In terms of hydrogen ion concentration, how much more acidic is solution A, with a pH of 1.6, than solution B, with a pH of 3.2? Show all your work to receive a full mark and round... In terms of hydrogen ion concentration, how much more acidic is solution A, with a pH of 1.6, than solution B, with a pH of 3.2? Show all your work to receive a full mark and round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
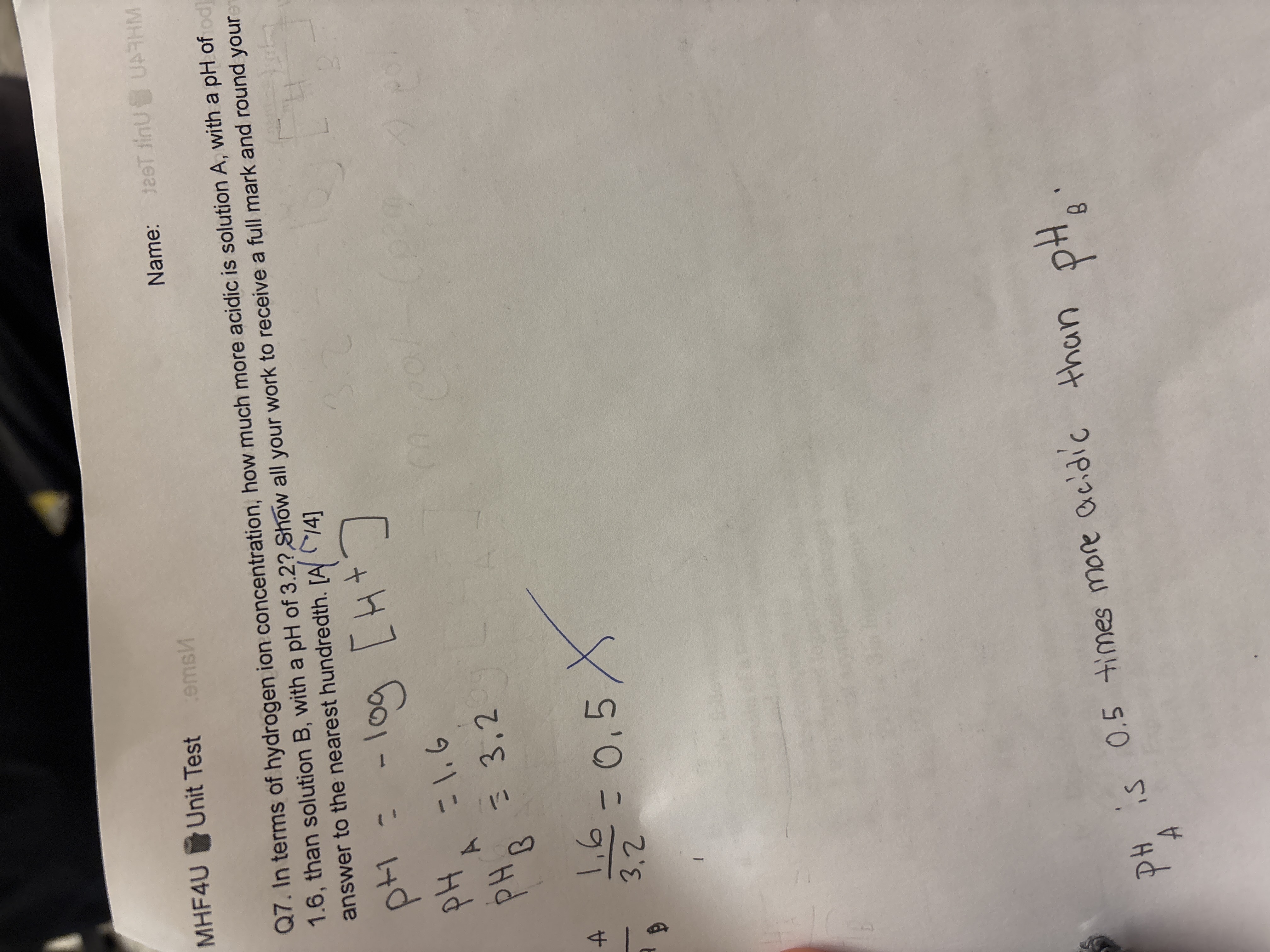
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for a comparison of the acidity of two solutions (A and B) based on their pH values. Specifically, it requires calculating how much more acidic solution A (pH 1.6) is compared to solution B (pH 3.2), using hydrogen ion concentration. The user is expected to show their work and round the final answer to the nearest hundredth.
Answer
Solution A is approximately $39.80$ times more acidic than solution B.
Answer for screen readers
Solution A is approximately 39.80 times more acidic than solution B.
Steps to Solve
-
Convert pH to Hydrogen Ion Concentration To find the hydrogen ion concentration ($[H^+]$) for each solution, use the formula: $$ [H^+] = 10^{-\text{pH}} $$
For solution A (pH = 1.6): $$ [H^+]_A = 10^{-1.6} $$
For solution B (pH = 3.2): $$ [H^+]_B = 10^{-3.2} $$
-
Calculate Hydrogen Ion Concentrations Now, calculate the concentrations:
-
For solution A: $$ [H^+]_A = 10^{-1.6} \approx 0.02512 , \text{mol/L} $$
-
For solution B: $$ [H^+]_B = 10^{-3.2} \approx 0.000630957 , \text{mol/L} $$
-
-
Compare the Acidity To find out how much more acidic solution A is compared to solution B, divide the hydrogen ion concentration of A by that of B: $$ \text{Acidity Ratio} = \frac{[H^+]_A}{[H^+]_B} $$
Substitute the values: $$ \text{Acidity Ratio} = \frac{0.02512}{0.000630957} $$
-
Calculate the Final Ratio Now perform the division: $$ \text{Acidity Ratio} \approx 39.8 $$
This means that solution A is approximately 39.80 times more acidic than solution B.
- Round to the Nearest Hundredth Finally, round the result to the nearest hundredth, which gives: $$ 39.80 $$
Solution A is approximately 39.80 times more acidic than solution B.
More Information
This calculation shows the logarithmic nature of pH, whereby a decrease of 1 in pH corresponds to a tenfold increase in hydrogen ion concentration. Hence, even a small change in pH can represent significant changes in acidity.
Tips
- Forgetting to convert the pH value to hydrogen ion concentration before comparison.
- Miscalculating the hydrogen ion concentrations by not following the correct logarithmic formula.
- Not rounding the final answer properly to the nearest hundredth.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information