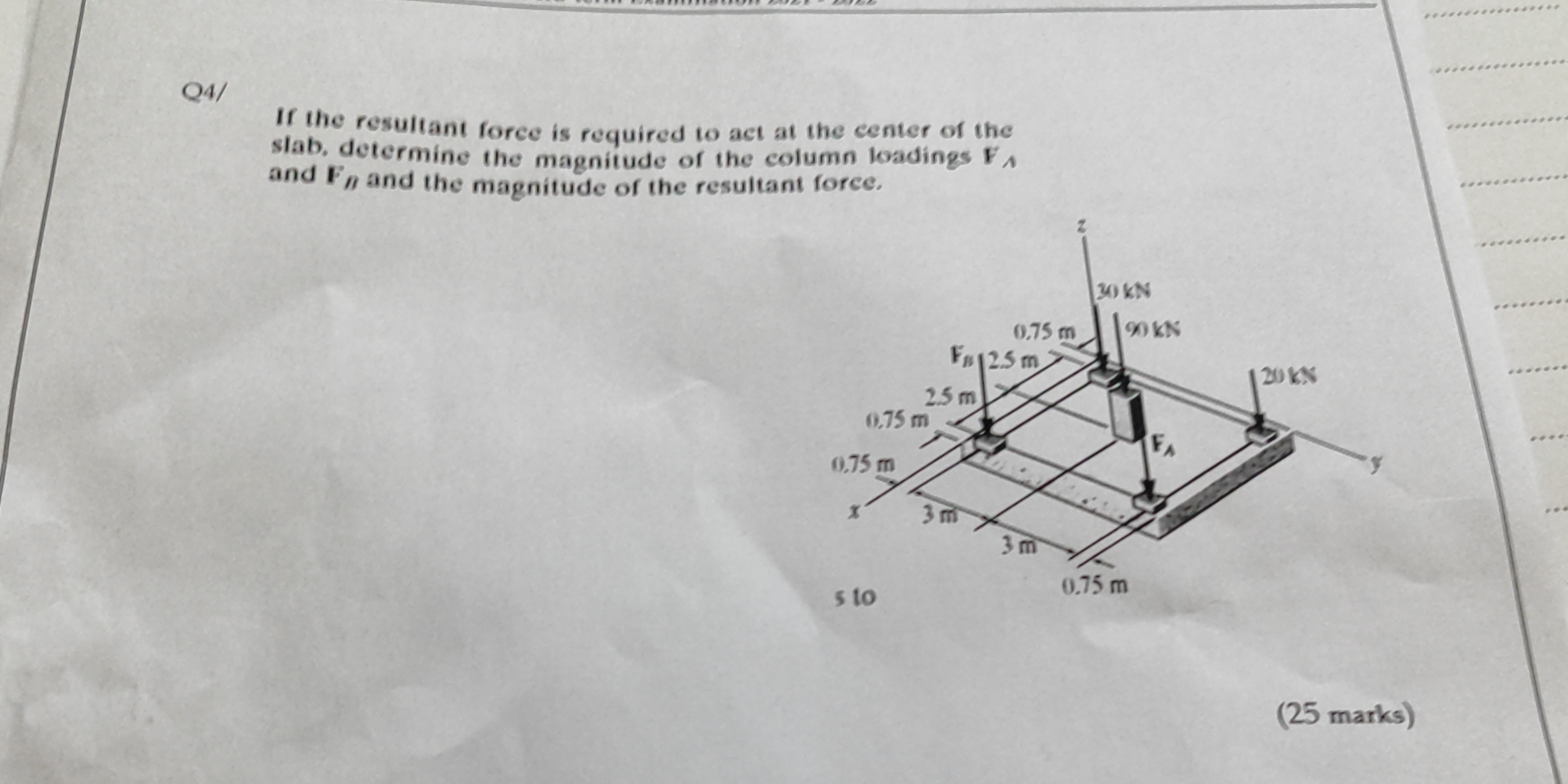
If the resultant force is required to act at the center of the slab, determine the magnitude of the column loadings $F_A$ and $F_B$ and the magnitude of the resultant force.
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to determine the magnitude of the column loadings $F_A$ and $F_B$, and the magnitude of the resultant force, given that the resultant force acts at the center of the slab. The problem involves static equilibrium and force analysis in 3D space.
Answer
$F_A = 187.5 \, \text{kN}$ $F_B = 70 \, \text{kN}$ $F_R = 22.5 \, \text{kN}$
Answer for screen readers
$F_A = 187.5 , \text{kN}$
$F_B = 70 , \text{kN}$
$F_R = 22.5 , \text{kN}$
Steps to Solve
- Establish Coordinate System and Define Positions
Establish a coordinate system. Let the bottom left corner of the slab be the origin (0,0,0). This means the coordinates of the forces are as follows:
Force of 30 kN: $ (0.75, 0.75, 0) $ Force of 90 kN: $ (5.25, 0.75, 0) $ Force of 20 kN: $ (0.75, 5.25, 0) $ Force $F_B$: $ (5.25, 5.25, 0) $ Force $F_A$: $ (3, 3, 0) $ The center of the slab: $ (3, 3, 0) $
- Sum of Forces in Z-direction
The sum of forces in the z-direction must equal the resultant force.
$F_R = F_A + F_B - 30 - 90 - 20$ $F_R = F_A + F_B - 140$
- Moment Equilibrium about X-axis
Sum of moments about the x-axis must be zero, and since the resultant force acts at the center, the moment caused by individual forces must equal the moment caused by the resultant force at centre.
$ \sum M_x = 0 $
$ F_A \cdot 3 + F_B \cdot 5.25 - 30 \cdot 0.75 - 90 \cdot 0.75 - 20 \cdot 5.25 = 0$
$ 3F_A + 5.25F_B = 30 \cdot 0.75 + 90 \cdot 0.75 + 20 \cdot 5.25 $
$ 3F_A + 5.25F_B = 22.5 + 67.5 + 105 $
$ 3F_A + 5.25F_B = 195 $ (Equation 1)
- Moment Equilibrium about Y-axis
Sum of moments about the y-axis must be zero, and since the resultant force acts at the center the moment caused by individual forces must equal the moment caused by the resultant force at centre.
$ \sum M_y = 0 $
$ F_A \cdot 3 + F_B \cdot 0.75 - 30 \cdot 0.75 - 90 \cdot 5.25 - 20 \cdot 0.75 = 0 $
$ 3F_A + 0.75F_B = 30 \cdot 0.75 + 90 \cdot 5.25 + 20 \cdot 0.75 $
$ 3F_A + 0.75F_B = 22.5 + 472.5 + 15 $
$ 3F_A + 0.75F_B = 510 $ (Equation 2)
- Solving the System of Equations
Solve the two equations simultaneously to find $F_A$ and $F_B$
Subtract Equation 2 from Equation 1:
$ (3F_A + 5.25F_B) - (3F_A + 0.75F_B) = 195 - 510 $ $ 4.5F_B = -315 $ $ F_B = -70 , kN $
Substitute $F_B$ into Equation 2:
$ 3F_A + 0.75(-70) = 510 $ $ 3F_A - 52.5 = 510 $ $ 3F_A = 562.5 $ $ F_A = 187.5 , kN $
- Calculate Resultant Force $F_R$
$ F_R = F_A + F_B - 140 $ $ F_R = 187.5 + (-70) - 140 $ $ F_R = -22.5 , kN $
Because the question asks for the magnitude, we take the absolute value.
$F_A = 187.5 , \text{kN}$
$F_B = 70 , \text{kN}$
$F_R = 22.5 , \text{kN}$
More Information
The negative sign for $F_B$ and $F_R$ indicates they are acting in the opposite direction to what was initially assumed (downwards). This makes sense since the other downward forces (30kN, 90kN, 20kN) are quite large, so $F_A$ needs to be a lot larger than $F_B$ to balance it out, meaning $F_B$ will point downwards. The resultant force then ends up pointing downwards as well since the total downward force is larger than $F_A$.
Tips
- Forgetting to convert units if they're mixed.
- Incorrectly setting up the moment equations (wrong distances or signs).
- Making algebraic errors when solving the system of equations.
- Not recognizing that the negative sign indicates the direction of the force.
- Not taking the absolute value after computing the result if the question asks for magnitude.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information