Verify the functions f and g are inverses of each other: i) f(x) = (x - 4) / 3, g(x) = 3x + 4; ii) f(x) = (x - 7) / 3, g(x) = 4x + 7. If f(x) = (x^2 - 1) / (5x + 8), x ≤ 1, find P(... Verify the functions f and g are inverses of each other: i) f(x) = (x - 4) / 3, g(x) = 3x + 4; ii) f(x) = (x - 7) / 3, g(x) = 4x + 7. If f(x) = (x^2 - 1) / (5x + 8), x ≤ 1, find P(2), P(-1), P(6), and P(a). Find integer values for f where x = 72, x = 6.2, and x = 4.
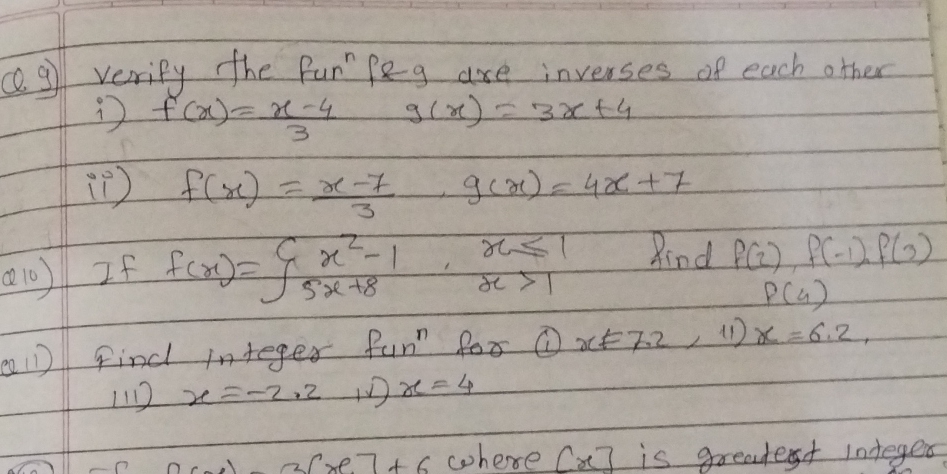
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to verify if the given functions f and g are inverses of each other, and then to find specific function values and the greatest integer function.
Answer
The functions are inverses for i) only. Values: \( P(2) = \frac{1}{6}, P(-1) = 0, P(6) = \frac{35}{38}, P(a) = \frac{a^2 - 1}{5a + 8} \). Integer values: \( \lfloor 72 \rfloor = 72, \lfloor 6.2 \rfloor = 6, \lfloor 4 \rfloor = 4 \).
Answer for screen readers
The functions are inverses for i) but not for ii). The values are: ( P(2) = \frac{1}{6}, P(-1) = 0, P(6) = \frac{35}{38}, P(a) = \frac{a^2 - 1}{5a + 8} ). Integer values: ( \lfloor 72 \rfloor = 72, \lfloor 6.2 \rfloor = 6, \lfloor 4 \rfloor = 4 ).
Steps to Solve
-
Verify if ( f ) and ( g ) are inverses (i) To confirm ( f(x) ) and ( g(x) ) are inverses, we check if ( f(g(x)) = x ) and ( g(f(x)) = x ).
For ( f(x) = \frac{x - 4}{3} ) and ( g(x) = 3x + 4 ):
- Calculate ( f(g(x)) ): $$ f(g(x)) = f(3x + 4) = \frac{(3x + 4) - 4}{3} = \frac{3x}{3} = x $$
- Calculate ( g(f(x)) ): $$ g(f(x)) = g\left(\frac{x - 4}{3}\right) = 3\left(\frac{x - 4}{3}\right) + 4 = x - 4 + 4 = x $$
Since both equal ( x ), ( f ) and ( g ) are inverses.
-
Verify if ( f ) and ( g ) are inverses (ii) For ( f(x) = \frac{x - 7}{3} ) and ( g(x) = 4x + 7 ):
-
Calculate ( f(g(x)) ): $$ f(g(x)) = f(4x + 7) = \frac{(4x + 7) - 7}{3} = \frac{4x}{3} $$
-
Calculate ( g(f(x)) ): $$ g(f(x)) = g\left(\frac{x - 7}{3}\right) = 4\left(\frac{x - 7}{3}\right) + 7 = \frac{4x - 28}{3} + 7 = \frac{4x - 28 + 21}{3} = \frac{4x - 7}{3} $$
Since neither equals ( x ), ( f ) and ( g ) are not inverses here.
- Evaluate function ( P(x) ) for specific values Given ( f(x) = \frac{x^2 - 1}{5x + 8} ), find ( P(2), P(-1), P(6), ) and ( P(a) ):
-
Calculate ( P(2) ): $$ P(2) = \frac{2^2 - 1}{5(2) + 8} = \frac{4 - 1}{10 + 8} = \frac{3}{18} = \frac{1}{6} $$
-
Calculate ( P(-1) ): $$ P(-1) = \frac{(-1)^2 - 1}{5(-1) + 8} = \frac{1 - 1}{-5 + 8} = \frac{0}{3} = 0 $$
-
Calculate ( P(6) ): $$ P(6) = \frac{6^2 - 1}{5(6) + 8} = \frac{36 - 1}{30 + 8} = \frac{35}{38} $$
-
For ( P(a) ), it remains as: $$ P(a) = \frac{a^2 - 1}{5a + 8} $$
- Evaluate integer values for ( f ) To find integer values:
-
For ( x = 72 ): $$ f(72) = \frac{72^2 - 1}{5(72) + 8} = \frac{5184 - 1}{360 + 8} = \frac{5183}{368} $$
-
For ( x = 6.2 ): $$ f(6.2) = \frac{6.2^2 - 1}{5(6.2) + 8} = \frac{38.44 - 1}{31 + 8} = \frac{37.44}{39} \approx 0.96 $$
-
For ( x = 4 ): $$ f(4) = \frac{4^2 - 1}{5(4) + 8} = \frac{16 - 1}{20 + 8} = \frac{15}{28} $$
- Greatest Integer Function The greatest integer function is denoted by ( \lfloor x \rfloor ), representing the largest integer less than or equal to ( x ):
- For ( x = 72 ): ( \lfloor 72 \rfloor = 72 )
- For ( x = 6.2 ): ( \lfloor 6.2 \rfloor = 6 )
- For ( x = 4 ): ( \lfloor 4 \rfloor = 4 )
The functions are inverses for i) but not for ii). The values are: ( P(2) = \frac{1}{6}, P(-1) = 0, P(6) = \frac{35}{38}, P(a) = \frac{a^2 - 1}{5a + 8} ). Integer values: ( \lfloor 72 \rfloor = 72, \lfloor 6.2 \rfloor = 6, \lfloor 4 \rfloor = 4 ).
More Information
This exercise highlights the relationship between functions and their inverses and the application of a function for specific inputs, as well as the greatest integer function's utility in rounding down numbers.
Tips
- Failing to confirm both ( f(g(x)) ) and ( g(f(x)) ) when testing for inverses.
- Miscalculating fractions when evaluating function values, especially simplifying the final results.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information