What are the functions of the different parts of the human eye as labeled in the image?
Understand the Problem
The question is likely related to the anatomy or functions of the human eye, focusing on its various parts as labeled in the image. The user might want to understand what each structure does or how they work together.
Answer
The human eye has various parts like the optic nerve, retina, cornea, lens, and iris, each playing crucial roles in vision by focusing light, transmitting signals, and maintaining eye structure.
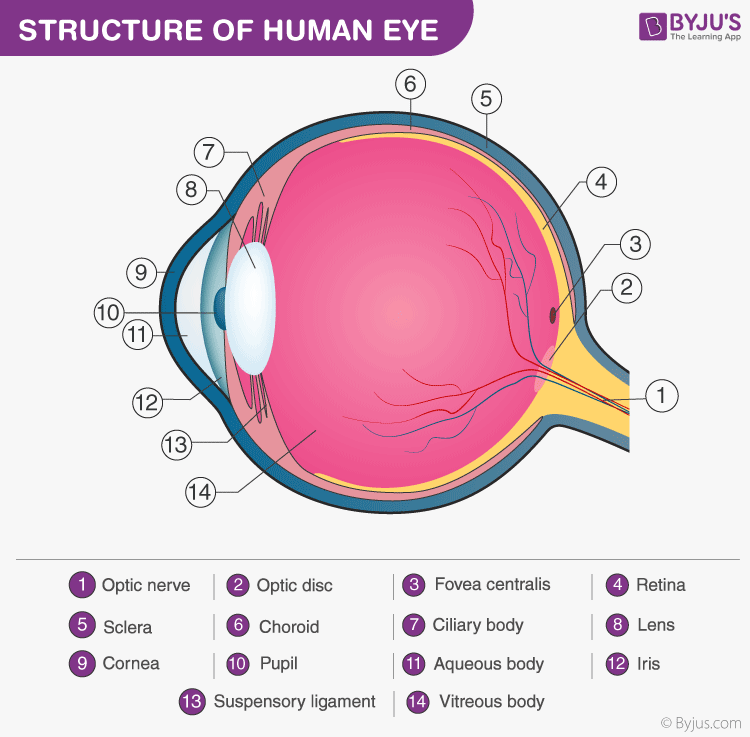
- Optic nerve: Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. 2. Optic disc: Location where the optic nerve exits the eye; no photoreceptors, creating a blind spot. 3. Fovea centralis: Responsible for sharp, central vision. 4. Retina: Contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) for converting light into neural signals. 5. Sclera: White outer layer providing structure and protection. 6. Choroid: Rich in blood vessels, supplies nutrients to the eye. 7. Ciliary body: Controls lens shape for focusing. 8. Lens: Focuses light onto the retina. 9. Cornea: Transparent front part that refracts light. 10. Pupil: Opening regulating the amount of light entering the eye. 11. Aqueous body: Fluid maintaining eye pressure and nourishing the cornea and lens. 12. Iris: Colored part controlling pupil size. 13. Suspensory ligament: Connects the lens to the ciliary body. 14. Vitreous body: Gel-like substance maintaining eye shape.
Answer for screen readers
- Optic nerve: Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. 2. Optic disc: Location where the optic nerve exits the eye; no photoreceptors, creating a blind spot. 3. Fovea centralis: Responsible for sharp, central vision. 4. Retina: Contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) for converting light into neural signals. 5. Sclera: White outer layer providing structure and protection. 6. Choroid: Rich in blood vessels, supplies nutrients to the eye. 7. Ciliary body: Controls lens shape for focusing. 8. Lens: Focuses light onto the retina. 9. Cornea: Transparent front part that refracts light. 10. Pupil: Opening regulating the amount of light entering the eye. 11. Aqueous body: Fluid maintaining eye pressure and nourishing the cornea and lens. 12. Iris: Colored part controlling pupil size. 13. Suspensory ligament: Connects the lens to the ciliary body. 14. Vitreous body: Gel-like substance maintaining eye shape.
More Information
The human eye functions much like a camera, with the lens focusing light and the retina acting as the film to capture the image.
Tips
A common mistake is mixing the functions of the cornea and lens; the cornea does initial focusing while the lens fine-tunes focus.
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information