The vapor pressure of a glucose (C6H12O6) solution is 17.01 mmHg at 20 °C, while that of pure water is 17.25 mmHg at the same temperature. Calculate the molality of the solution.
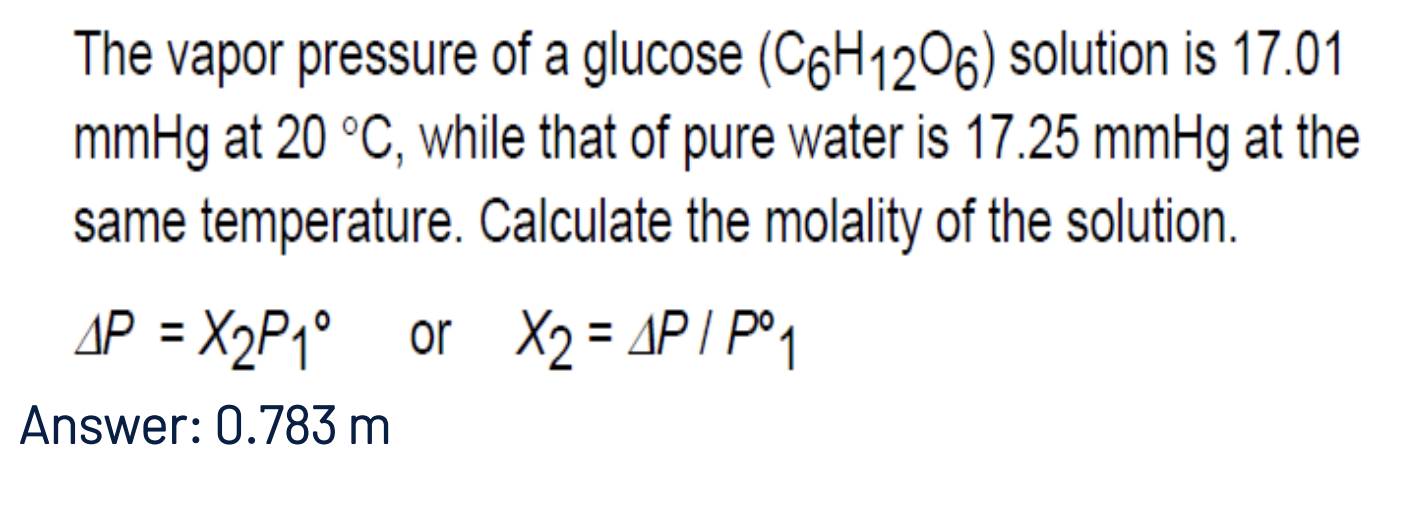
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to calculate the molality of a glucose solution using its vapor pressure and the vapor pressure of pure water. It provides the relevant equations and necessary values, which will help in solving the problem step by step.
Answer
The molality of the glucose solution is $0.783 \, m$.
Answer for screen readers
The molality of the glucose solution is approximately $0.783 , m$.
Steps to Solve
- Calculate the change in vapor pressure ($\Delta P$)
To find $\Delta P$, subtract the vapor pressure of the solution from the vapor pressure of pure water.
[ \Delta P = P_1^\circ - P = 17.25 , \text{mmHg} - 17.01 , \text{mmHg} = 0.24 , \text{mmHg} ]
- Calculate the mole fraction of the solute ($X_2$)
Using the formula $X_2 = \frac{\Delta P}{P_1^\circ}$, we can find the mole fraction of glucose (the solute).
[ X_2 = \frac{0.24 , \text{mmHg}}{17.25 , \text{mmHg}} \approx 0.0139 ]
- Calculate the mole fraction of the solvent ($X_1$)
Since the total mole fraction must equal 1, we can find the mole fraction of the solvent (water):
[ X_1 = 1 - X_2 = 1 - 0.0139 \approx 0.9861 ]
- Calculate the molality ($m$)
Next, we know that molality ($m$) is calculated as:
[ m = \frac{X_2}{X_1} \times \frac{1000 , \text{g of solvent}}{molar , mass , of , solvent , (g/mol)} ]
The molar mass of water (H₂O) is approximately 18.015 g/mol, so:
[ m = \frac{0.0139}{0.9861} \times \frac{1000}{18.015} \approx 0.783 , \text{m} ]
The molality of the glucose solution is approximately $0.783 , m$.
More Information
Molality is a measure of concentration expressed as moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. In this case, we calculated the concentration of glucose in a water solution based on vapor pressure changes.
Tips
- Not properly calculating $\Delta P$: Ensure to subtract the solution's vapor pressure from the pure vapor pressure.
- Confusing mole fractions: Remember that $X_1 + X_2 = 1$. It's important to correctly associate which fraction corresponds to solvent and solute.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information