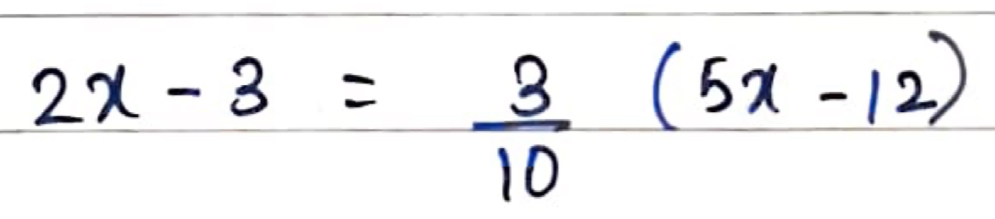
Solve for x: 2x - 3 = (3/10) * (5x - 12)
Understand the Problem
The question involves solving a linear equation. You'll need to isolate the variable 'x' by performing algebraic operations on both sides of the equation to find its value.
Answer
$x = -\frac{6}{5}$
Answer for screen readers
$x = -\frac{6}{5}$
Steps to Solve
- Distribute $\frac{3}{10}$ on the right side of the equation
Multiply $\frac{3}{10}$ by both terms inside the parentheses:
$$2x - 3 = \frac{3}{10}(5x) - \frac{3}{10}(12)$$
$$2x - 3 = \frac{15x}{10} - \frac{36}{10}$$
- Simplify the fractions
Simplify $\frac{15x}{10}$ to $\frac{3x}{2}$ and $\frac{36}{10}$ to $\frac{18}{5}$:
$$2x - 3 = \frac{3x}{2} - \frac{18}{5}$$
- Eliminate the fractions
Multiply both sides of the equation by the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators, which is 10: $$10(2x - 3) = 10(\frac{3x}{2} - \frac{18}{5})$$
$$20x - 30 = 15x - 36$$
- Isolate x terms
Subtract $15x$ from both sides:
$$20x - 15x - 30 = 15x - 15x - 36$$
$$5x - 30 = -36$$
- Isolate the x term
Add 30 to both sides:
$$5x - 30 + 30 = -36 + 30$$
$$5x = -6$$
- Solve for x
Divide both sides by 5:
$$\frac{5x}{5} = \frac{-6}{5}$$
$$x = -\frac{6}{5}$$
$x = -\frac{6}{5}$
More Information
The solution to the linear equation $2x - 3 = \frac{3}{10} (5x - 12)$ is $x = -\frac{6}{5}$. This means that if you substitute $-\frac{6}{5}$ for $x$ in the original equation, both sides of the equation will be equal.
Tips
A common mistake is not distributing the $\frac{3}{10}$ correctly to both terms inside the parentheses. Another common mistake is making errors when simplifying fractions or when adding/subtracting numbers during the isolation of x. Finally, not multiplying all terms by 10 can lead to an incorrect result.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information