What are the chemical reactions that occur when vinegar interacts with an egg compared to water?
Understand the Problem
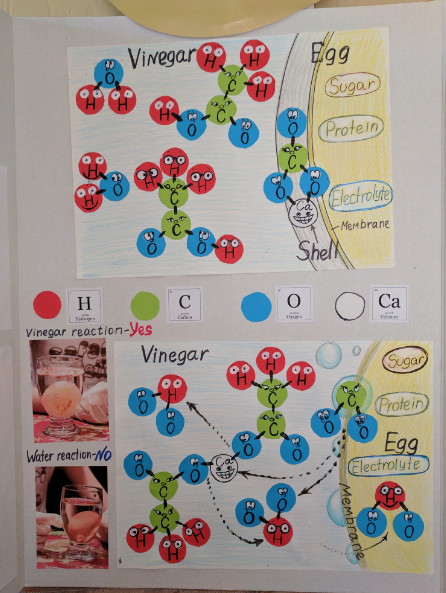
The question appears to be about the chemical reactions involving vinegar and their effects, particularly on an egg. It presents a visual representation of molecular interactions in these reactions, highlighting differences between vinegar and water. The focus is on the reactions indicated and the components involved, such as sugar, protein, and electrolytes.
Answer
Vinegar breaks down the eggshell; water does not react.
The image shows the reaction of vinegar with an egg shell, highlighting the dissolution of calcium carbonate. Vinegar, containing acetic acid, breaks down the shell into calcium and carbonate ions, resulting in carbon dioxide bubbles. Water does not cause this reaction.
Answer for screen readers
The image shows the reaction of vinegar with an egg shell, highlighting the dissolution of calcium carbonate. Vinegar, containing acetic acid, breaks down the shell into calcium and carbonate ions, resulting in carbon dioxide bubbles. Water does not cause this reaction.
More Information
The acetic acid in vinegar reacts with the calcium carbonate in the eggshell, dissolving it and forming carbon dioxide gas. This is an acid-base reaction. Water, lacking an acidic component, does not react with the eggshell.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming water has a similar effect on the eggshell as vinegar. It does not because water lacks acetic acid.
Sources
- Naked Eggs - Science World - scienceworld.ca
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information