Podcast
Questions and Answers
Kolb学习风格测试的目的是什么?
Kolb学习风格测试的目的是什么?
- 测量学习成绩
- 分析学习动机
- 确定个人的学习风格 (correct)
- 评估学生的智力水平
以下哪种情况最能反映一种学习风格?
以下哪种情况最能反映一种学习风格?
- 通过观察其他人学习
- 通过阅读教科书
- 通过实践和实验探索 (correct)
- 通过讨论理论知识
Kolb学习风格理论中,不包括哪个阶段?
Kolb学习风格理论中,不包括哪个阶段?
- 抽象概念
- 反思观察
- 主动实验 (correct)
- 具体经验
Kolb认为有效学习的关键是什么?
Kolb认为有效学习的关键是什么?
在Kolb学习风格测试中,哪种风格主要关注参与和实践?
在Kolb学习风格测试中,哪种风格主要关注参与和实践?
Flashcards
学习风格测试
学习风格测试
一种评估个人学习偏好的方式。
Kolb学习风格
Kolb学习风格
一种常用的学习风格分类模型。
学习偏好
学习偏好
个人在学习过程中更倾向于使用的特定方法。
评估学习风格
评估学习风格
Signup and view all the flashcards
学习类型
学习类型
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Kolb Learning Style Inventory (LSI) Overview
- The Kolb Learning Style Inventory (LSI) is a self-assessment tool used to identify an individual's preferred learning style.
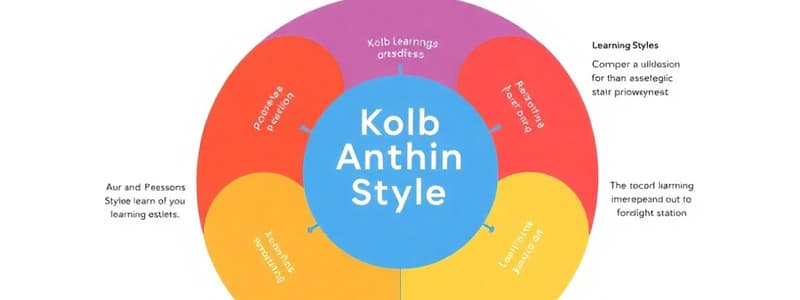
- It categorizes learning styles based on four distinct modes of learning: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
- Individuals often demonstrate a blend of these styles, with one or two typically being preferred or stronger.
- Understanding one's learning style can inform educational choices, improve learning effectiveness, and enhance personal development.
Learning Style Dimensions
- Concrete Experience (CE): Learning by doing, experiencing, and gathering firsthand information. Individuals prefer to learn through practical experience, hands-on activities, and concrete examples. They are often enthusiastic and involved learners.
- Reflective Observation (RO): Learning by watching, listening, considering, and processing information. Individuals prefer to learn by observing and analyzing situations, gathering data, and reflecting on the insights observed. They are often thoughtful and observant learners.
- Abstract Conceptualization (AC): Learning by developing ideas, formulating theories, and creating models. Individuals prefer to learn by understanding concepts, identifying patterns, forming ideas, and applying logic to solve problems. They are often analytical and systematic learners.
- Active Experimentation (AE): Learning by applying ideas, testing assumptions, and implementing solutions. Individuals prefer to learn by applying new knowledge and skills, experimenting with ideas, and trying new things to generate results. They are often practical and hands-on learners.
LSI Results and Interpretation
- The LSI typically presents a learning style profile based on the individual's preferences for the four dimensions (CE, RO, AC, and AE).
- Profiles can be described by strengths or a balance of preference across these four learning styles.
- Knowing one's preferred learning style helps in self-directed learning. An individual can leverage their strong areas while compensating for weaknesses.
- The LSI is not meant to be diagnostic or prescriptive; it provides a self-assessment that allows the individual to better understand their learning preferences.
Applications and Benefits
- Educational Context: Understanding learning styles can help students identify their strengths and tailor studying habits accordingly. It also allows educators to provide various learning methods to cater to diverse styles and cater to a wider range of learners effectively.
- Professional Development: Understanding preferred learning styles can benefit professionals by creating tailored training opportunities and identifying approaches to improve skill acquisition. This can include choosing learning materials and strategies that best suit their learning preferences.
- Personal Development: Identifying learning styles can enable greater self-awareness. Individuals can use this self-awareness to optimize their learning process and maximize their personal development. This may include selecting optimal learning environments or identifying tasks that are aligned with learning preferences.
- Team Dynamics: Acknowledging different learning styles within a team or a group environment can improve collaboration. Diverse perspectives and methods can lead to better problem-solving and decision making (a group with varied preferences can learn from each other to become more well-rounded).
Limitations of the LSI
- The LSI is a self-report inventory, meaning its reliability and validity depend on the individual's honesty and self-awareness.
- Learning styles may not remain static and can develop or shift throughout one's life. The LSI identifies preferences at a given point in time.
- While the LSI can be a useful tool, it is essential to remember that it isn't the only factor influencing learning. Other aspects, like motivation, experience, and external factors also play roles in the learning process.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.