What are the properties of first and second generation antibacterial drugs that are susceptible to beta-lactamase?
Understand the Problem
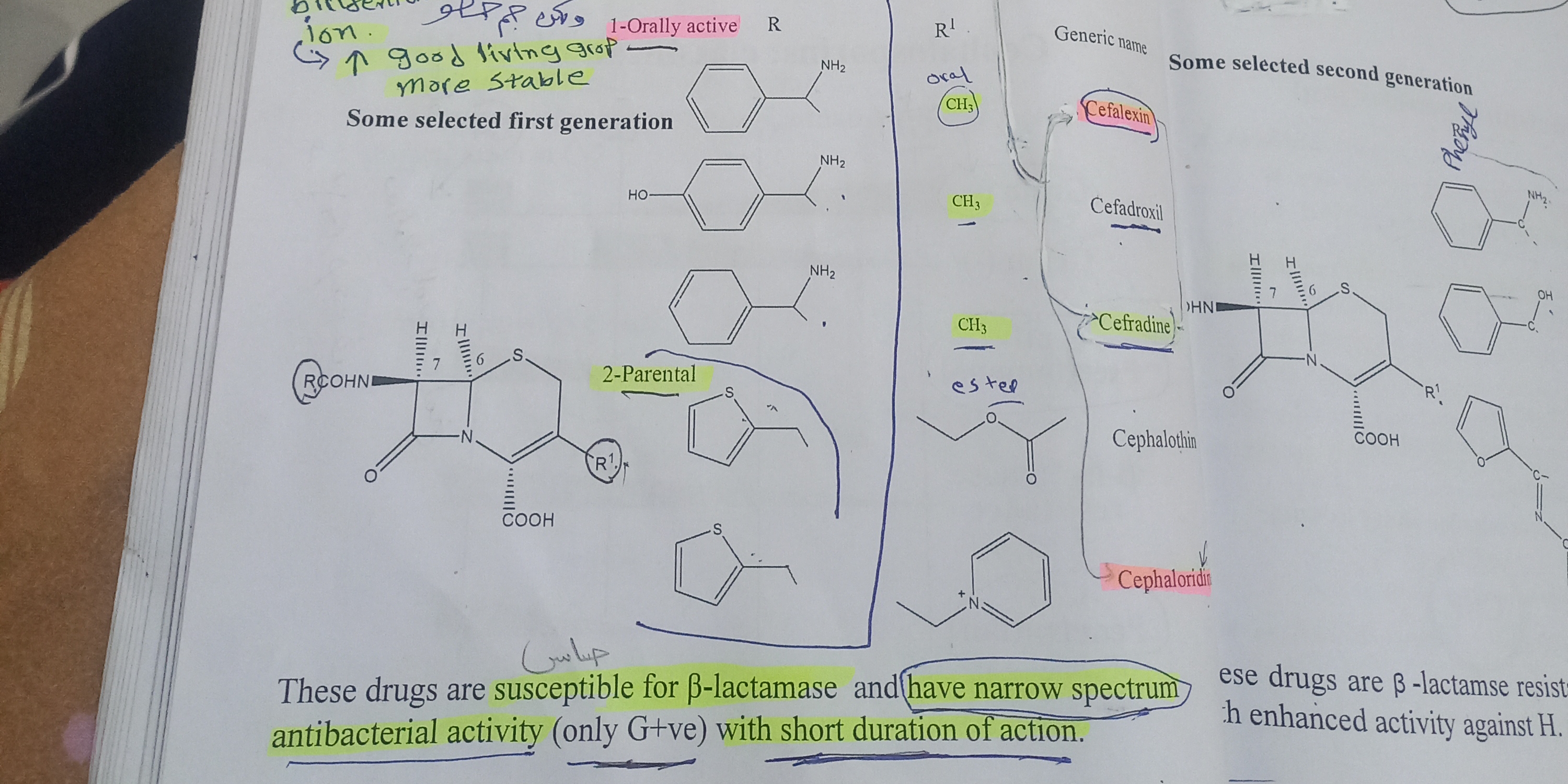
The question seems to relate to the classification and properties of certain antibacterial drugs, particularly focusing on their structure, spectrum of activity, and susceptibility to beta-lactamase. It lists first and second generation drugs and describes their antibacterial characteristics.
Answer
First-generation drugs are beta-lactamase susceptible, narrow-spectrum, Gram-positive, short duration.
First-generation antibacterial drugs, such as certain cephalosporins, are typically susceptible to beta-lactamase. They have a narrow spectrum of activity, primarily effective against Gram-positive bacteria, and generally have a short duration of action.
Answer for screen readers
First-generation antibacterial drugs, such as certain cephalosporins, are typically susceptible to beta-lactamase. They have a narrow spectrum of activity, primarily effective against Gram-positive bacteria, and generally have a short duration of action.
More Information
First-generation cephalosporins, like cephalexin, cefadroxil, and cephradine, were among the earliest developed, offering a basic antibacterial profile primarily against Gram-positive organisms. Their susceptibility to beta-lactamase, an enzyme produced by resistant bacteria, limits their effectiveness.
Tips
Mistaking broad-spectrum activity for narrow-spectrum. Ensure to identify drug generation based on spectrum and beta-lactamase susceptibility.
Sources
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Beta-lactamase - Wikipedia - en.wikipedia.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information