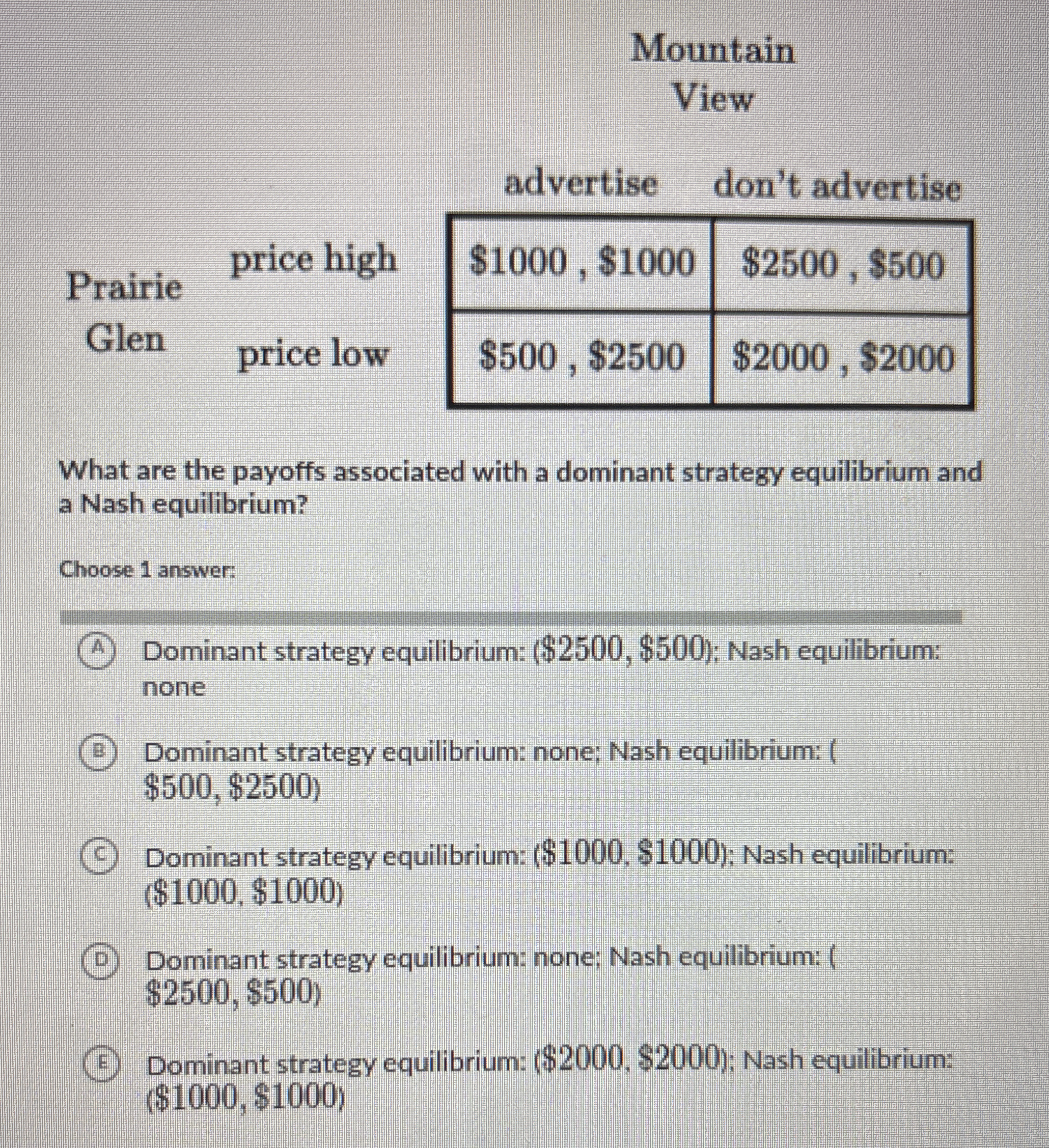
What are the payoffs associated with a dominant strategy equilibrium and a Nash equilibrium?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the payoffs associated with a dominant strategy equilibrium and a Nash equilibrium, which involves analyzing the provided payoffs in a game matrix to determine these values.
Answer
Dominant strategy equilibrium: $(1000, 1000)$; Nash equilibrium: $(1000, 1000)$.
Answer for screen readers
Dominant strategy equilibrium: $(1000, 1000)$; Nash equilibrium: $(1000, 1000)$.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the Players and Strategies
We have two players: Prairie Glen and Mountain View. The strategies for Prairie Glen are to set a high or low price, and Mountain View can choose to advertise or not. -
Construct the Payoff Matrix
From the game matrix, we list the possible outcomes based on different strategy combinations:- If Prairie Glen sets a high price and Mountain View advertises: $(1000, 1000)$
- If Prairie Glen sets a high price and Mountain View doesn't advertise: $(2500, 500)$
- If Prairie Glen sets a low price and Mountain View advertises: $(500, 2500)$
- If Prairie Glen sets a low price and Mountain View doesn't advertise: $(2000, 2000)$
-
Determine Dominant Strategies
A dominant strategy is one that yields a higher payoff regardless of the other player's action.-
For Prairie Glen:
- If Mountain View advertises: High price gives $1000$, low price gives $500$ — High price is better.
- If Mountain View doesn’t advertise: High price gives $2500$, low price gives $2000$ — High price is better.
-
Hence, Prairie Glen’s dominant strategy is to set a high price.
-
For Mountain View:
- If Prairie Glen sets a high price: Advertising gives $1000$, not advertising gives $500$ — Advertising is better.
- If Prairie Glen sets a low price: Advertising gives $2500$, not advertising gives $2000$ — Advertising is better.
-
Hence, Mountain View’s dominant strategy is to advertise.
-
-
Identify the Dominant Strategy Equilibrium
Both players have dominant strategies:- Prairie Glen: High price
- Mountain View: Advertise
- The payoff for this combination is $(1000, 1000)$.
-
Find Nash Equilibrium
A Nash equilibrium occurs when both players choose strategies where neither has an incentive to deviate unilaterally:- The dominant strategy combination is $(1000, 1000)$, which is also the Nash equilibrium because neither player can improve their payoff by changing their strategy given the other's choice.
Dominant strategy equilibrium: $(1000, 1000)$; Nash equilibrium: $(1000, 1000)$.
More Information
In game theory, a dominant strategy equilibrium occurs when a player has a strategy that is optimal regardless of the opponent's actions. A Nash equilibrium is where no player can benefit by changing their strategy while the others keep theirs unchanged.
Tips
- Misidentifying dominant strategies by not considering both players' payoffs.
- Confusing dominant strategy equilibrium with Nash equilibrium; the two can be the same but aren't always.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information