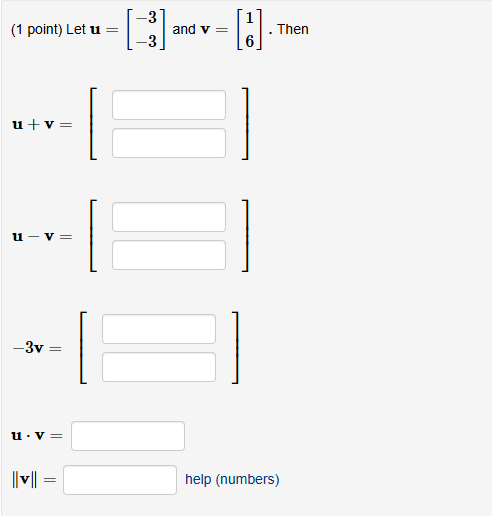
Let u = [-3, -3] and v = [1, 6]. Then find u + v, u - v, -3v, u . v, and ||v||.
Understand the Problem
The question asks to perform several vector operations given two vectors u and v. We need to calculate the sum (u + v), the difference (u - v), a scalar multiple (-3v), the dot product (u . v), and the magnitude (||v||) of vector v.
Answer
u + v = $\begin{bmatrix} -2 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix}$ u - v = $\begin{bmatrix} -4 \\ -9 \end{bmatrix}$ -3v = $\begin{bmatrix} -3 \\ -18 \end{bmatrix}$ u $\cdot$ v = -21 ||v|| = $\sqrt{37}$
Answer for screen readers
u + v = $\begin{bmatrix} -2 \ 3 \end{bmatrix}$
u - v = $\begin{bmatrix} -4 \ -9 \end{bmatrix}$
-3v = $\begin{bmatrix} -3 \ -18 \end{bmatrix}$
u $\cdot$ v = -21
||v|| = $\sqrt{37}$
Steps to Solve
- Calculate u + v
Add the corresponding components of vectors u and v:
$$ u + v = \begin{bmatrix} -3 \ -3 \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -3 + 1 \ -3 + 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -2 \ 3 \end{bmatrix} $$
- Calculate u - v
Subtract the corresponding components of vectors u and v:
$$ u - v = \begin{bmatrix} -3 \ -3 \end{bmatrix} - \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -3 - 1 \ -3 - 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -4 \ -9 \end{bmatrix} $$
- Calculate -3v
Multiply each component of vector v by -3:
$$ -3v = -3 \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -3 \cdot 1 \ -3 \cdot 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -3 \ -18 \end{bmatrix} $$
- Calculate u $\cdot$ v
Compute the dot product of vectors u and v:
$$ u \cdot v = (-3)(1) + (-3)(6) = -3 - 18 = -21 $$
- Calculate ||v||
Find the magnitude of vector v:
$$ ||v|| = \sqrt{(1)^2 + (6)^2} = \sqrt{1 + 36} = \sqrt{37} $$
u + v = $\begin{bmatrix} -2 \ 3 \end{bmatrix}$
u - v = $\begin{bmatrix} -4 \ -9 \end{bmatrix}$
-3v = $\begin{bmatrix} -3 \ -18 \end{bmatrix}$
u $\cdot$ v = -21
||v|| = $\sqrt{37}$
More Information
The magnitude of a vector represents its length. The dot product is a scalar value that represents the projection of one vector onto another, scaled by the magnitude of the other vector.
Tips
A common mistake is to add or subtract the components of the vectors in the wrong order. Another common mistake is to forget to square the components when calculating the magnitude of a vector. Also, one must remember that the dot product of two vectors gives you a scalar (a single number), not another vector.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information