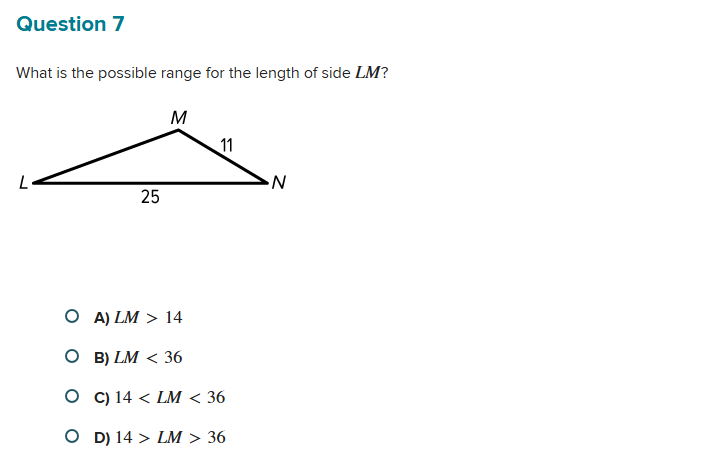
What is the possible range for the length of side LM?
Understand the Problem
The question asks for the possible range of the length of side LM in a triangle given the lengths of the other two sides. To solve it, we'll apply the triangle inequality theorem, which states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the remaining side.
Answer
The possible range for the length of side \( LM \) is \( 14 < LM < 36 \).
Answer for screen readers
The possible range for the length of side ( LM ) is ( 14 < LM < 36 ).
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the triangle's sides Let side ( LM = x ), the other two sides are ( LN = 25 ) and ( MN = 11 ).
-
Apply the triangle inequality theorem According to the triangle inequality theorem, we have three inequalities to satisfy:
- ( LM + MN > LN )
- ( LM + LN > MN )
- ( MN + LN > LM )
-
Set up the inequalities
-
For ( LM + MN > LN ): $$ x + 11 > 25 $$ Simplifying gives: $$ x > 14 $$
-
For ( LM + LN > MN ): $$ x + 25 > 11 $$ Simplifying gives: $$ x > -14 $$ (This inequality is always true since ( x ) is positive.)
-
For ( MN + LN > LM ): $$ 11 + 25 > x $$ Simplifying gives: $$ 36 > x $$ Or: $$ x < 36 $$
-
-
Combine the valid inequalities From the valid inequalities, we have: $$ 14 < x < 36 $$
-
State the possible range for ( LM ) Thus, the solution indicates that the possible range for the length of side ( LM ) is: $$ 14 < LM < 36 $$
The possible range for the length of side ( LM ) is ( 14 < LM < 36 ).
More Information
This means that side ( LM ) must be greater than 14 units and less than 36 units to satisfy the conditions of forming a triangle with the given sides.
Tips
- Ignoring any of the triangle inequalities: Always remember that all three must be satisfied.
- Misunderstanding the direction of the inequalities: Pay attention to whether to use greater than or less than when setting up the inequalities.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information