Solve for x: $(x+1)^2 = (x+1)(2x+3)$
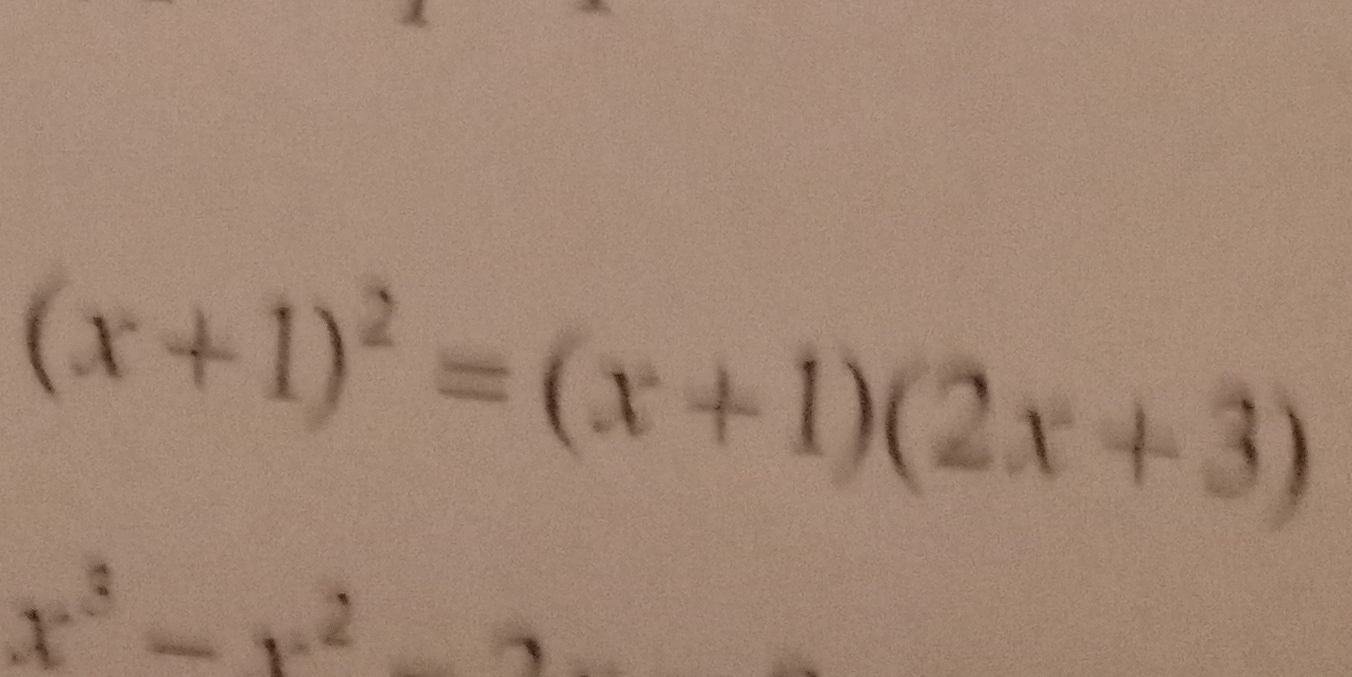
Understand the Problem
The question asks to solve the equation $(x+1)^2 = (x+1)(2x+3)$ for the variable $x$. This involves expanding both sides of the equation, simplifying, and then finding the values of $x$ that satisfy the equation.
Answer
$x = -1, -2$
Answer for screen readers
$x = -1, -2$
Steps to Solve
- Expand both sides of the equation
Expand $(x+1)^2$ to $x^2 + 2x + 1$, and expand $(x+1)(2x+3)$ to $2x^2 + 3x + 2x + 3 = 2x^2 + 5x + 3$. So the equation becomes $x^2 + 2x + 1 = 2x^2 + 5x + 3$.
- Rearrange the equation
Move all terms to one side of the equation to set it to zero: $0 = 2x^2 - x^2 + 5x - 2x + 3 - 1$ $0 = x^2 + 3x + 2$
- Factor the quadratic equation
Factor the quadratic equation $x^2 + 3x + 2 = 0$. Look for two numbers that multiply to 2 and add to 3. Those numbers are 1 and 2. So, we can factor the quadratic equation as $(x+1)(x+2) = 0$.
- Solve for x
Set each factor equal to zero and solve for $x$: $x+1 = 0$ or $x+2 = 0$ $x = -1$ or $x = -2$
$x = -1, -2$
More Information
These are the two possible values of $x$ that satisfy the equation. To verify, substitute each value back into the original equation to see if it holds true.
Tips
A common mistake is dividing both sides by $(x+1)$ too early in the solution. This would eliminate the solution $x=-1$.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information