Solve the equation: 4^(2x+1) * 5^(x-2) = 6^(1-x)
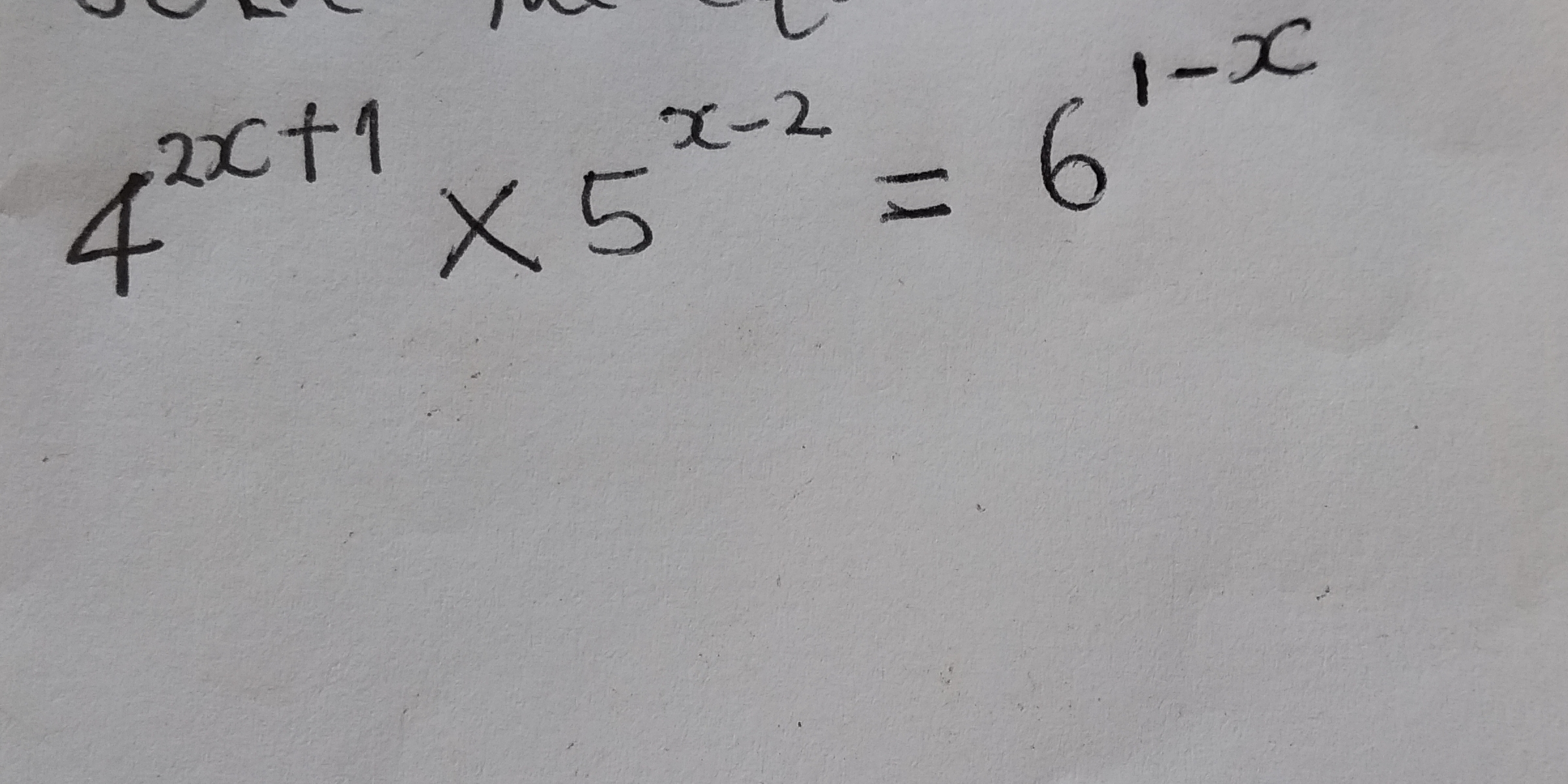
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to solve an exponential equation. We need to find the value of 'x' that satisfies the equation 4^(2x+1) * 5^(x-2) = 6^(1-x). This will likely involve using logarithms to isolate x.
Answer
$x = \frac{ln(37.5)}{ln(480)}$
Answer for screen readers
$x = \frac{ln(37.5)}{ln(480)}$
Steps to Solve
-
Apply the logarithm to both sides of the equation We can apply logarithms to both sides of the equation, using the property that if $a = b$, then $\log(a) = \log(b)$. Using the natural logarithm (ln) helps simplify the equation.
$ln(4^{2x+1} \times 5^{x-2}) = ln(6^{1-x})$
-
Use logarithm properties to expand the equation Apply the logarithm properties: $\log(ab) = \log(a) + \log(b)$ and $\log(a^b) = b\log(a)$:
$ln(4^{2x+1}) + ln(5^{x-2}) = ln(6^{1-x})$ $(2x+1)ln(4) + (x-2)ln(5) = (1-x)ln(6)$
-
Expand the terms Distribute the $ln$ terms across the parentheses:
$2x \cdot ln(4) + ln(4) + x \cdot ln(5) - 2 \cdot ln(5) = ln(6) - x \cdot ln(6)$
-
Collect terms with 'x' on one side and constants on the other side Rearrange the equation to group the terms containing $x$ on the left side and the constant terms on the right side:
$2x \cdot ln(4) + x \cdot ln(5) + x \cdot ln(6) = ln(6) - ln(4) + 2 \cdot ln(5)$
-
Factor out 'x' from the left side Factor out $x$ from the left side of the equation:
$x(2 \cdot ln(4) + ln(5) + ln(6)) = ln(6) - ln(4) + 2 \cdot ln(5)$
-
Isolate 'x' Divide both sides by $(2 \cdot ln(4) + ln(5) + ln(6))$ to solve for $x$:
$x = \frac{ln(6) - ln(4) + 2 \cdot ln(5)}{2 \cdot ln(4) + ln(5) + ln(6)}$
-
Simplify using logarithm properties Use properties of logarithms to simplify: $a \cdot ln(b) = ln(b^a)$, $ln(a) + ln(b) = ln(ab)$, and $ln(a) - ln(b) = ln(\frac{a}{b})$.
$x = \frac{ln(6) - ln(4) + ln(5^2)}{ln(4^2) + ln(5) + ln(6)}$
$x = \frac{ln(6) - ln(4) + ln(25)}{ln(16) + ln(5) + ln(6)}$
$x = \frac{ln(\frac{6}{4}) + ln(25)}{ln(16) + ln(30)}$
$x = \frac{ln(\frac{3}{2}) + ln(25)}{ln(480)}$
$x = \frac{ln(\frac{3}{2} \times 25)}{ln(480)}$
$x = \frac{ln(\frac{75}{2})}{ln(480)}$
$x = \frac{ln(37.5)}{ln(480)}$
-
Final Answer
$x = \frac{ln(37.5)}{ln(480)} \approx \frac{3.6243}{6.1738} \approx 0.5870$
$x = \frac{ln(37.5)}{ln(480)}$
More Information
The solution to the equation $4^{2x+1} \times 5^{x-2} = 6^{1-x}$ is $x = \frac{ln(37.5)}{ln(480)}$, where $ln$ is the natural logarithm.
Tips
A common mistake is not applying the logarithm properties correctly when expanding and simplifying the equation. Also, errors can occur when collecting like terms and isolating x. Ensure to double-check each step.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information