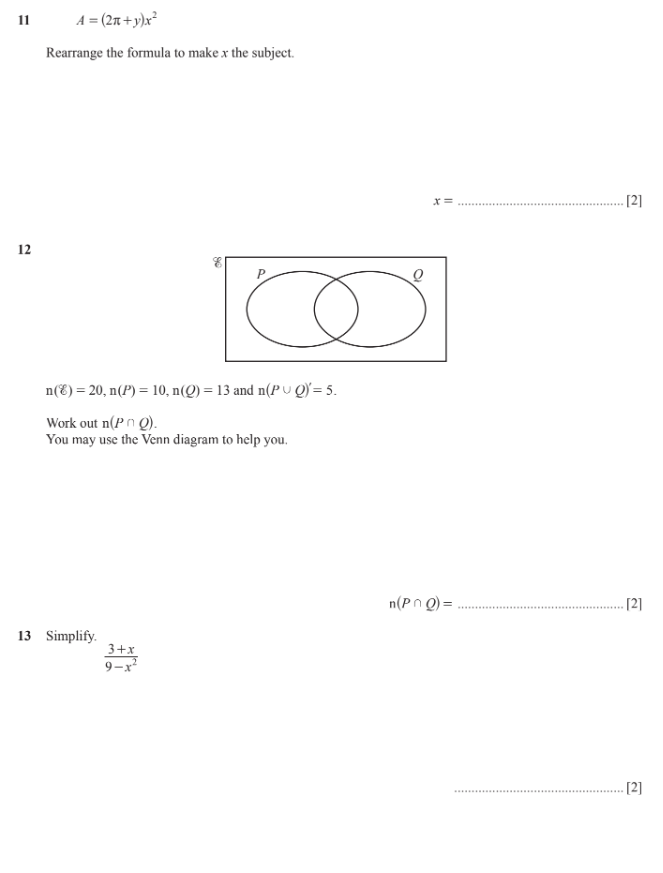
Solve the following math problems: 1. Rearrange the formula A = (2π+y)x² to make x the subject. 2. If n(ξ) = 20, n(P) = 10, n(Q) = 13 and n((P ∪ Q)') = 5, work out n(P ∩ Q). 3.... Solve the following math problems: 1. Rearrange the formula A = (2π+y)x² to make x the subject. 2. If n(ξ) = 20, n(P) = 10, n(Q) = 13 and n((P ∪ Q)') = 5, work out n(P ∩ Q). 3. Simplify (3+x) / (9-x²).
Understand the Problem
The image contains three separate math problems:
- Rearrange the formula A = (2π+y)x² to make x the subject,
- Given information about sets P and Q within a universal set, find the number of elements in the intersection of P and Q,
- Simplify the algebraic expression (3+x) / (9-x²).
Answer
11. $x = \sqrt{\frac{A}{2\pi + y}}$ 12. $8$ 13. $\frac{1}{3-x}$
Answer for screen readers
- $x = \sqrt{\frac{A}{2\pi + y}}$
- $n(P \cap Q) = 8$
- $\frac{1}{3-x}$
Steps to Solve
- Isolate the $x^2$ term
Divide both sides of the equation $A = (2\pi + y)x^2$ by $(2\pi + y)$ to isolate the $x^2$ term:
$$ \frac{A}{2\pi + y} = x^2 $$
- Solve for x
Take the square root of both sides of the equation to solve for $x$:
$$ x = \sqrt{\frac{A}{2\pi + y}} $$
Since we are only asked to rearrange the formula, we only consider the positive square root.
- Find $n(P \cup Q)$
We are given that the number of elements in the universal set $n(\xi) = 20$ and the number of elements outside the union of P and Q, $n((P \cup Q)') = 5$. Therefore, the number of elements inside the union of P and Q is:
$$n(P \cup Q) = n(\xi) - n((P \cup Q)') = 20 - 5 = 15$$
- Use the inclusion-exclusion principle
We know that $n(P \cup Q) = n(P) + n(Q) - n(P \cap Q)$. We are given $n(P) = 10$, $n(Q) = 13$, and we found that $n(P \cup Q) = 15$. Substitute these values into the equation and solve for $n(P \cap Q)$:
$$ 15 = 10 + 13 - n(P \cap Q) $$
$$ 15 = 23 - n(P \cap Q) $$
Add $n(P \cap Q)$ to both sides and subtract 15 from both sides:
$$ n(P \cap Q) = 23 - 15 = 8 $$
- Factor the denominator
The given expression is $\frac{3+x}{9-x^2}$. The denominator $9 - x^2$ is a difference of squares, which can be factored as:
$$9 - x^2 = (3 - x)(3 + x)$$
- Simplify the expression
Now we have:
$$ \frac{3+x}{(3-x)(3+x)} $$
Since $(3+x)$ is a common factor in the numerator and the denominator, we can cancel it out, provided that $x \ne -3$:
$$ \frac{3+x}{(3-x)(3+x)} = \frac{1}{3-x} $$
- $x = \sqrt{\frac{A}{2\pi + y}}$
- $n(P \cap Q) = 8$
- $\frac{1}{3-x}$
More Information
- In question 11, we only considered the positive square root, as we are asked to rearrange the formula only.
- In question 12, the inclusion-exclusion principle is a fundamental concept in set theory.
- In question 13, factoring the difference of squares is a common algebraic technique.
Tips
- When rearranging formulas, forgetting to take the square root after isolating the $x^2$ term.
- Forgetting the difference of squares factorization: $a^2 - b^2 = (a-b)(a+b)$.
- Attempting to cancel terms that are added or subtracted incorrectly.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information