Solve for C given: D = m/r + Ce^(-rt) and 0.5 = 3/r + Ce^(-rt)
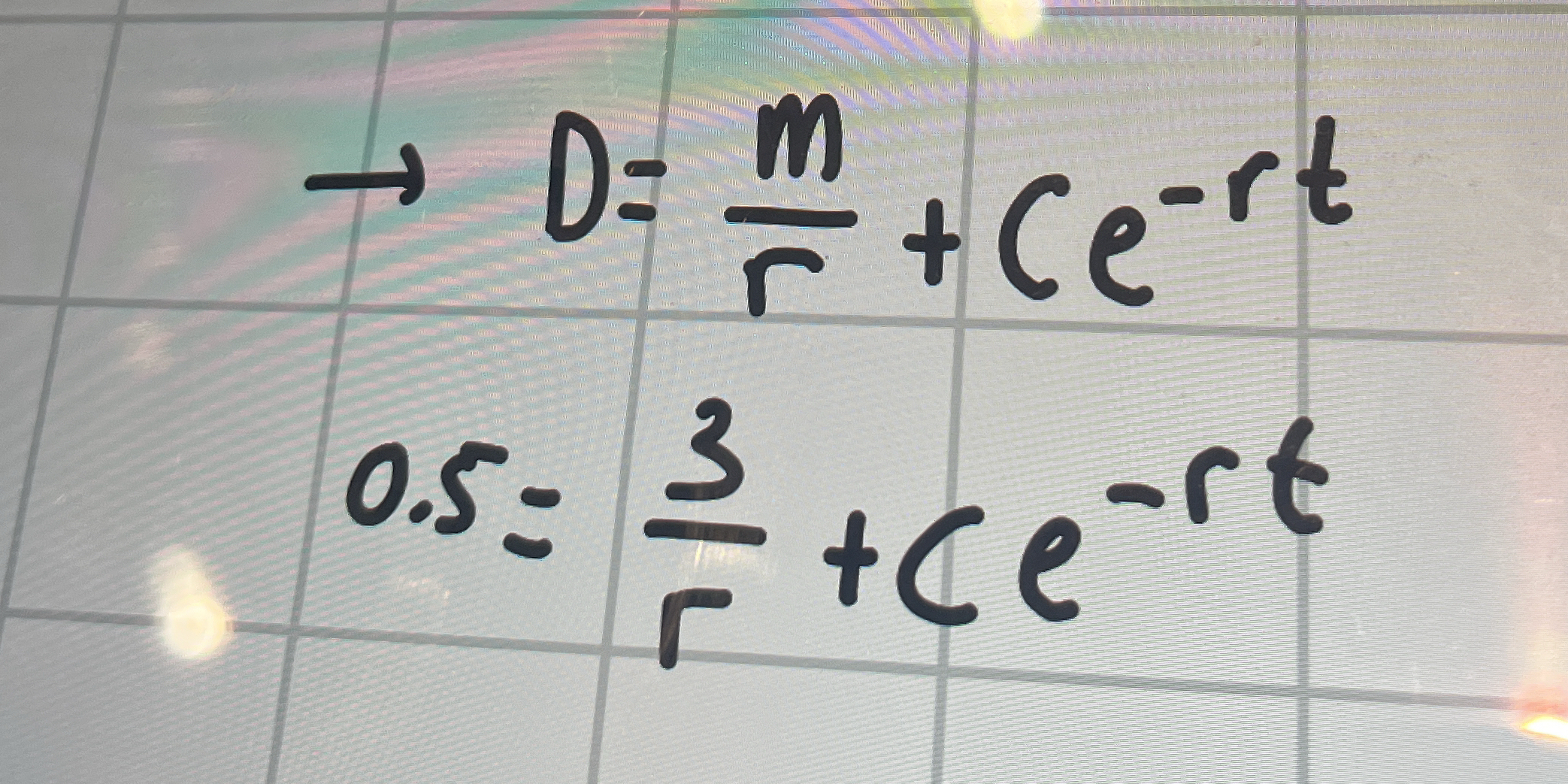
Understand the Problem
The question provides two equations: one general and one with specific values substituted. The goal is likely to solve for the constant 'C' in order to fully define the relationship given by the first equation. This involves algebraic manipulation and solving for 'C' using the provided values.
Answer
$C = (0.5 - \frac{3}{r})e^{rt}$
Answer for screen readers
$C = (0.5 - \frac{3}{r})e^{rt}$ or $C = 0.5e^{rt} - \frac{3e^{rt}}{r}$
Steps to Solve
-
Isolate the term with C
Start with the equation $0.5 = \frac{3}{r} + Ce^{-rt}$. Subtract $\frac{3}{r}$ from both sides to isolate the term containing $C$. $$ 0.5 - \frac{3}{r} = Ce^{-rt} $$
-
Solve for C
Divide both sides of the equation by $e^{-rt}$ to solve for $C$: $$ C = \frac{0.5 - \frac{3}{r}}{e^{-rt}} $$
-
Simplify the expression (optional)
Multiply the numerator and denominator by $e^{rt}$: $$ C = (0.5 - \frac{3}{r})e^{rt} $$ $$ C = 0.5e^{rt} - \frac{3e^{rt}}{r} $$
$C = (0.5 - \frac{3}{r})e^{rt}$ or $C = 0.5e^{rt} - \frac{3e^{rt}}{r}$
More Information
The constant $C$ depends on the variables $r$ and $t$. Without specific values for $r$ and $t$, the expression for $C$ cannot be simplified further.
Tips
A common mistake is to incorrectly isolate $C$. Make sure to subtract the term $\frac{3}{r}$ before dividing by $e^{-rt}$. Another common mistake is to incorrectly simplify the exponential term when solving for $C$.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information