What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for a comparison between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their structures and functions.
Answer
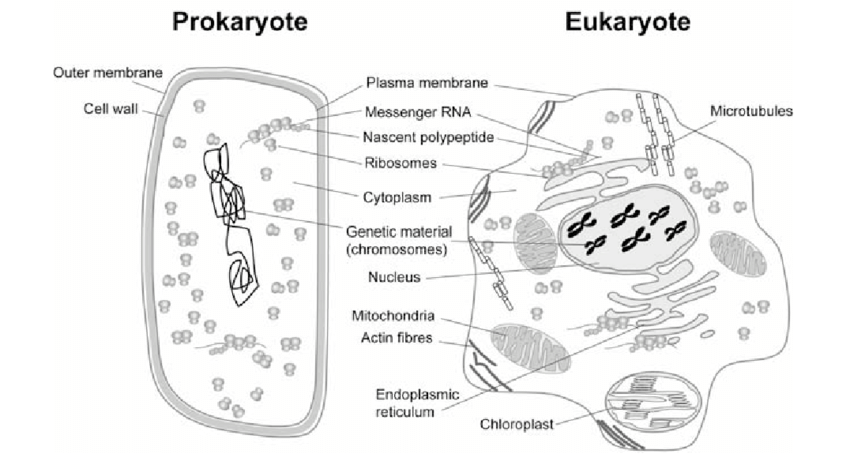
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and organelles; eukaryotes have them.
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Answer for screen readers
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
More Information
Prokaryotic cells are typically unicellular, like bacteria, while eukaryotic cells can be unicellular or part of multicellular organisms. Eukaryotic cells' organelles help in performing specialized functions.
Tips
Confusing the presence of a nucleus in eukaryotes with prokaryotes is common. Remember, 'pro-' means 'before' and 'karyon' means 'nucleus' in Greek.
Sources
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - BYJU'S - byjus.com
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information