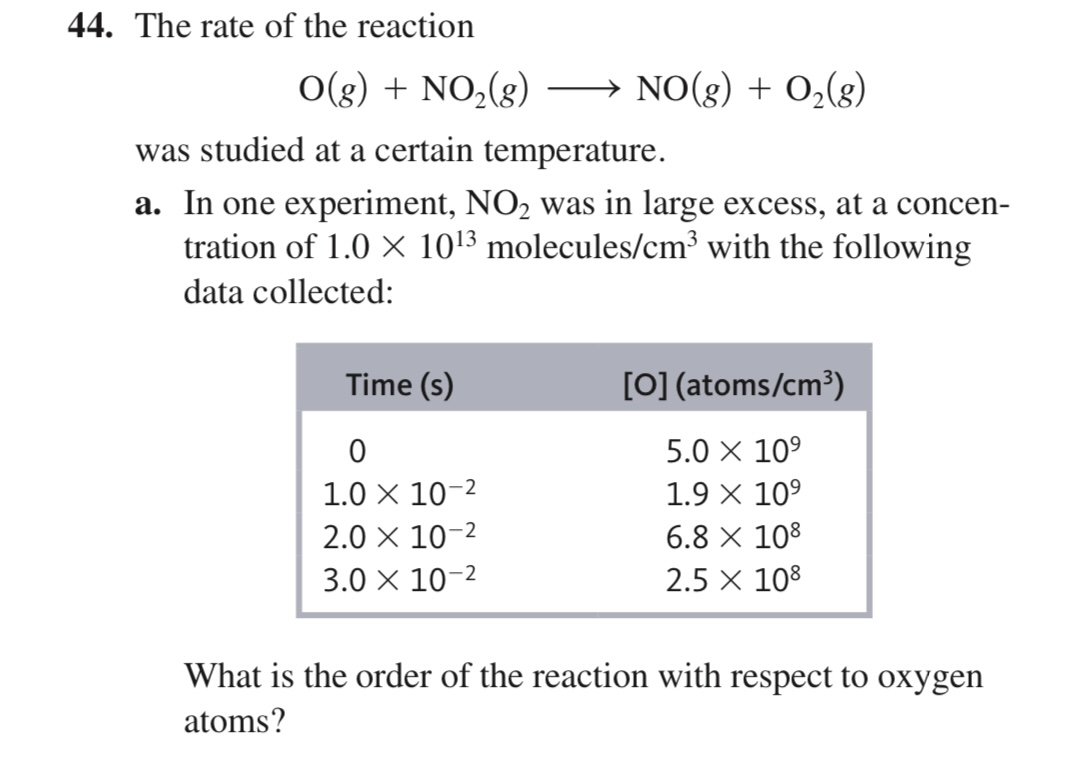
What is the order of the reaction with respect to oxygen atoms?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the calculation of the reaction order related to the concentration of oxygen atoms, based on the data collected during an experiment involving the reaction of O(g) and NO2(g). This involves analyzing the concentration changes over time to establish the relationship between the concentrations and the reaction rate.
Answer
The reaction order with respect to oxygen atoms is $n = 2$.
Answer for screen readers
The order of the reaction with respect to oxygen atoms ($n$) is approximately 2.
Steps to Solve
- Identify the rate expression for the reaction
Since NO₂ is in excess, the reaction can be simplified to focus on [O]. The rate can be expressed as: $$ Rate = k[O]^n $$ where $n$ is the order of the reaction with respect to [O].
- Determine the change in concentration over time
From the provided data, determine the change in concentration of [O] at different time intervals:
- At $t = 0$: [O] = $5.0 \times 10^9$
- At $t = 1.0 \times 10^{-2}$ s: [O] = $1.9 \times 10^9$
- At $t = 2.0 \times 10^{-2}$ s: [O] = $6.8 \times 10^8$
- At $t = 3.0 \times 10^{-2}$ s: [O] = $2.5 \times 10^8$
- Calculate the rate of change of concentration
Using the change in concentration for two successive time intervals, derive the average rate of reaction:
For the first interval from $t = 0$ to $t = 1.0 \times 10^{-2}$ s: $$ \Delta [O]_1 = [O](1.0 \times 10^{-2}) - O = 1.9 \times 10^9 - 5.0 \times 10^9 = -3.1 \times 10^9 $$
The average rate is given by: $$ Rate_1 = \frac{\Delta [O]}{\Delta t} = \frac{-3.1 \times 10^9}{1.0 \times 10^{-2}} = -3.1 \times 10^{11} $$
Repeat for subsequent intervals to establish averages.
- Plot on a log-log scale to determine order
To find the reaction order, plot log(rate) versus log([O]). The slope of the line will give the order $n$. The equation of the line can be expressed as: $$ \log(Rate) = n \log([O]) + \log(k) $$
- Calculate the slope of the log-log plot
Using the values computed for rate at different concentrations,
- Calculate $\log(Rate)$
- Calculate $\log([O])$
Using the resulting values to determine $n$ through linear regression or by calculating the slope directly.
The order of the reaction with respect to oxygen atoms ($n$) is approximately 2.
More Information
This reaction order indicates that the rate of reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of oxygen atoms, implying that, as the concentration of [O] increases, the rate increases by the square factor.
Tips
- Not clearly identifying the conditions under which the data was collected, particularly the excess of NO₂ which simplifies the reaction.
- Forgetting to change the signs in the rate calculations, as concentration decreases.
- Misinterpretation of the log-log slope as it must be derived accurately from calculated rates.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information