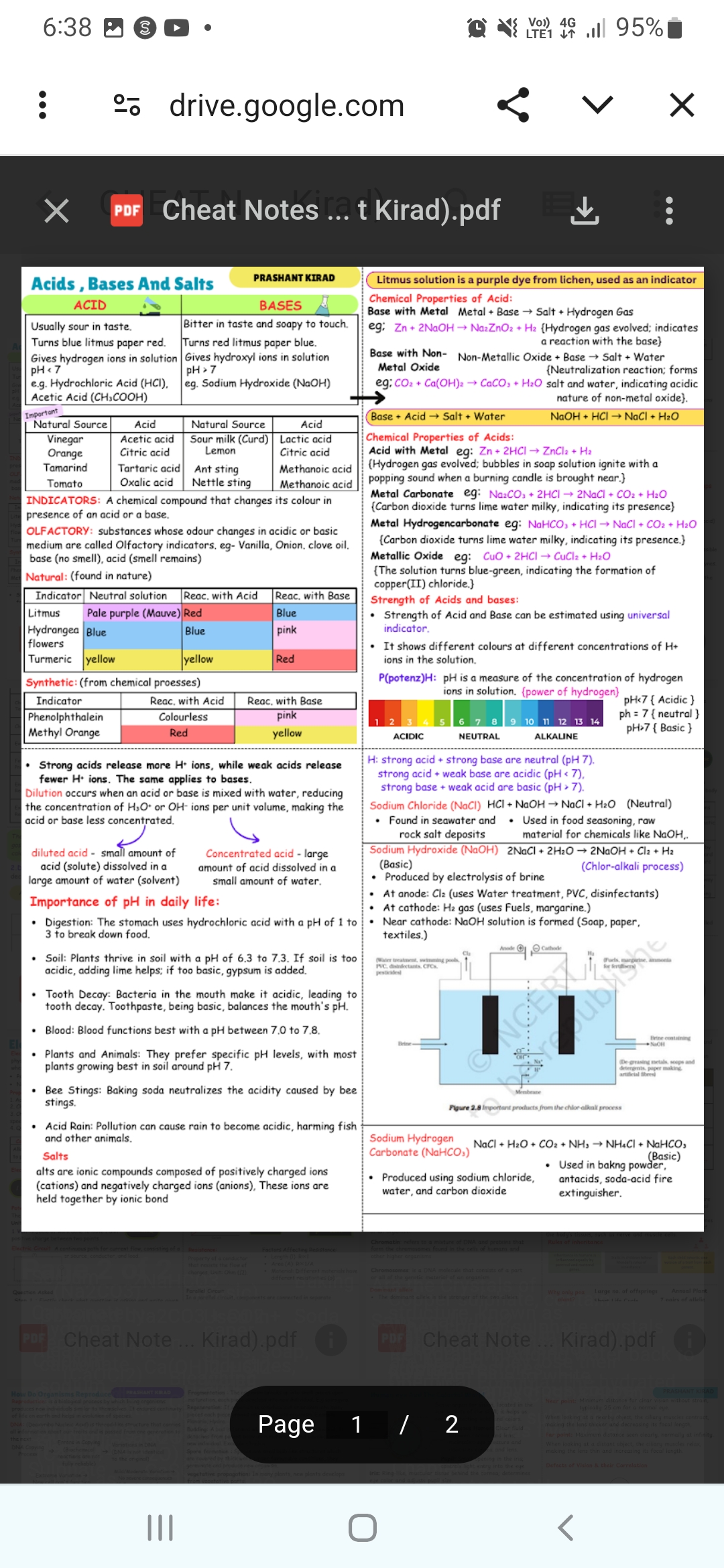
Provide the information shown in the image about acids, bases, and salts.
Understand the Problem
The image provides a summary of acids, bases, and salts, covering their properties, reactions, indicators, importance of pH, and examples. It also includes information on the chlor-alkali process and products.
Answer
Acids are sour, turn blue litmus red, and have a pH < 7. Bases are bitter, turn red litmus blue, and have a pH > 7. Salts are ionic compounds with cations and anions.
Acids:
- Sour taste.
- Turns blue litmus paper red.
- Gives hydrogen ions in solution, pH < 7.
Bases:
- Bitter taste and soapy touch.
- Turns red litmus paper blue.
- Gives hydroxyl ions in solution, pH > 7.
Salts: Ionic compounds of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions).
Answer for screen readers
Acids:
- Sour taste.
- Turns blue litmus paper red.
- Gives hydrogen ions in solution, pH < 7.
Bases:
- Bitter taste and soapy touch.
- Turns red litmus paper blue.
- Gives hydroxyl ions in solution, pH > 7.
Salts: Ionic compounds of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions).
More Information
Litmus solution is a purple dye from lichen, used as an indicator. Olfactory indicators change their odor in acidic or basic mediums (e.g., vanilla, onion, clove oil).
Tips
Pay close attention to the pH scale and how it relates to acids, bases, and neutral substances. Remember the role of litmus paper in identifying acids and bases.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information