What are the processes involved in the asexual reproduction of fungi, particularly relating to chlamydospores and Candida albicans?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking about the asexual reproduction of fungi, specifically focusing on the processes involving chlamydospores and different types of spores in yeast like Candida albicans. It involves understanding biological processes and terminology related to fungal reproduction.
Answer
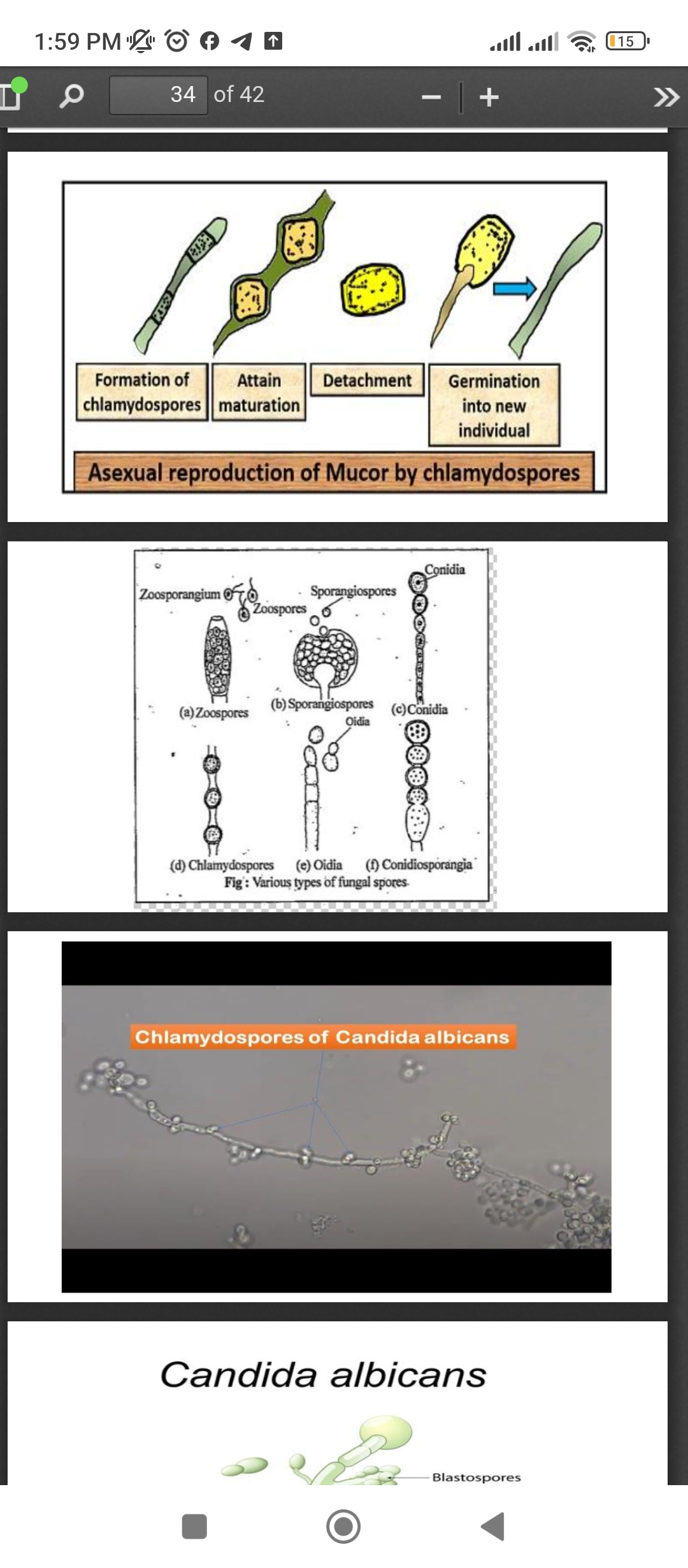
Chlamydospores in fungi, including Candida albicans, form through asexual reproduction involving formation, maturation, detachment, and germination.
Chlamydospores in fungi form as thick-walled resting spores through asexual reproduction. The process involves formation, maturation, detachment, and germination into a new individual. In Candida albicans, chlamydospores develop under specific environmental conditions and are distinct from other asexual reproduction forms like budding.
Answer for screen readers
Chlamydospores in fungi form as thick-walled resting spores through asexual reproduction. The process involves formation, maturation, detachment, and germination into a new individual. In Candida albicans, chlamydospores develop under specific environmental conditions and are distinct from other asexual reproduction forms like budding.
More Information
Chlamydospores can act as a survival mechanism for fungi, allowing them to endure unfavorable conditions. In Candida albicans, they are used as an identification marker in laboratory settings.
Tips
Avoid confusing chlamydospores with other fungal reproductive structures, such as conidia or spores produced through sexual reproduction.
Sources
- Chlamydospore - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics - sciencedirect.com
- Introduction to Mycology - Medical Microbiology - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information