their corresponding descriptions:
Match the following actions in Cura with their corresponding descriptions:
Name a solution for filament grinding.
Name a solution for filament grinding.
Which step is NOT typically required for leveling the heat bed?
Which step is NOT typically required for leveling the heat bed?
What action should you take if the nozzle is too high above the platform?
What action should you take if the nozzle is too high above the platform?
To manipulate the 3D model in Cura, you must only use the mouse's right-click function.
To manipulate the 3D model in Cura, you must only use the mouse's right-click function.
What could cause stripes or bulges on the surface during printing?
What could cause stripes or bulges on the surface during printing?
A high printing temperature can lead to wrinkles on the surface.
A high printing temperature can lead to wrinkles on the surface.
Name one issue that can cause extruding unevenly.
Name one issue that can cause extruding unevenly.
If the Z axis is not straight, it can lead to __________ on the surface.
If the Z axis is not straight, it can lead to __________ on the surface.
Match the following printing issues with their causes:
Match the following printing issues with their causes:
Which of the following can indicate a motor shaking or abnormal sound?
Which of the following can indicate a motor shaking or abnormal sound?
What should you check if the touch screen of the printer is unresponsive?
What should you check if the touch screen of the printer is unresponsive?
A corrupted Gcode file can cause a print to stop halfway.
A corrupted Gcode file can cause a print to stop halfway.
What is the main advantage of using laser machining in industrial applications?
What is the main advantage of using laser machining in industrial applications?
The Nd:YAG laser is primarily used for cutting applications.
The Nd:YAG laser is primarily used for cutting applications.
What gas mixture is primarily used in the emission of CO2 lasers?
What gas mixture is primarily used in the emission of CO2 lasers?
The classic wavelength of CO2 laser emission is around ______ μm.
The classic wavelength of CO2 laser emission is around ______ μm.
Match the following types of lasers with their primary usage:
Match the following types of lasers with their primary usage:
What is one future scope mentioned for laser cutting machines?
What is one future scope mentioned for laser cutting machines?
CO2 lasers have a high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency.
CO2 lasers have a high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency.
Name one application of CO2 lasers in the automotive industry.
Name one application of CO2 lasers in the automotive industry.
Which type of laser is best suited for high power boring and engraving applications?
Which type of laser is best suited for high power boring and engraving applications?
CO2 lasers are known for their high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency.
CO2 lasers are known for their high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency.
What is the primary gas used in the emission of CO2 lasers?
What is the primary gas used in the emission of CO2 lasers?
CNC-controlled lasers do not require a __________ mask when engraving.
CNC-controlled lasers do not require a __________ mask when engraving.
Match the following types of lasers with their applications:
Match the following types of lasers with their applications:
What is one advantage of using laser machining in industrial applications?
What is one advantage of using laser machining in industrial applications?
Name one application of CO2 lasers in the automotive industry.
Name one application of CO2 lasers in the automotive industry.
The classic wavelength of emission for CO2 lasers is approximately 10.6 μm.
The classic wavelength of emission for CO2 lasers is approximately 10.6 μm.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Safety Instructions
- Refer to the manual for safety instructions.
Technical Specifications
- The manual provides technical specifications but does not list them explicitly.
Printing Parameters
- Temperature Parameter: The text mentions preheating the hotend before inserting the filament.
- Software Parameter: Cura is the recommended slicing software.
- Electrical: Check local voltage ratings (110V/220V) and ensure the switch on the power supply is set accordingly. The factory default is 220V.
- Physical Parameter: The text covers assembly, but specific physical parameters are not provided.
Part List
- The text includes an image (image11.jpeg) of the part list, but the specific parts are not listed in the text.
Product Overview
- The text includes an image (image13.jpeg) of the product overview but does not provide further details.
Menu Directory
- Home Menu: The home menu is the main menu.
- APPLICATION Menu: This menu contains options for "Leveling", "Resume from Outage", and more.
- SYSTEM Menu: The system menu includes settings and adjustments.
- PRINT Menu: The print menu contains options for printing and managing prints.
Assembly Instructions
- Figure 1: Steps 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 involve assembling components.
- Figure 6: Step 7 involves installing the top aluminum (AL-5) as shown in Figure 7.
- Figure 8 and 9: The manual provides images (Figure 8 and 9) for steps 8 and 9, but the text does not specify the steps themselves.
- Figure 10: The main board wiring diagram is displayed in Figure 10.
- Figure 11: The power supply switch for voltage selection is located inside the base box as shown in Figure 11.
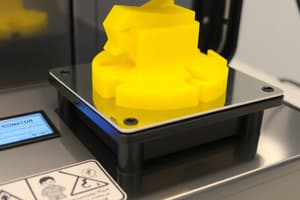
- Figure 12: The instruction details filament installation, emphasizing the need to preheat the hotend before inserting. It advises trimming the bent tip of the filament and rotating it if encountered resistance.
Leveling Instructions
- Step 1: Home the platform by clicking the "HOME" button on the menu.
- Step 2: Level the platform by adjusting the four corner nuts under the platform.
- Step 3: Manually insert the filament through the Teflon tubing all the way into the hotend when the temperature reaches over 180-190°C.
- Step 4: Remove extruded filament at the nozzle tip before printing using tweezers. Inspect the first layer of the test print (Figure 17) to assess the bed leveling.
- Step 5: Adjust the 4 nuts under the platform to ensure the heat bed is horizontal.
- Step 6: Loosen the Z adjustable nut if the nozzle is lower than the platform, and tighten it if the nozzle is too high. Adjust until the nozzle is at the correct height. It might be necessary to adjust multiple times.
- Step 7: Verify the results by clicking "APPLICATION" > "LEVELING" on the Home menu and then home.
Cura Instructions
- Cura Installation: Follow the instructions provided in the manual for installing Cura. Several images illustrate these steps.
- Cura Settings:
- Machine Settings: Choose the correct printer settings for the DMSCREATE DP-X 3D printer in Cura.
- Basic and Advanced Options: Explore the basic and advanced options for further customization.
- Plugins: Install and manage Cura plugins, including Start/End-GCode.
Load 3D Model into Cura
- Step 1: Clear the platform in Cura by clicking "File" > "Clear platform."
- Step 2: Load a 3D model into Cura by going to "File" > "Load model file...". The supported file types include "STL", "OBJ", "DAE", and "AMF."
Manipulate 3D Model in Cura
- Zoom in/out: Use the mouse wheel to zoom in and out.
- Change viewing angle: Right-click the model and move the cursor to change the view.
- Position change: Click and drag the model to change its position.
- Rotate: Click the model to activate the rotate button.
- Lay Flat: Ensure the flat portion of the model is attached to the platform by selecting the "Lay Flat" option after rotating it.
- Reset: Click the "Reset" button to return the model to its original orientation.
Offline Printing Instruction
- The manual provides specific offline printing instructions alongside an image (image78.jpeg).
Change Filament Instruction
- Ensure that the filament passes through the filament sensor before reaching the extruder.
- Trim the bent tip of the filament to facilitate easier feeding before inserting it.
Resume from Outage
- Figure 37: The manual includes an illustration (Figure 37) for resuming from an outage.
- Insert the SD card and reprint the saved file (for example, "test.gcode"). The printer will automatically heat up and resume printing.
Trouble Shooting
-
Not extruding at the start of print:
- Ensure nozzle temperature matches the filament.
- Check if the nozzle is too close to the heat bed.
- Inspect the nozzle for clogs and consider cleaning or replacing it.
- Check if the Teflon tubing is tangled, squeezed, or bent.
- Inspect the filament for tangles on the spool.
- Ensure sufficient cooling for the hot end.
-
The first layer doesn't adhere on the heat bed:
- Reduce the bottom layer printing speed to 20mm/s.
- Clean the print platform with alcohol if necessary.
- Ensure proper bed leveling.
- Verify that the bed temperature matches the filament.
- Check if the filament type matches the heat bed.
- Ensure the nozzle distance from the heat bed is appropriate.
- Make sure the bottom area of the printing model is large enough.
- Enable cooling for the first layer, especially for ABS.
- Consider adding a brim or raft to the model in Cura.
-
Filament flowing insufficient:
- Measure the diameter of the filament to confirm it meets the specifications.
- Check if the Flow (%) value is set correctly in the slicer software.
-
Filament leaking or flowing too much:
- Ensure the nozzle and throat tube are tightened properly. If necessary, fix or replace them after cooling.
- Measure the diameter of the filament to confirm it meets the specifications.
- Examine the Pulse Number of the extrusion motor.
- Adjust the Flow (%) value in the slicer software.
-
There are gaps or hollows on the top layer:
- Increase the number of layers for the printing model.
- Ensure the Fill value in the slicing software is not too low.
- Confirm there is sufficient filament flow.
-
Wire drawing:
- Increase the withdrawal distance.
- Increase the withdrawal speed.
- Reduce the printing temperature.
- Optimize the tangential path.
-
Printing model melting because of high printing temperature:
- Ensure sufficient cooling for the hot end.
- Reduce the printing temperature in the slicer software.
- Reduce the printing speed.
-
Layer shifting or lost step:
- Slow down the print speed.
- Check if the X/Y belt and the driving wheel are properly installed.
- Grease the rods and ensure all nuts and bolts are tightened.
- Inspect the main board.
-
There are gaps between layers:
- Reduce the layer thickness value in the slicing software.
- Increase the printing temperature.
- Minimize temperature fluctuations to prevent cracking, especially for ABS.
-
Grinding filament or filament wore out:
- Increase the printing temperature.
- Reduce the printing speed.
- Clean or replace the clogged nozzle.
-
Hot end clogged:
- After checking the printing temperature, manually feed the filament to see if it flows out.
- Clean or replace the nozzle and throat tube.
-
Not extruding at the process of print:
- Check if the filament has run out.
- Check for filament grinding and slipping at the extruder gear. The gear may rotate but filament may not flow out.
- Inspect the nozzle for clogs.
- Ensure the extrusion motor driver is not overheating.
-
Filling virtual filament:
- Adjust the Fill value in the slicer software.
- Reduce the Fill Speed value in the slicer software.
- Modify the Fill Width value (some slicer software allows adjustment).
-
Stripes or bulge on the surface:
- Reduce the printing temperature.
- Ensure the Z-axis is straight.
- Optimize the Slice path settings.
- Address extrusion instability.
-
Rough angle:
- Reduce the printing temperature.
- Increase cooling for the hot end.
-
Path line on the surface:
- Reduce the filament extrusion.
- Address Z-axis uplift.
-
Wrinkles on the surface:
- Inspect the quality of the filament, as inconsistent diameter can cause wrinkles.
- Minimize temperature fluctuations.
- Ensure the heat bed is not shaking.
- Verify the Z-axis is straight and properly installed.
-
Vibration:
- Reduce the printing speed.
- Identify and address vibrations in the entire machine.
- Ensure the firmware settings are correct.
-
Extruding unevenly:
- Ensure smooth filament feeding.
- Clean or replace a clogged hot end.
- Adjust the layer thickness to ensure it is not too small.
- Correct the extrusion width (typically 100-150%).
- Inspect the quality of the filament.
- Adjust the extrusion force regulation for the extrusion gear.
-
Motor shaking or abnormal sound:
- Ensure the corresponding end stop is triggered when homing. Check the wiring and inspect for any obstacles.
- Verify all motor cables are connected properly. Review the cable routing for issues.
-
File not printing or SD card failure:
- Remove the SD card and insert it into a PC. Open the Gcode files using a text editor (e.g., Notepad) and check if the Gcode is readable.
- Ensure the SD card is readable. You might need to change the SD card and avoid using special characters in the filenames.
- Reboot the machine and retry printing.
-
Print stopped halfway:
- Examine the Gcode file for corruption.
- Consider deleting plugins from the Gcode file.
- Use print offline mode (SD card) instead of print online via USB.
-
Touch screen no response:
- Check if the touch screen is being obstructed by the metal frame at the edge.
- Examine the cables and wires connected to the screen for any looseness.
- Check if the screen is damaged. If so, contact the service team.
Laser Technology
- Laser is a non-conventional energy source, known for its high precision and quality in industrial machining.
- Laser machining boasts superior dimensional tolerances, accuracy, and a minimal heat-affected zone.
- CNC capabilities in laser cutting machines ensure quality and timely outputs.
- The intensity of the laser beam can be adjusted to cut or engrave various materials.
- CNC-controlled laser engraving eliminates the need for a resistive mask.
- The CNC system precisely controls the laser tool's path and, consequently, the laser beam.
Types of Laser Cutting Machines
- CO2 Laser: Ideal for cutting, boring, and engraving; operates in the infrared spectrum (around 10.6 μm).
- Nd Laser: Suitable for boring and applications requiring high energy but low repetition rates.
- Nd:YAG Laser: Utilized when very high power is needed, particularly for boring and engraving.
CO2 Lasers
- CO2 lasers have been widely employed in material processing since the discovery of lasers.
- Emission occurs due to an electric discharge within a gas mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium.
- CO2 lasers offer high average power output, ranging from a few watts to 50 kW.
- They find extensive use in the automotive industry and other manufacturing activities involving steel parts.
- CO2 lasers are also ideal for industrial marking, annealing, engraving, or welding metals, plastics, and wood.
- They exhibit excellent beam quality but lower electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency compared to other laser types.
Applications of CO2 Laser Cutting
- Cutting and engraving a variety of materials, including plastics, wood, metals, glass, and ceramics.
- Producing intricate designs and patterns for applications like artwork, signage, and industrial components.
- Rapid prototyping and creating custom-designed products.
Future Scope of Laser Technology
- Integrating design software like SolidWorks to provide a user-friendly graphical interface and automated part program generation based on drafted profiles.
- Increasing the working area of the machine for handling larger materials and projects.
Laser Technology
- Lasers are a non-conventional energy source gaining popularity in industrial machining for their precision and high-quality output.
- Laser-machined products have superior dimensional tolerances, accuracy, and a minimal heat-affected zone.
- Most laser-cutting machines are equipped with CNC capabilities for quality assurance and timely production.
- Laser beam intensity can be controlled for cutting and engraving various materials.
- CNC-controlled laser engraving differs from traditional methods as it doesn't require a resistive mask. The laser beam path is precisely controlled by the CNC system.
CO2 Lasers
- CO2 lasers are the most widely used in material processing due to their high power output (from a few Watts up to 50 kW).
- They emit in the infrared spectrum, primarily at 10.6 μm, but lower wavelengths are also used for specific polymer processing.
- CO2 lasers are commonly used in automotive and steel part manufacturing.
- They are also ideal for industrial marking, annealing, engraving, and welding metals, plastics, or wood.
- CO2 lasers offer excellent beam quality but have lower electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency (typically 10-20%).
Applications of CO2 Lasers
- Automotive industry
- Steel part manufacturing
- Greeting card customization
- Limited edition product creation
Future Scope
- Integrating design software like SolidWorks for a graphical user interface (GUI) and automatic part program generation based on drafted profiles.
- Increasing the working area of laser machining machines for larger-scale projects.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.